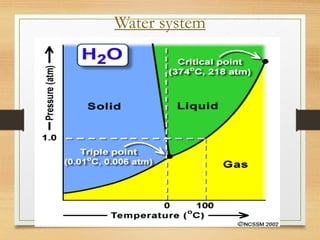
The Gibbs phase rule relates the number of degrees of freedom (F) of a system to the number of components (C) and phases (P) present, given by the equation F = C - P + 2. A phase is a homogeneous, physically distinct portion of a heterogeneous system separated by well-defined boundaries. The number of components is the number of independently varying chemical constituents that can describe the composition of all phases. The degrees of freedom represent the minimum number of variables needed to specify the system.



![-
• Solid
• Various allotropes [e.g. diamond; graphite] or compositions
like NaCl, NaCl.2H2O
• Alloys
• Liquid
• Miscible liquids (solutions) are one phase
• Immiscible liquids are multiple phases (P>1)
• Gas
• Systems consisting of gases can have only one phase](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gibbsphaserule-230223093342-8014b4fd/85/Gibbs-Phase-Rule-pdf-5-320.jpg)





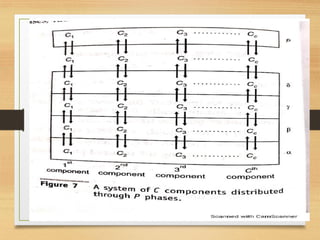
![• Degree of Freedom or Variance =
• [total no of variable that need to be specified]- [tot no of
restricting condition that are imposed by interdependent
variables]
• (a) To find out the total no of Variables :
(I) Temperature: same for all phases =1 variable
(ii) pressure: same for all phases =1 variable
(iii) concentration: conc. term for 1 phase=C
conc. term for P phase=PC
Total no of variable= PC+2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gibbsphaserule-230223093342-8014b4fd/85/Gibbs-Phase-Rule-pdf-11-320.jpg)