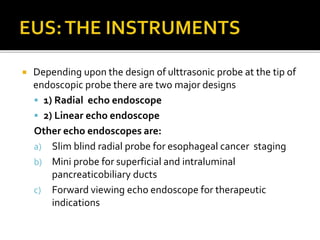
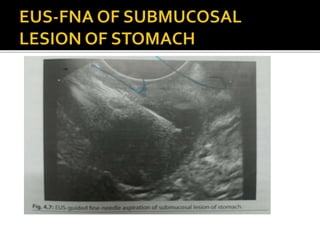
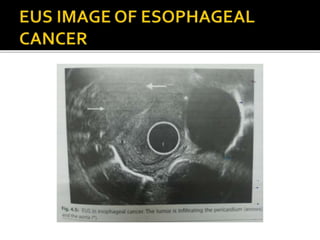
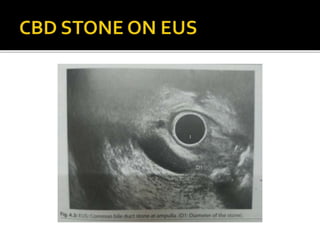
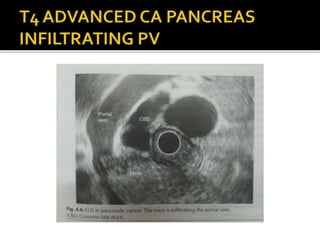
EUS has revolutionized both the diagnostic and therapeutic aspects of gastroenterology. It combines an endoscope with an ultrasound probe to examine the GI tract walls and nearby structures. EUS is very useful for staging cancers of the esophagus, pancreas, and biliary tract, and is the most sensitive method for distinguishing between benign and malignant pancreatic tumors. EUS also has several important therapeutic roles, including draining pancreatic fluid collections, accessing the biliary tree non-surgically, celiac plexus neurolysis for pancreatic cancer pain relief, and delivering targeted cancer treatments. Recent advances have further increased the diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities of EUS.