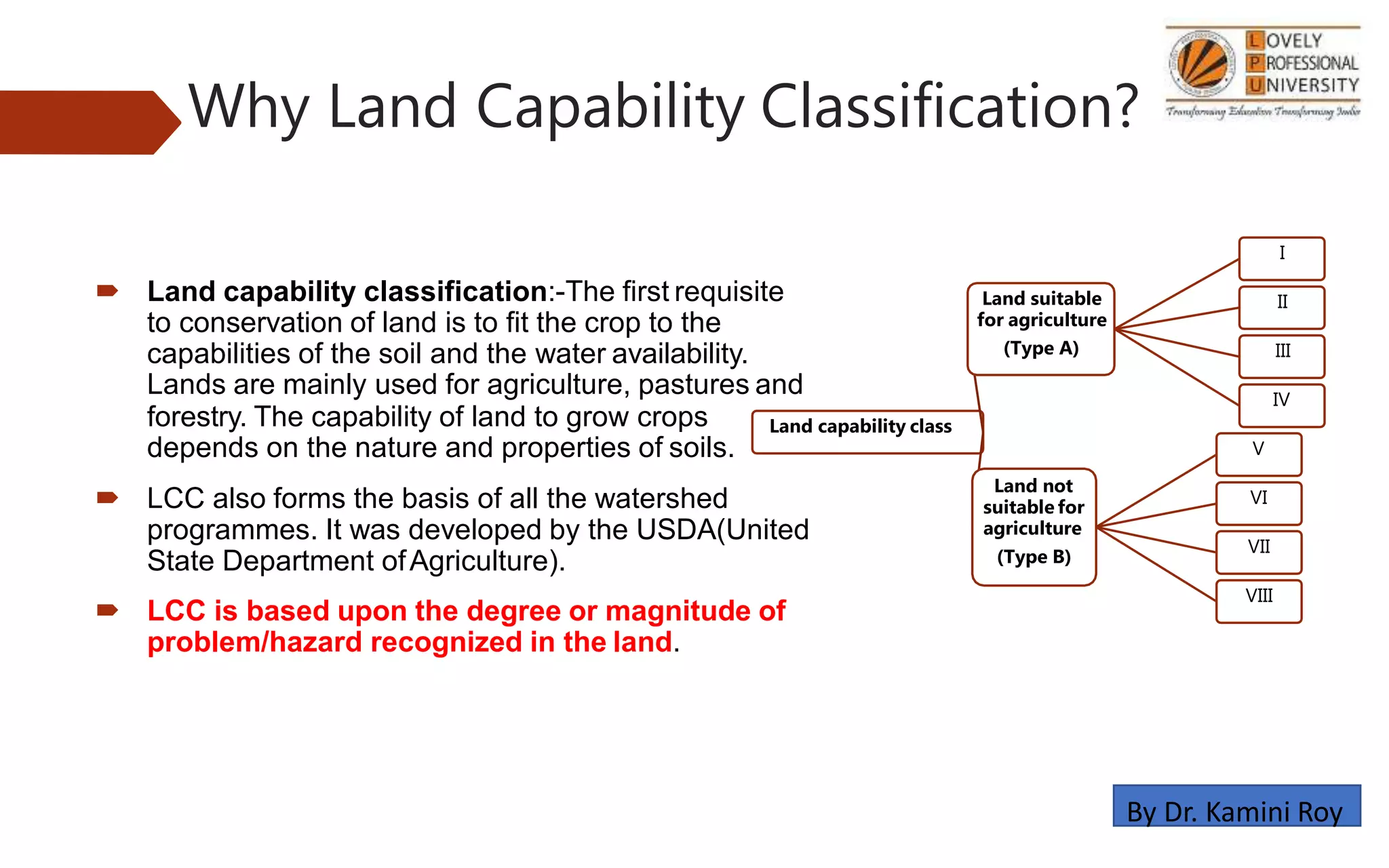
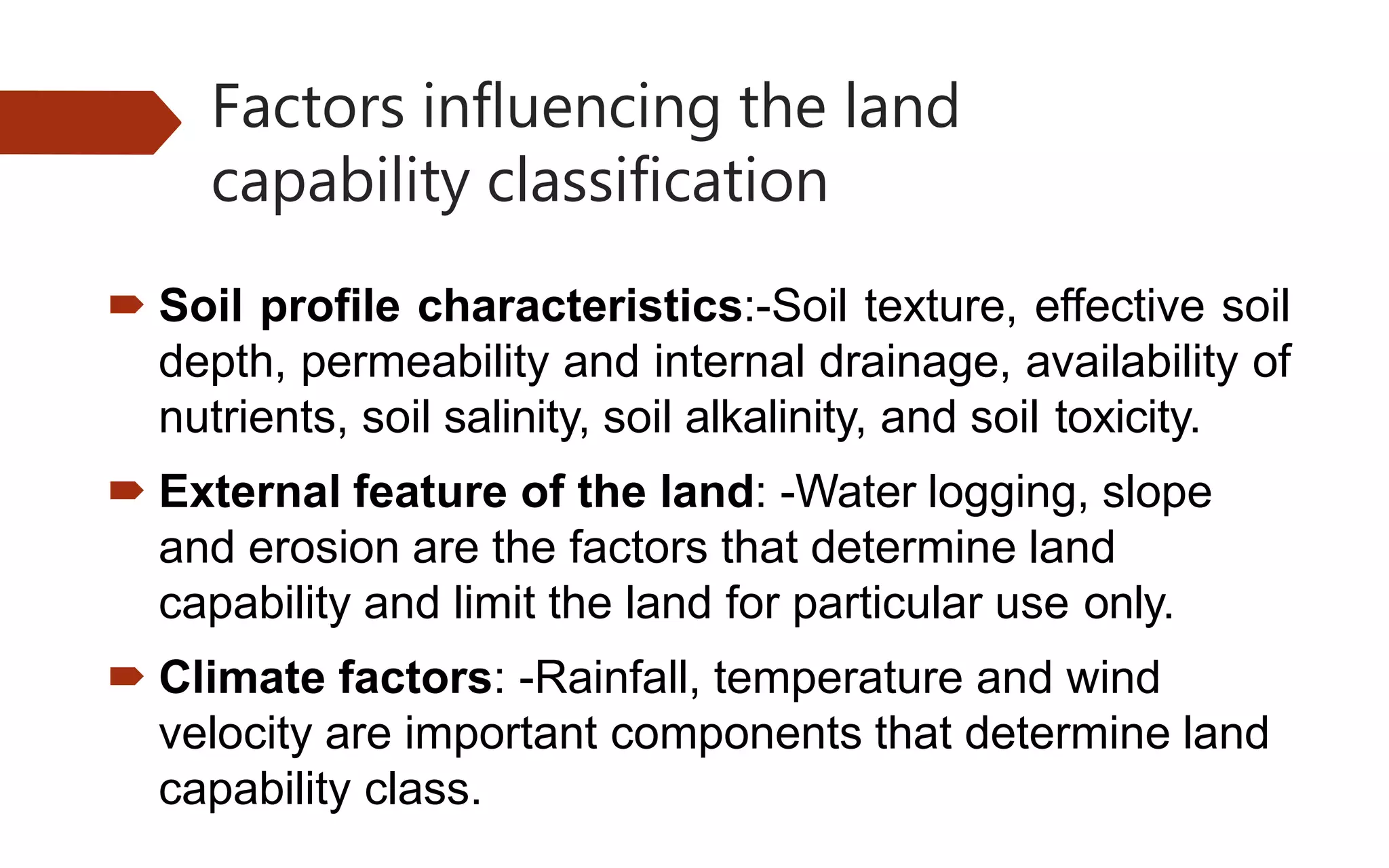
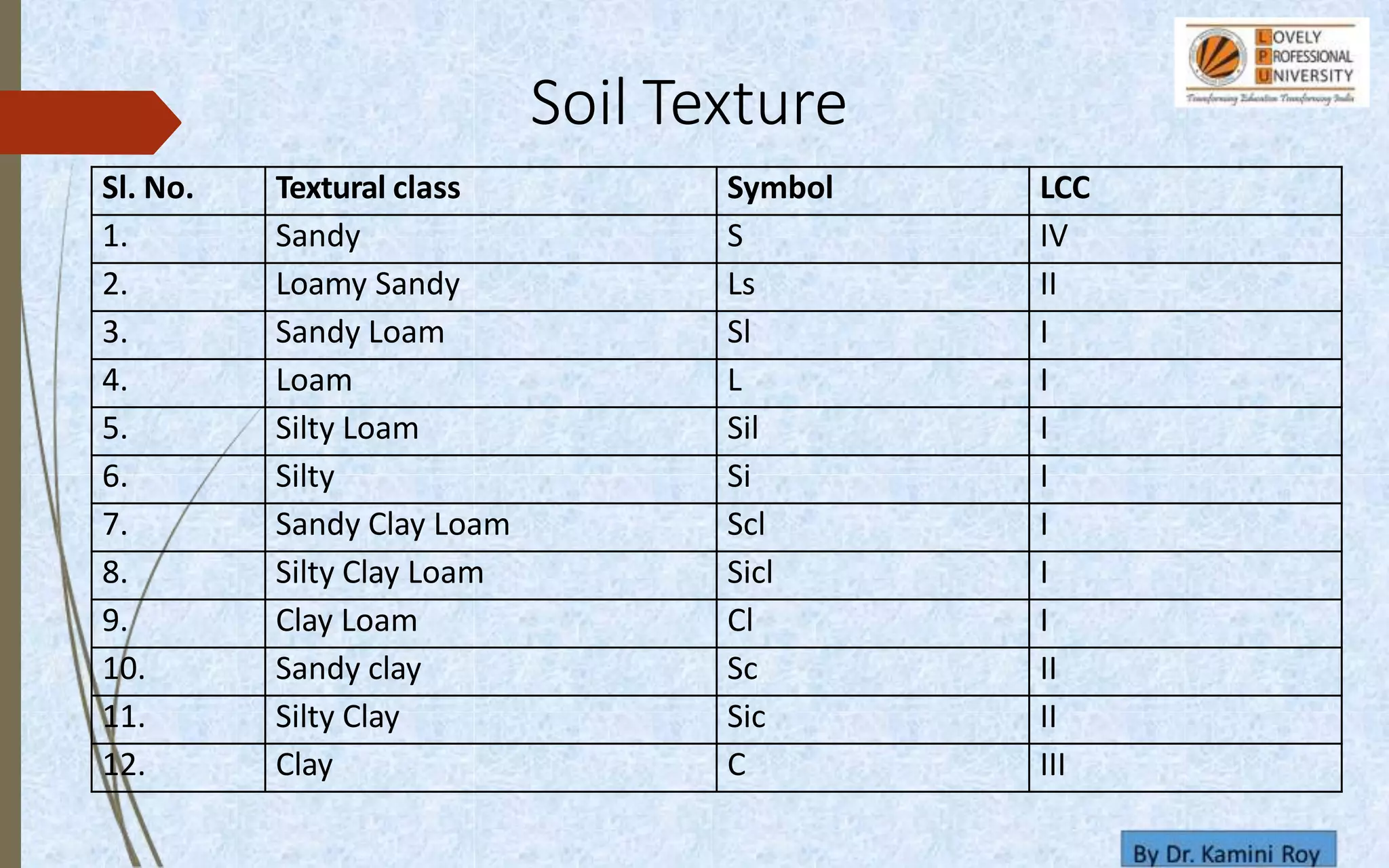
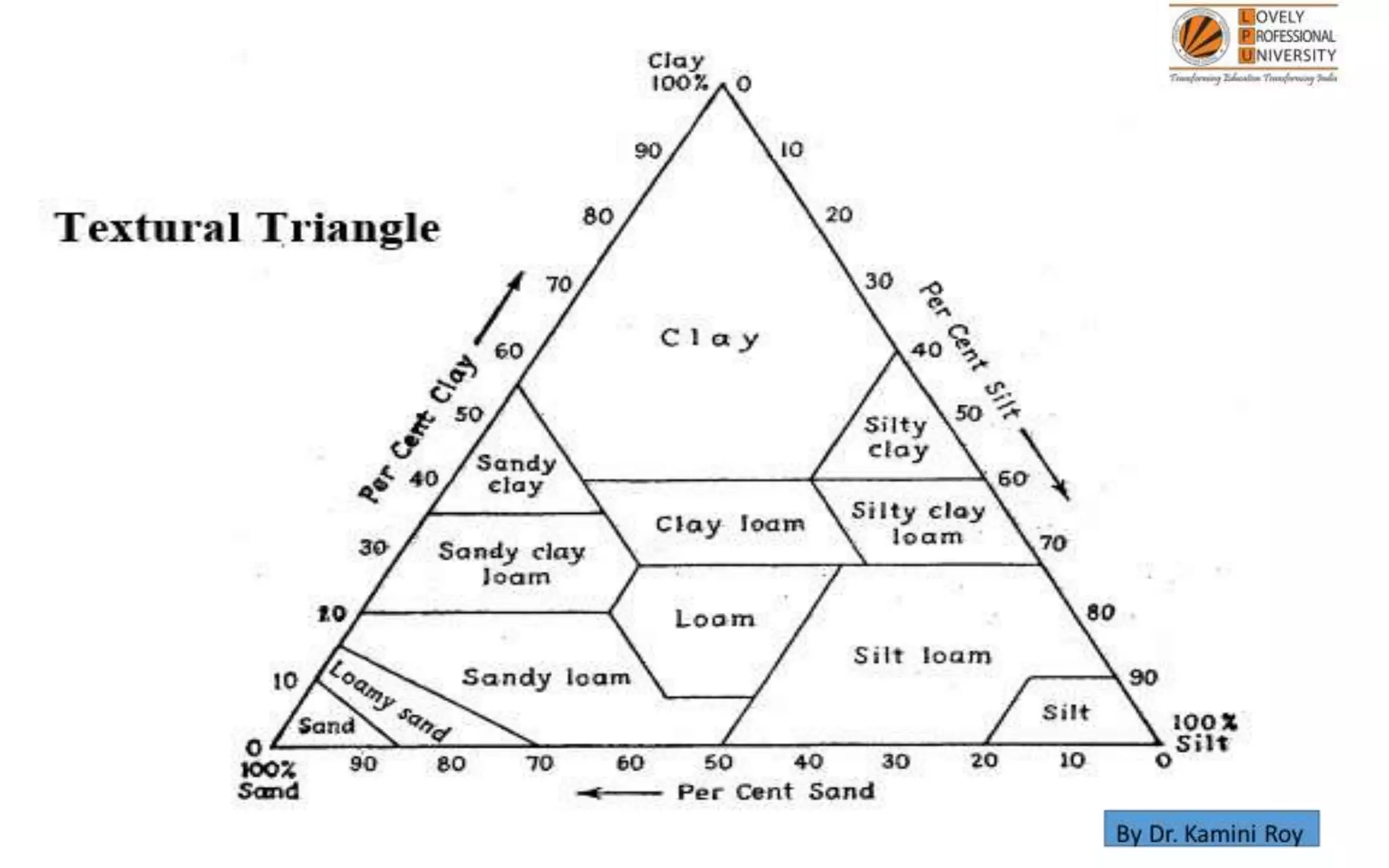
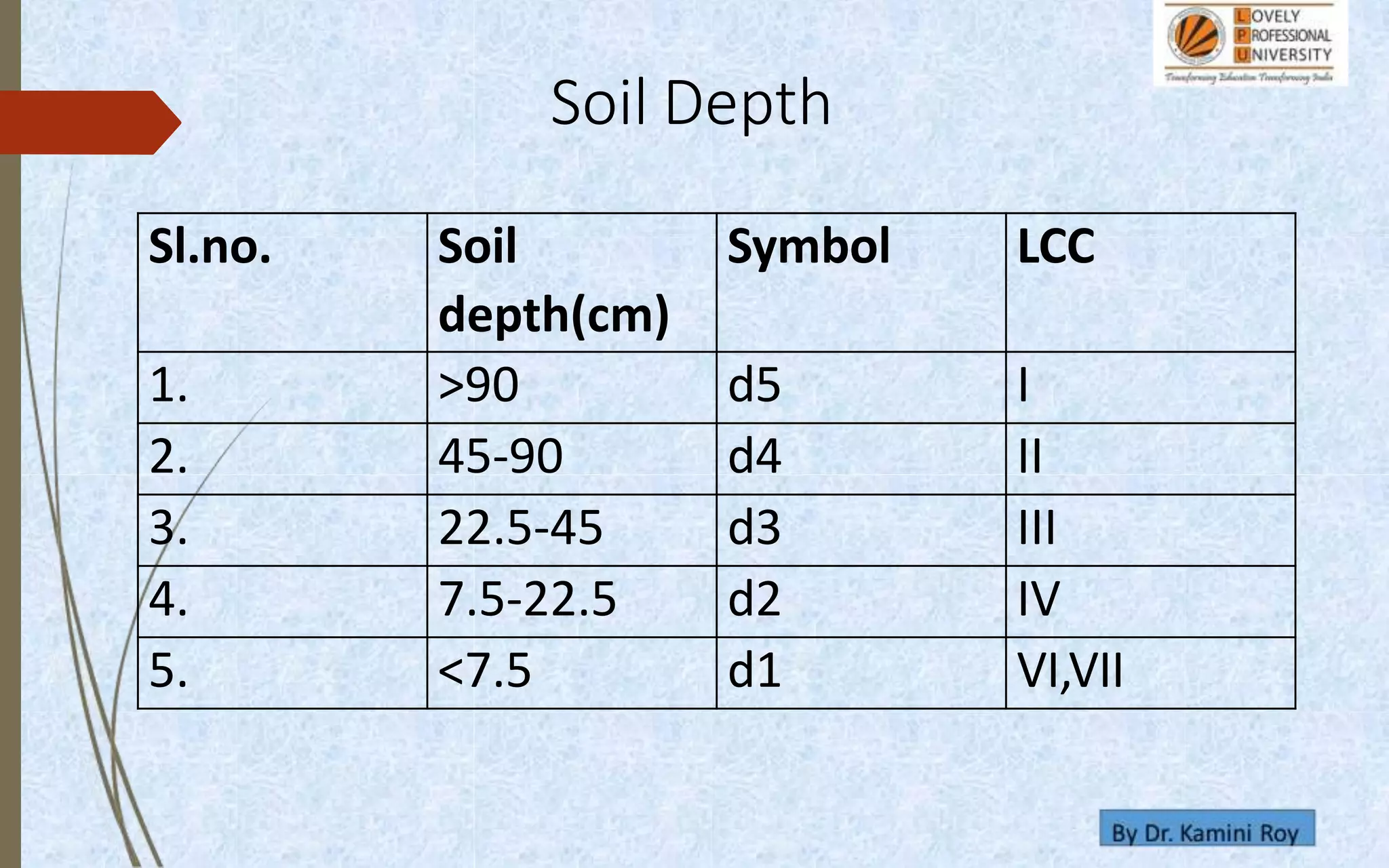
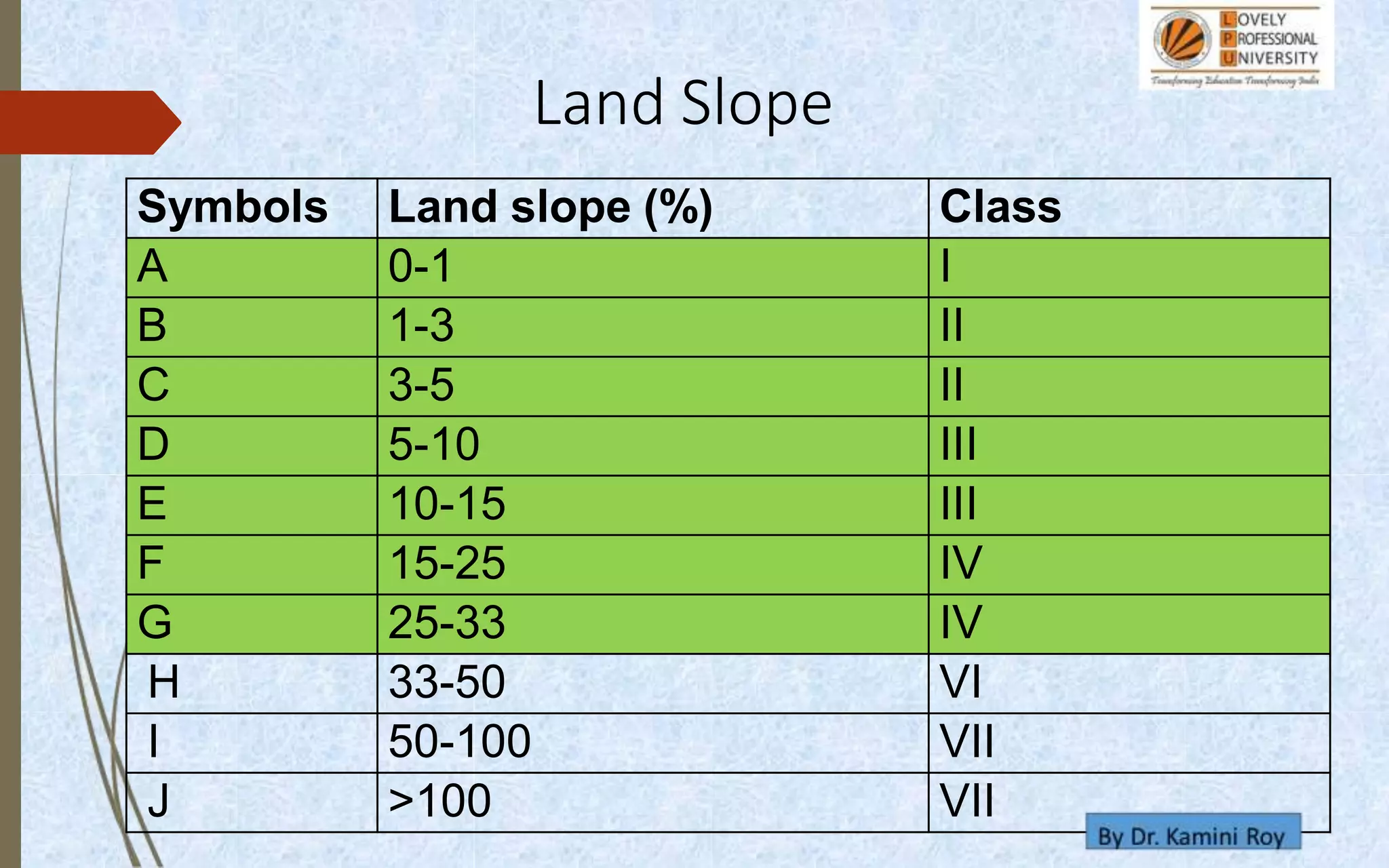
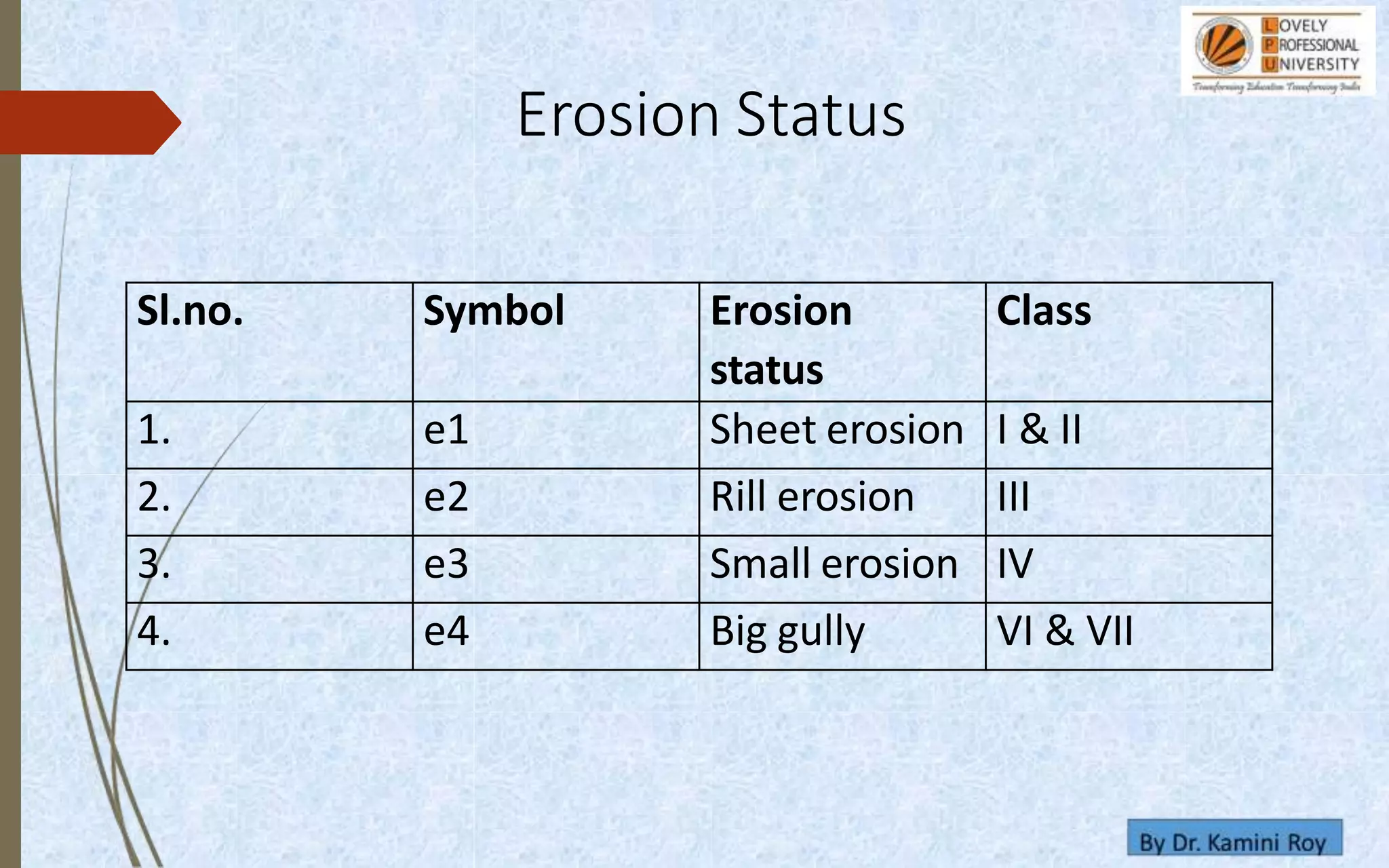
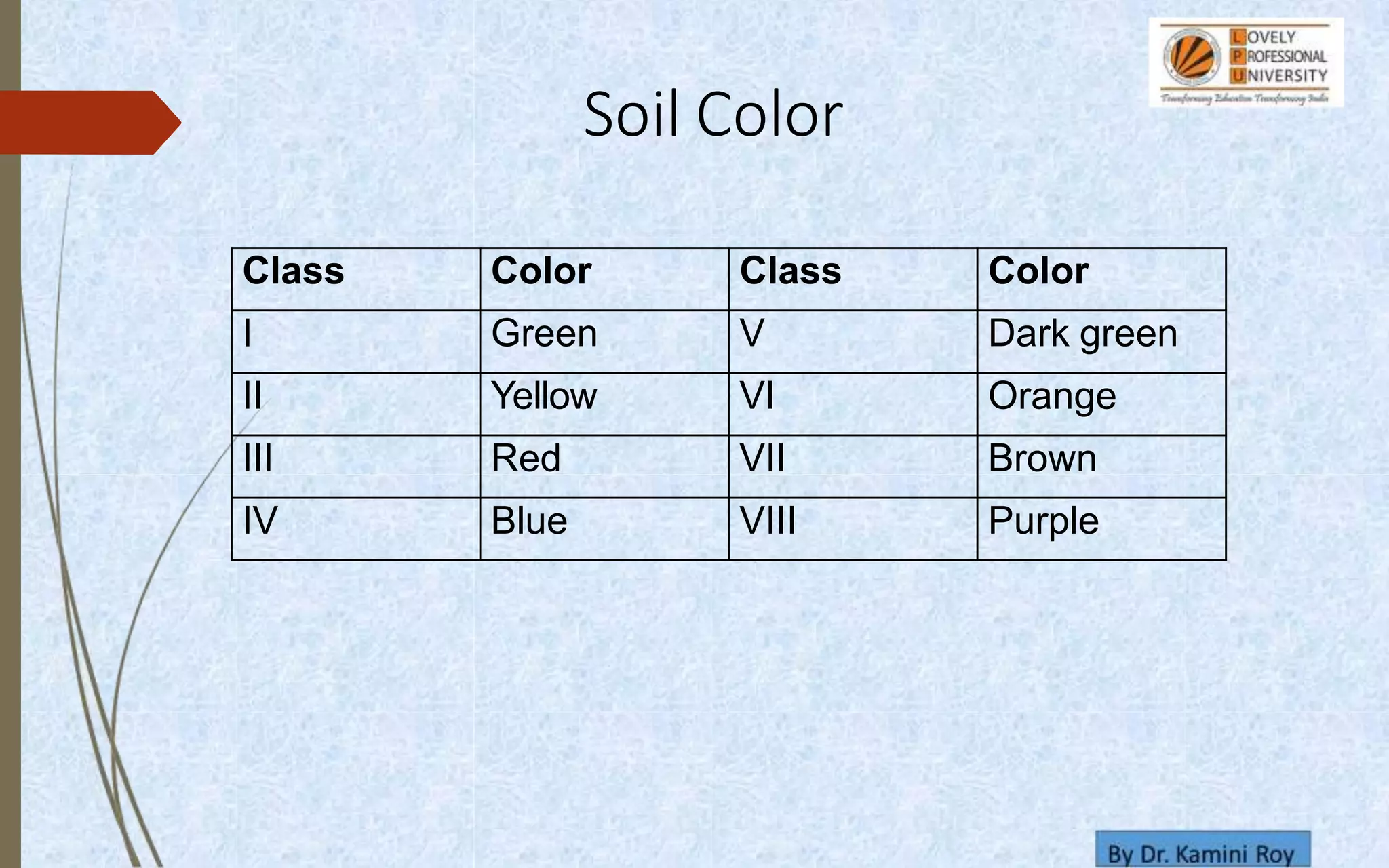
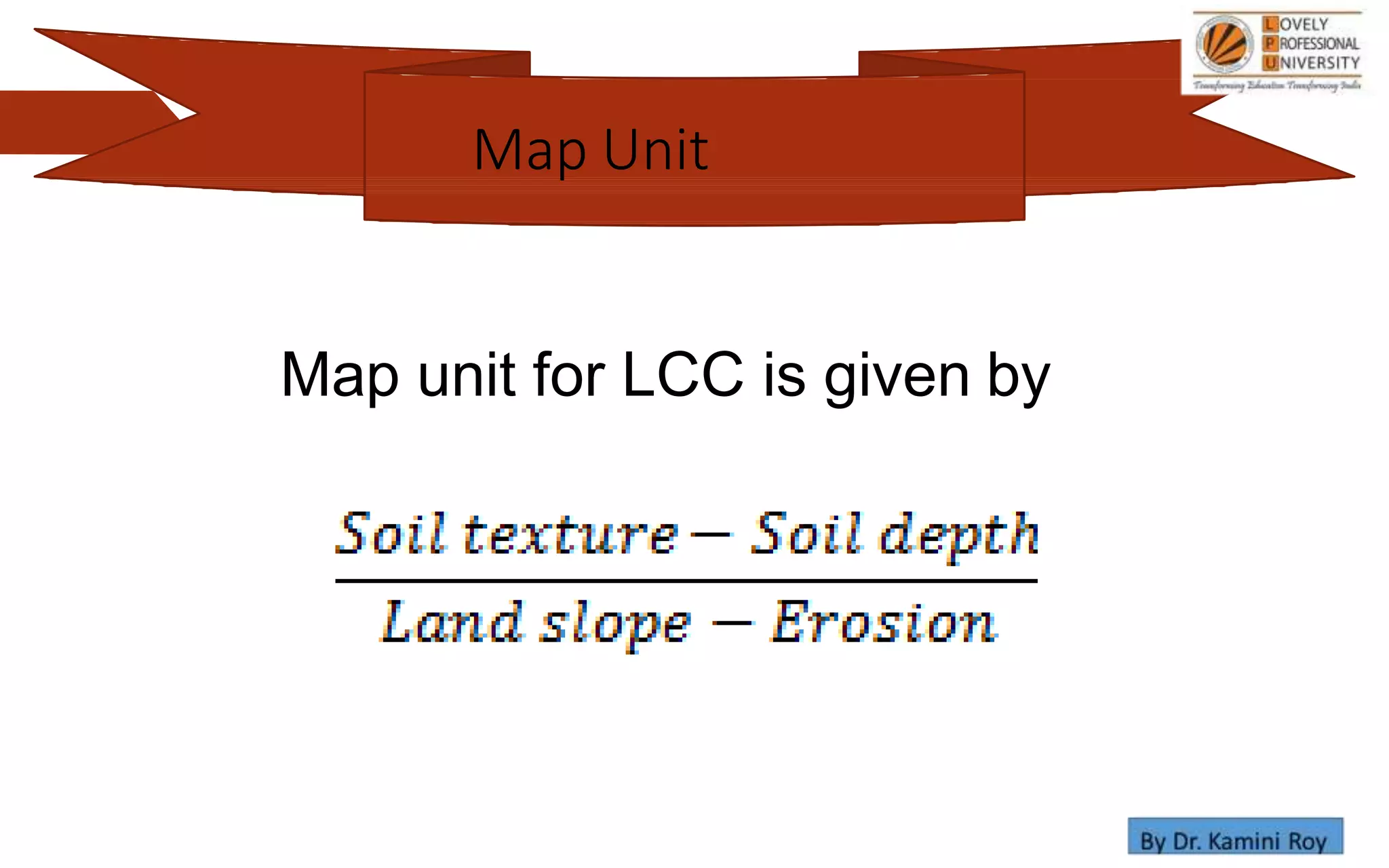
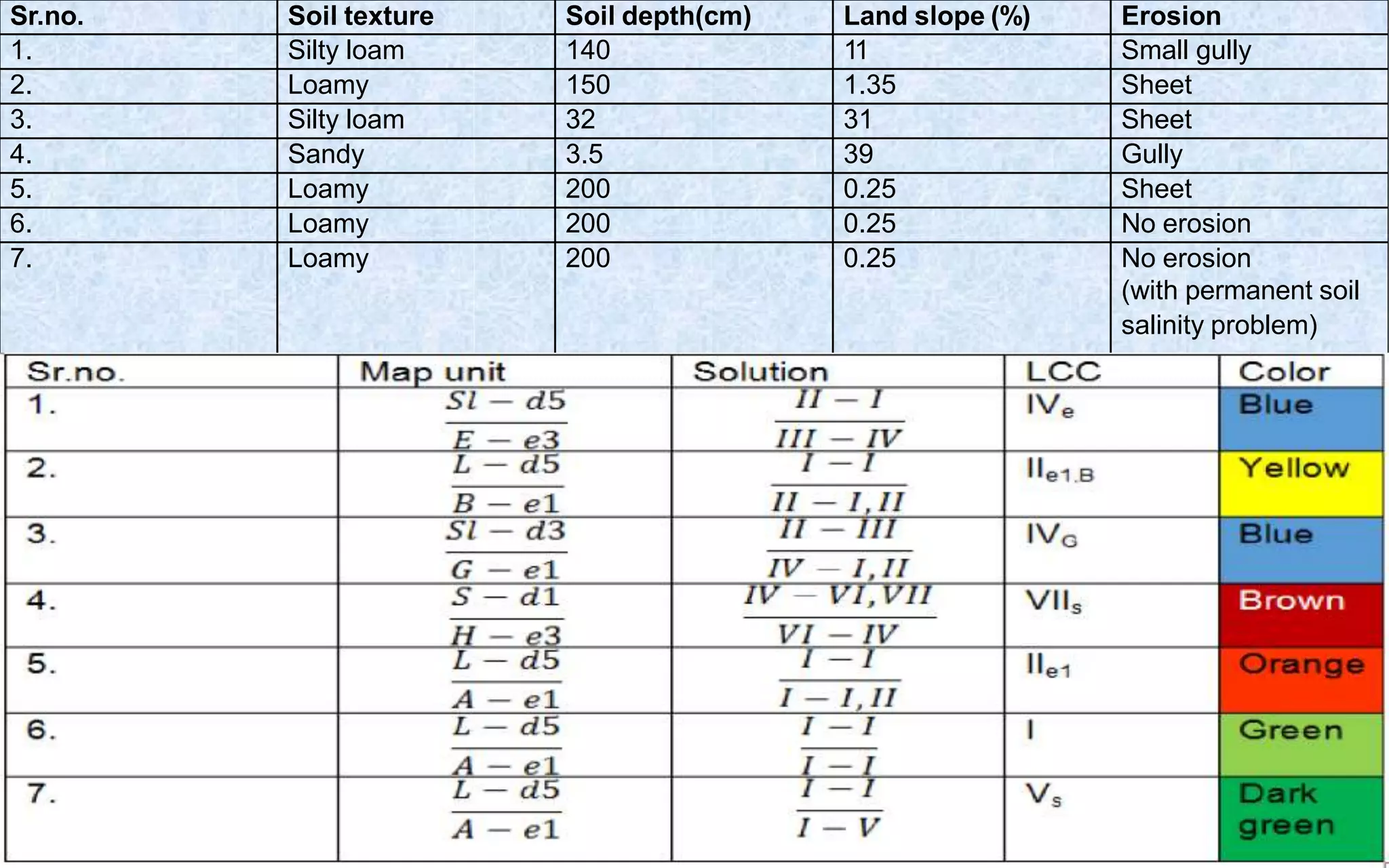
This document provides information on land capability classification (LCC). It begins with definitions of soil and an explanation of why LCC is important. LCC assesses land suitability for agriculture based on soil properties, slope, erosion risk and other factors. Lands are classified on a scale of I to VIII, with I being best suited for agriculture and VIII not suitable. Class I land has deep, fertile soil with no hazards. Factors like soil type, depth, texture, slope and erosion level determine the classification. The document provides details on each class and examples of how different soil properties correspond to classes. It aims to help identify appropriate land uses and conservation practices based on capability.