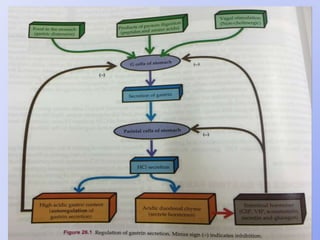
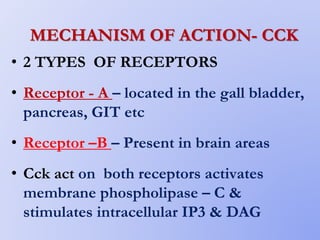
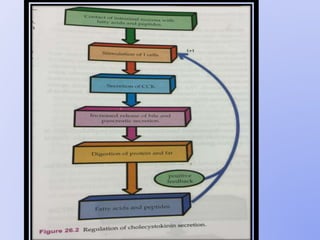
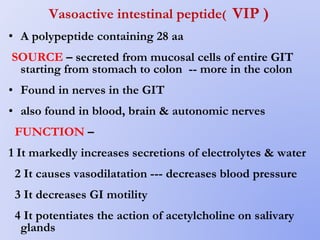
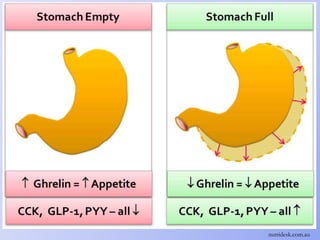
This document summarizes gastrointestinal hormones. It describes that GI hormones are secreted from endocrine cells in the stomach and small intestine. They are broadly divided into 3 categories: the gastrin family including gastrin and CCK; the secretin family including secretin, VIP, and GIP; and other polypeptides like motilin, neurotensin, substance P, somatostatin, ghrelin, guanylin, and PYY. For each hormone, it provides information on source, structure, functions, mechanisms, and factors that regulate their secretion.