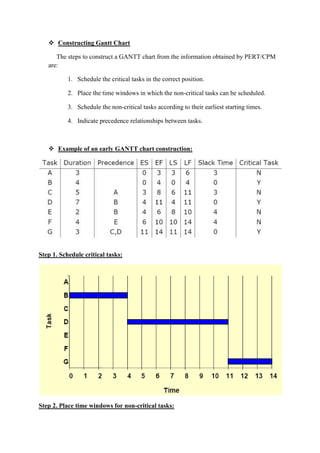
A Gantt chart is a bar chart that illustrates a project schedule and the timing of tasks and activities. It was created by Henry Gantt in the early 1900s and shows the start and finish times of each task or event as horizontal bars placed against a calendar scale. Gantt charts make it easy to visualize task durations and dependencies and are useful for resource allocation and schedule management.