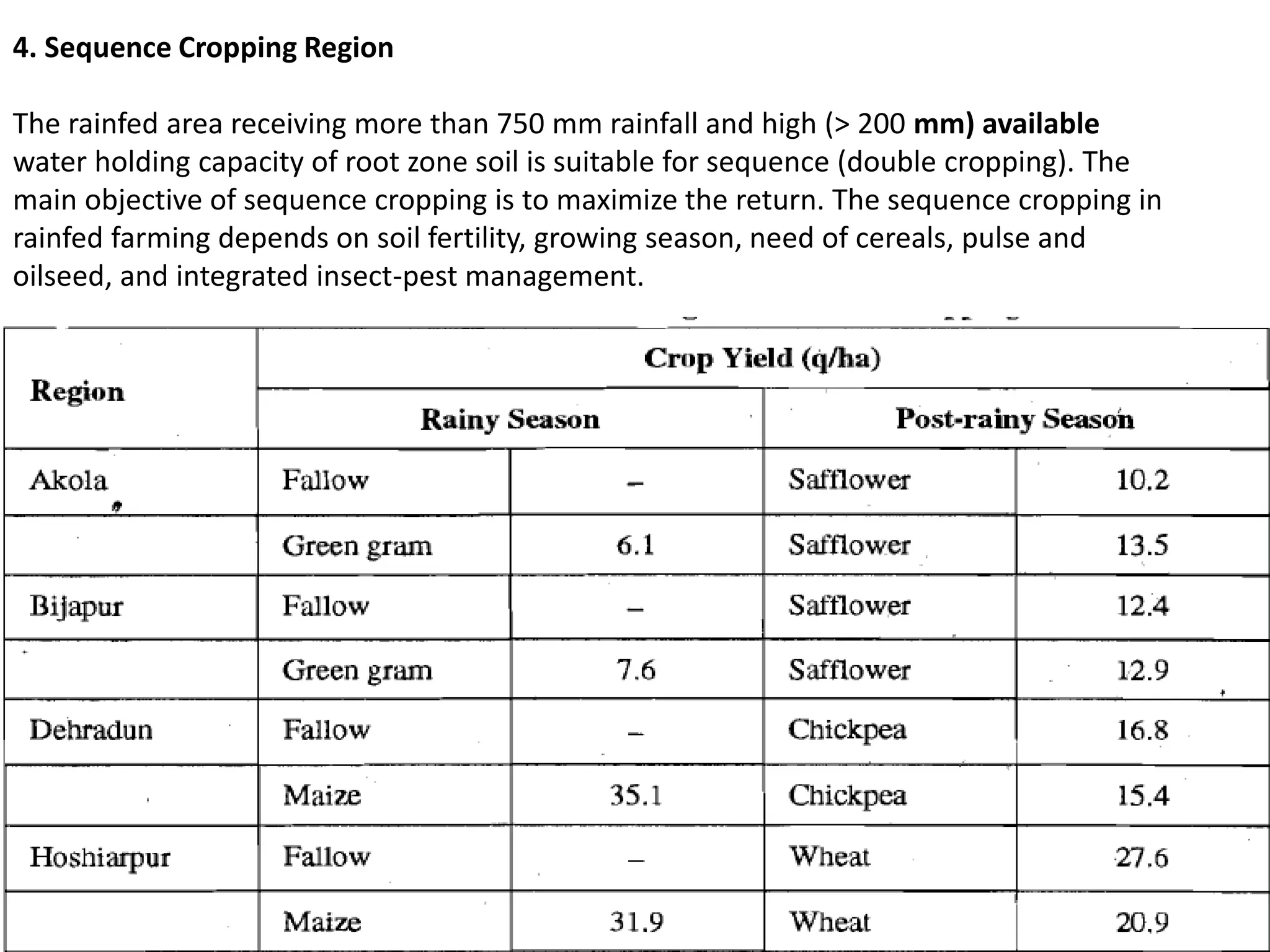
This document discusses crop management practices for rainfed farming. It begins by defining rainfed areas as those with arid, semi-arid, or sub-humid climates prone to drought. Improved practices for rainfed crops involve selecting short-duration, drought-resistant varieties and maximizing cropping intensity through mixed/intercropping. Key practices include fertilizer use, tillage, forage crops, agroforestry, weed management, and making mid-season corrections if drought occurs. The overall goal is to utilize more of the available rainwater and improve historically low and unstable yields for farmers in rainfed regions.