This document contains an agenda and presentation materials for a talk on IPv6. The key points covered include:
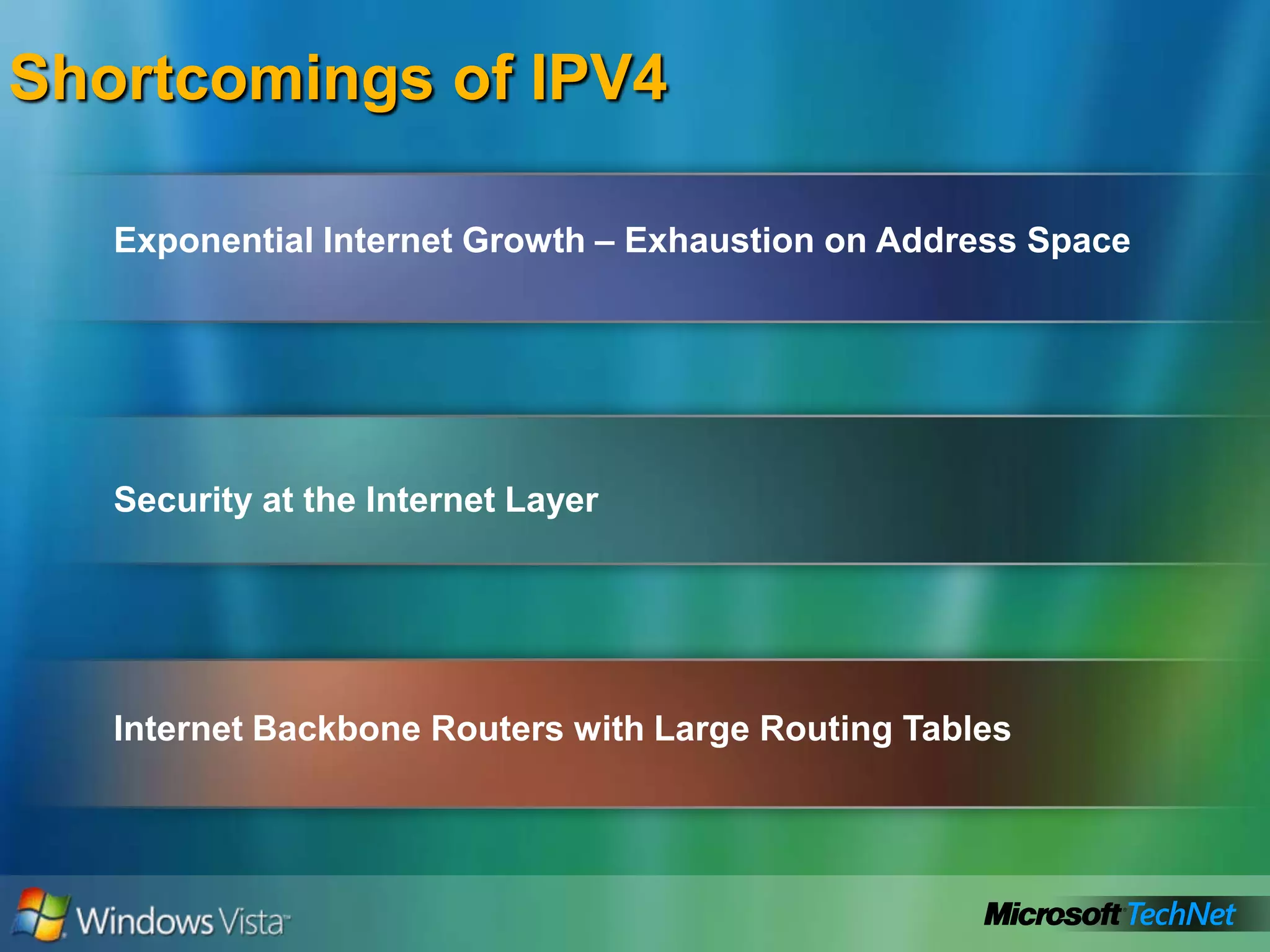
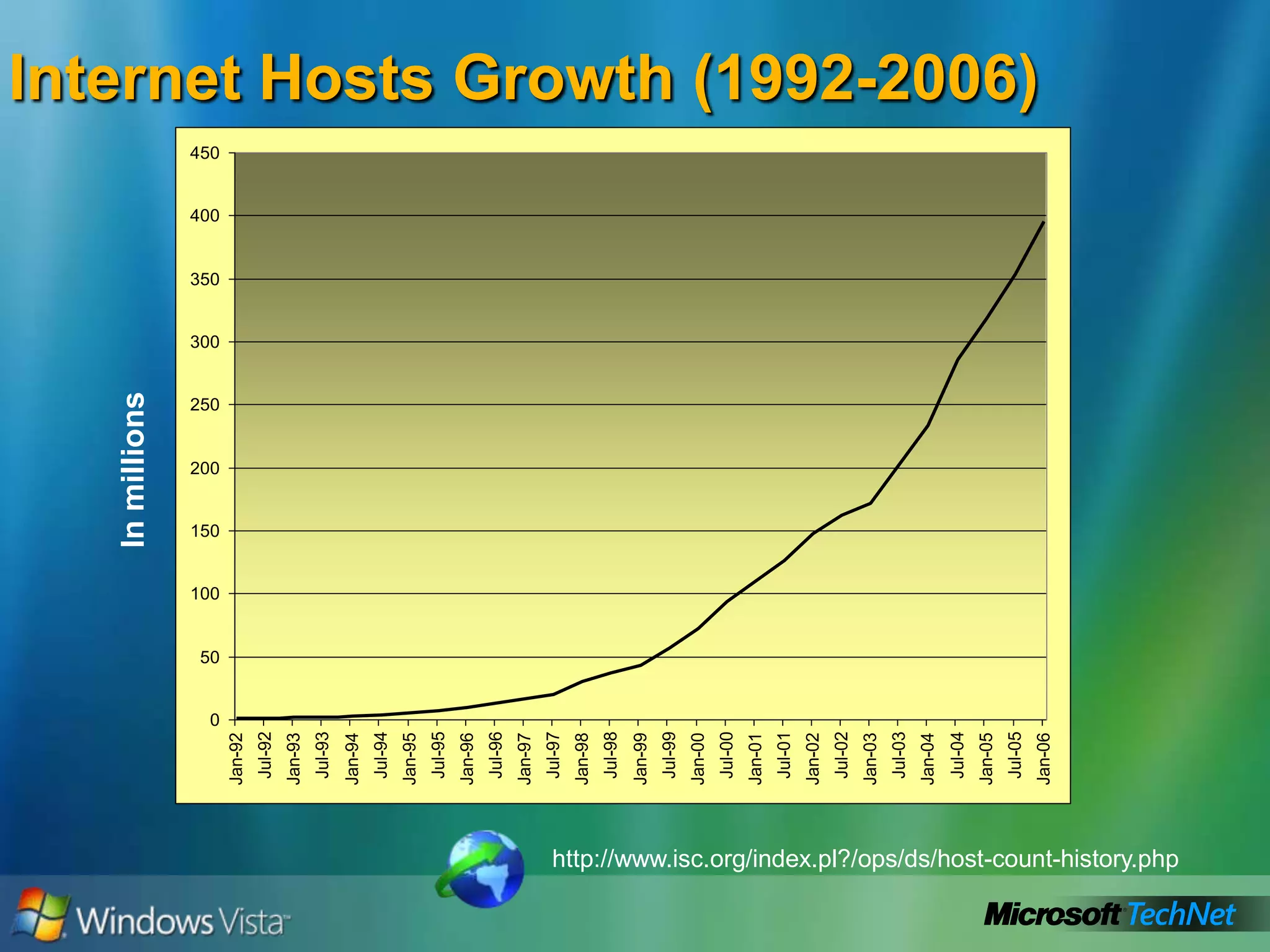
- Limitations of IPv4 like limited address space and large routing tables
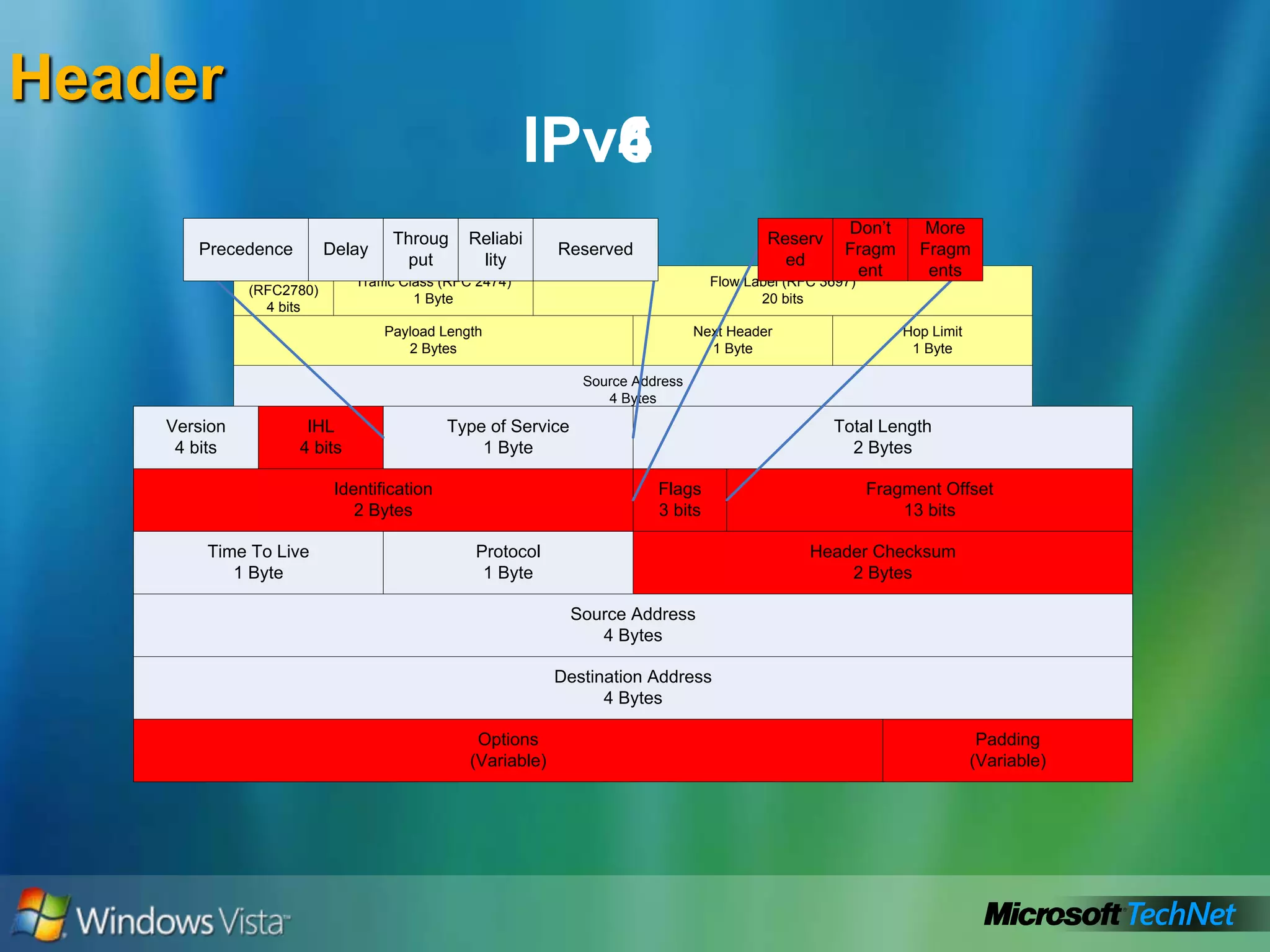
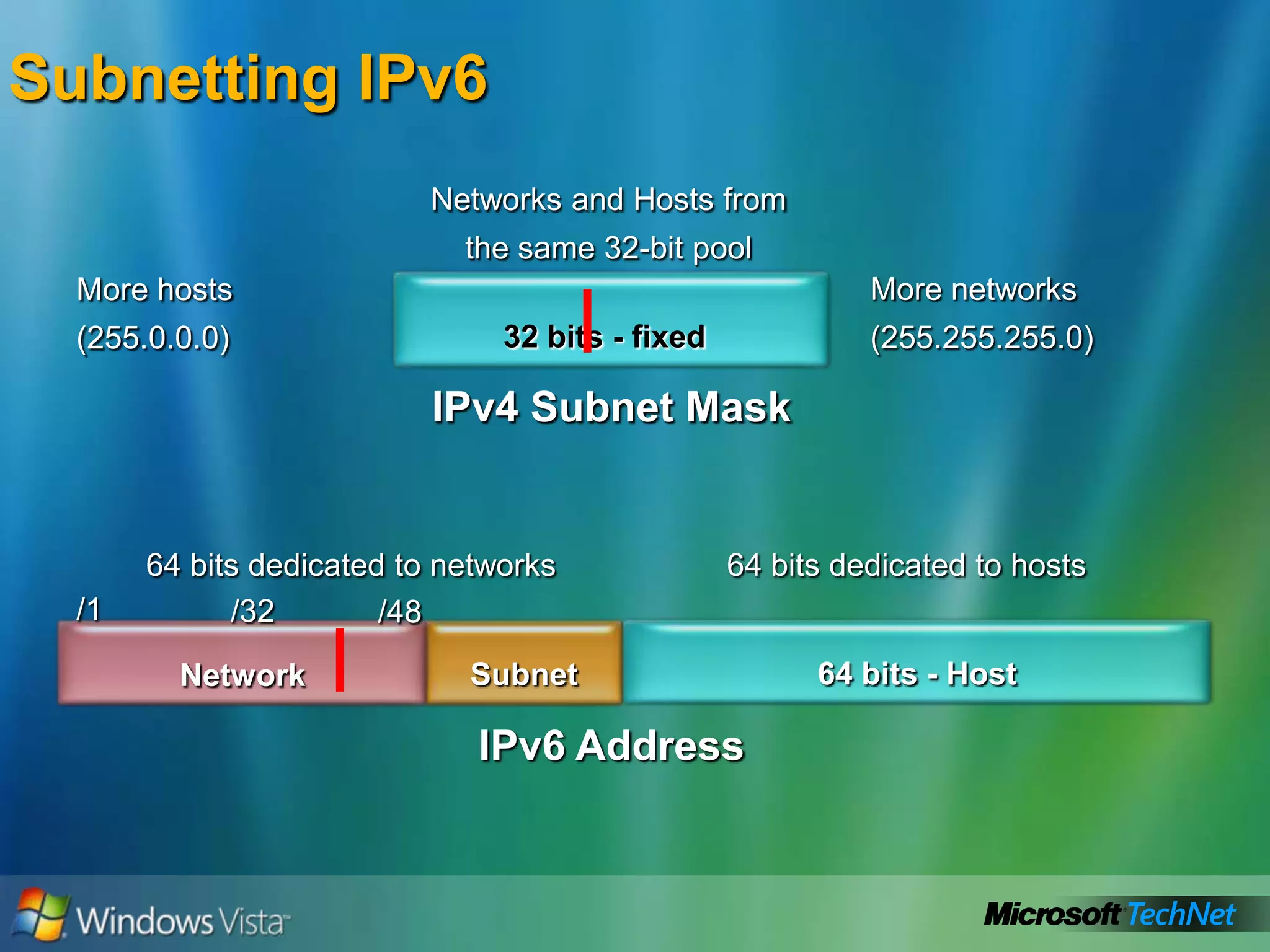
- IPv6 addresses how it uses 128-bit addresses to vastly increase available addresses
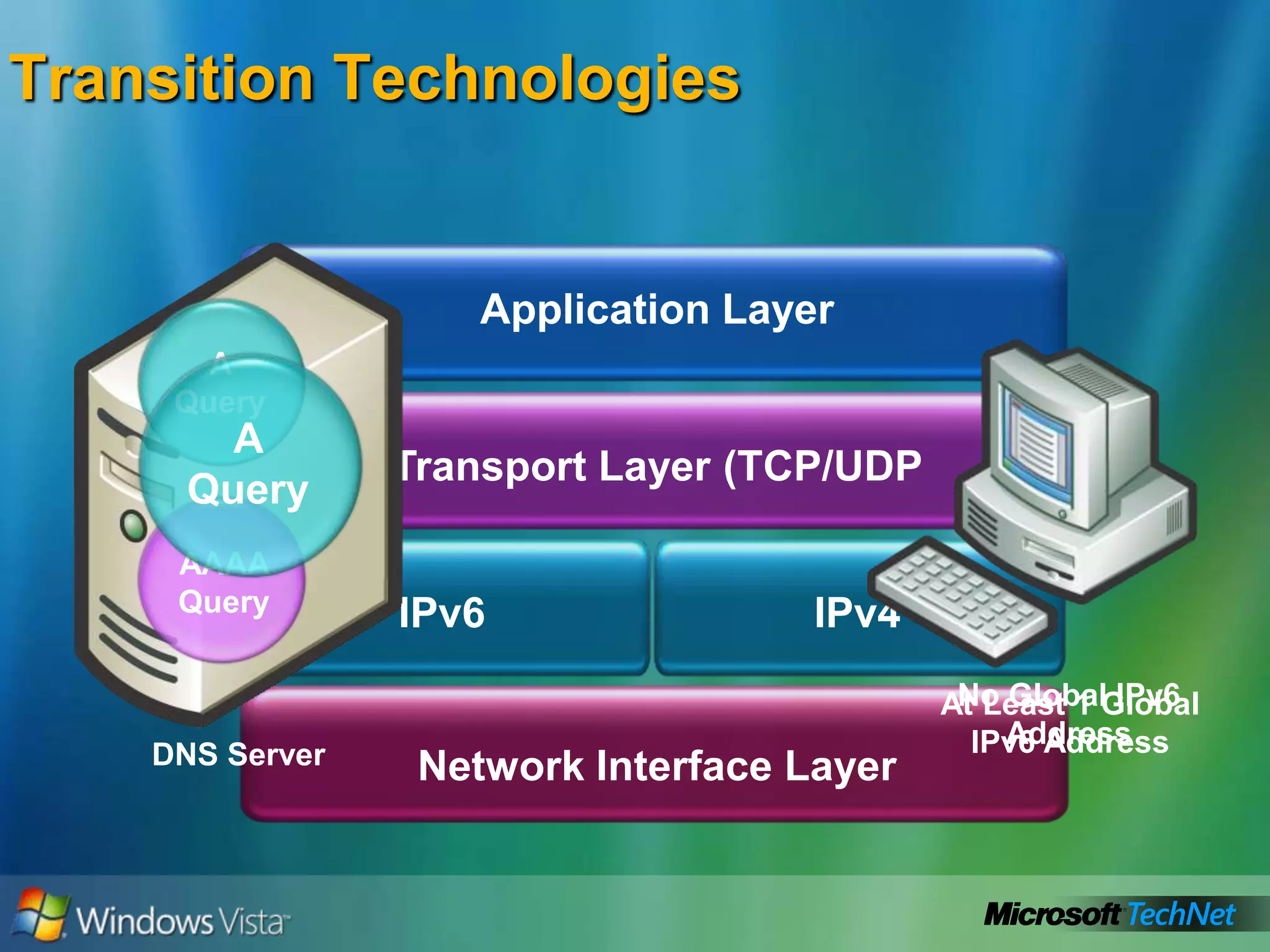
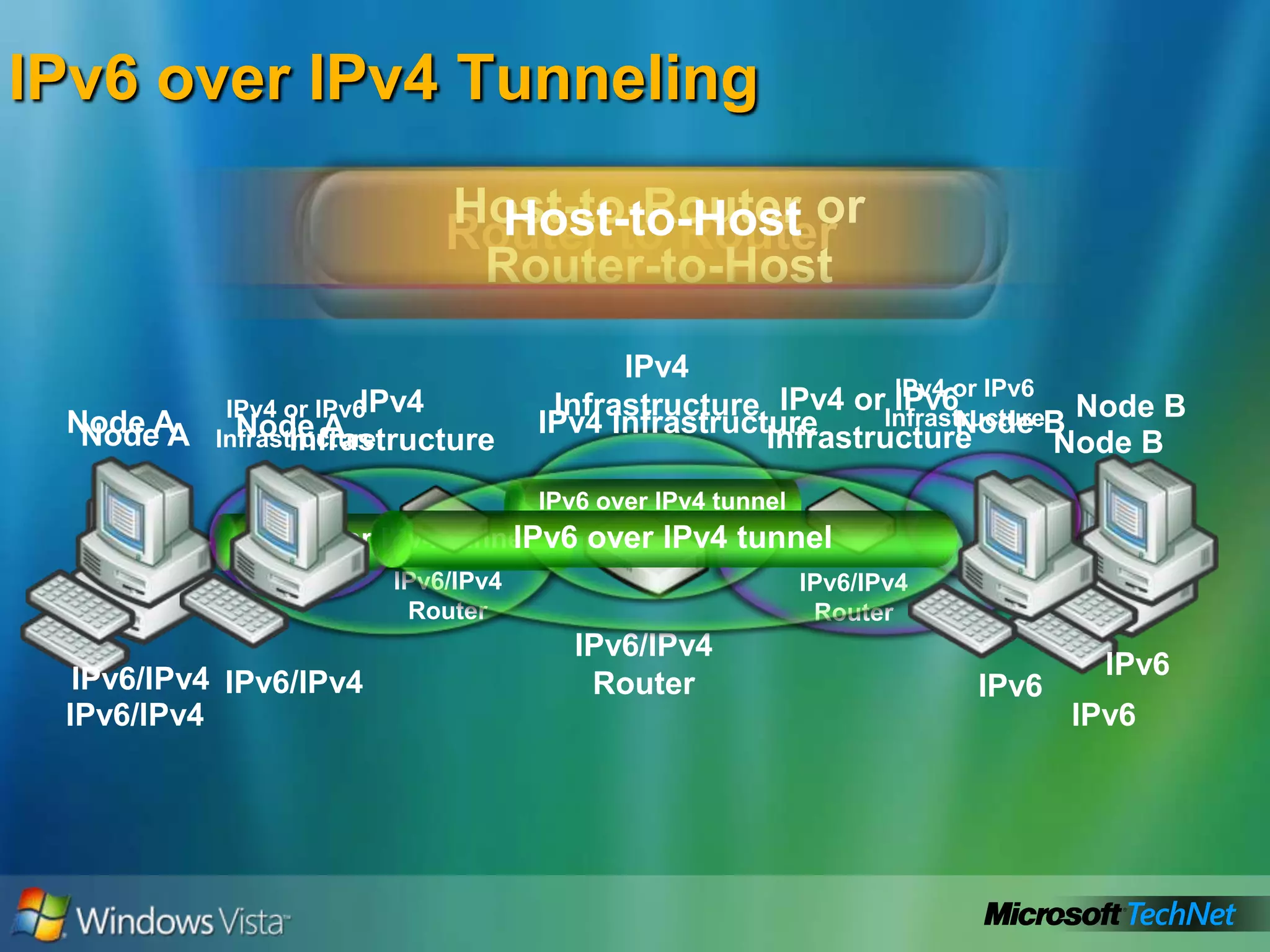
- Transition technologies for moving from IPv4 to IPv6 like tunneling
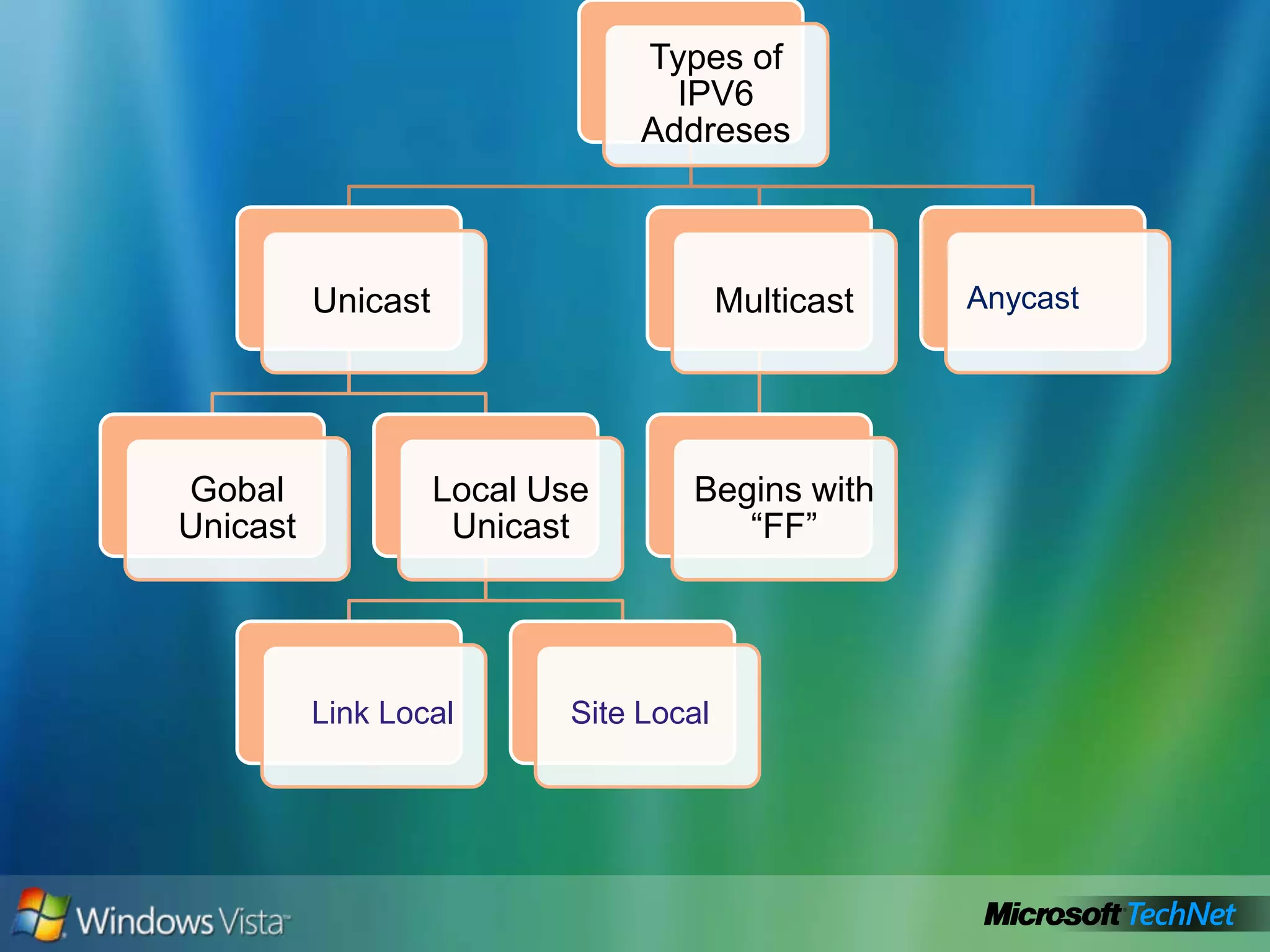
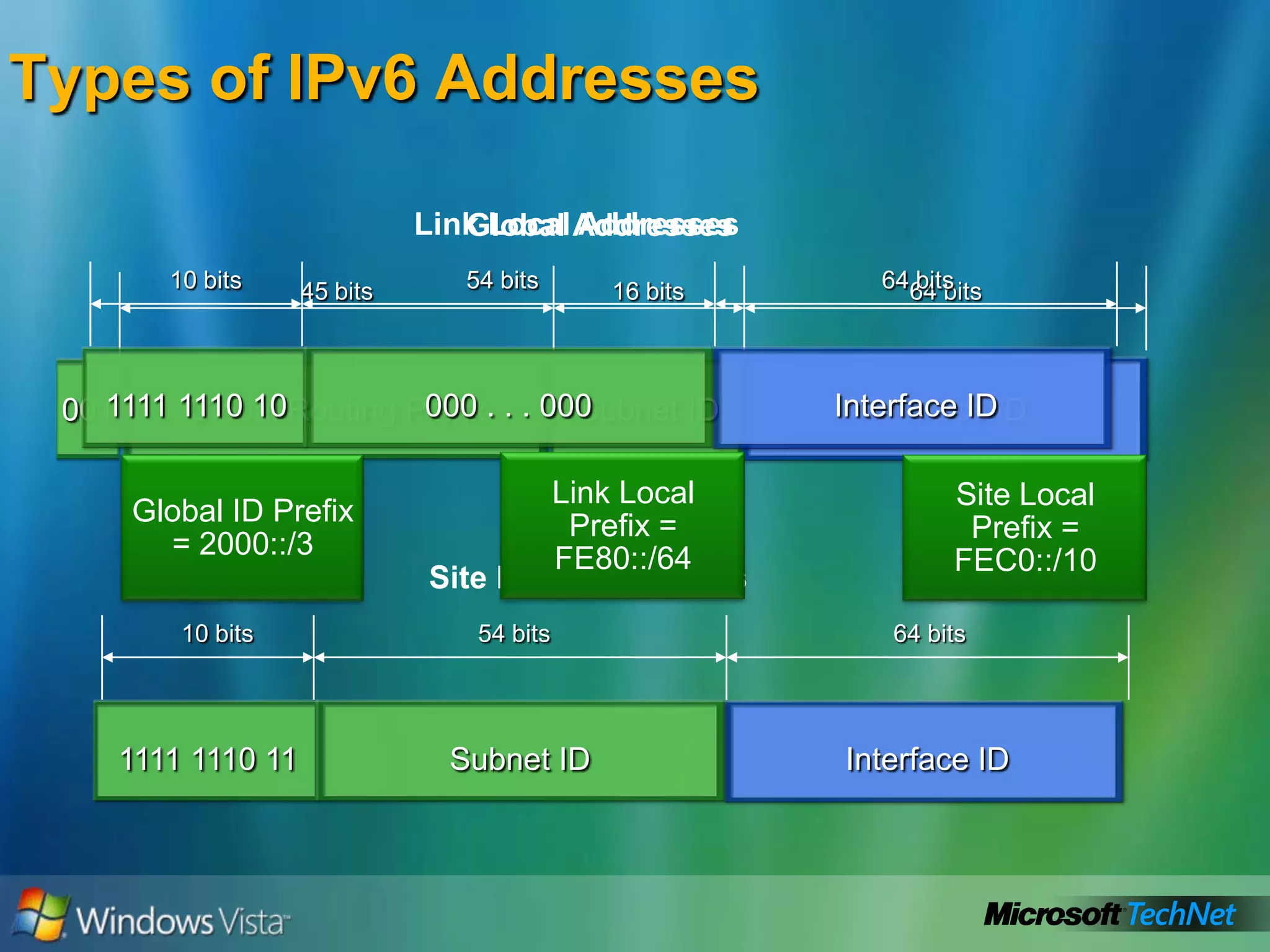
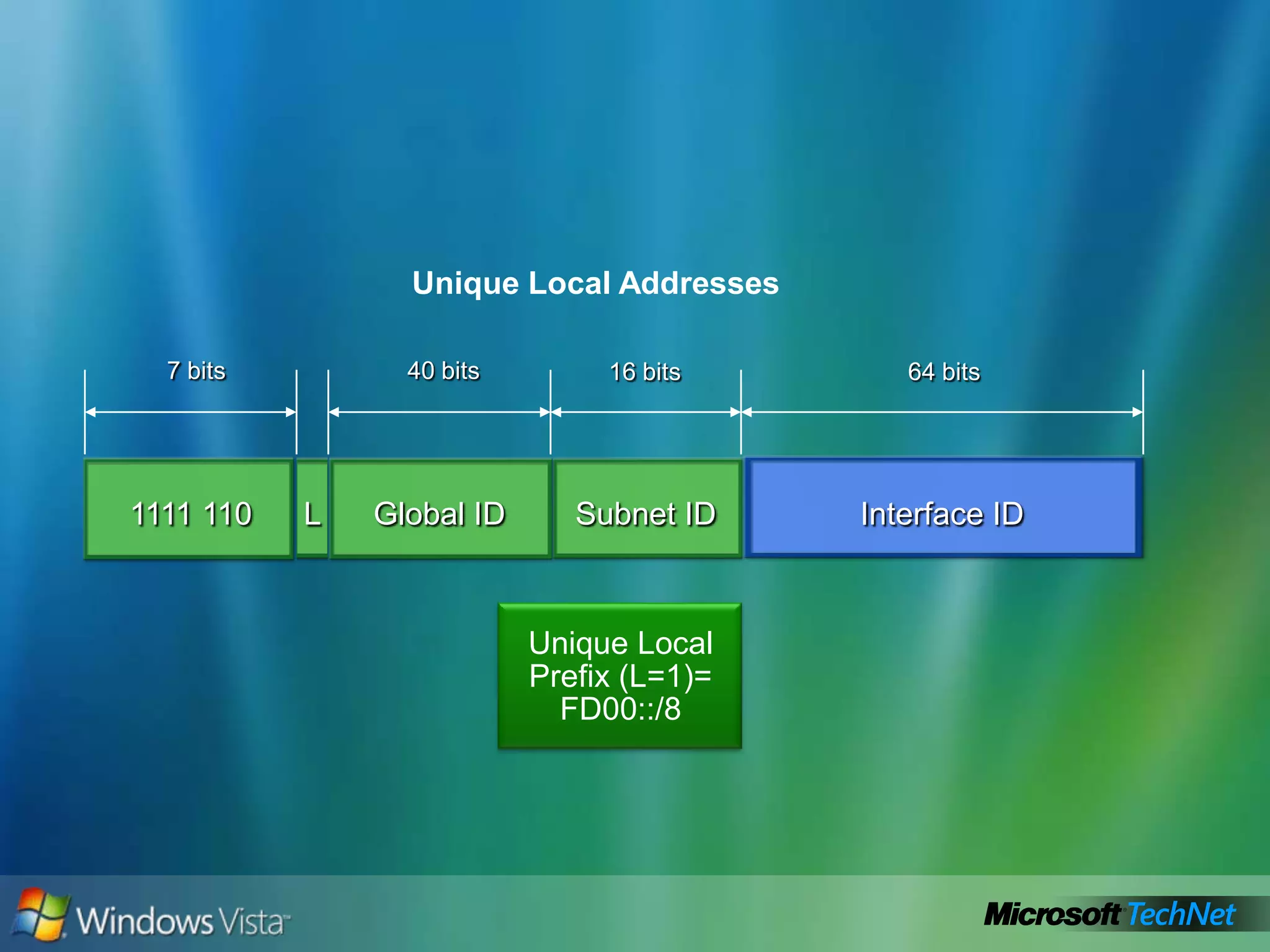
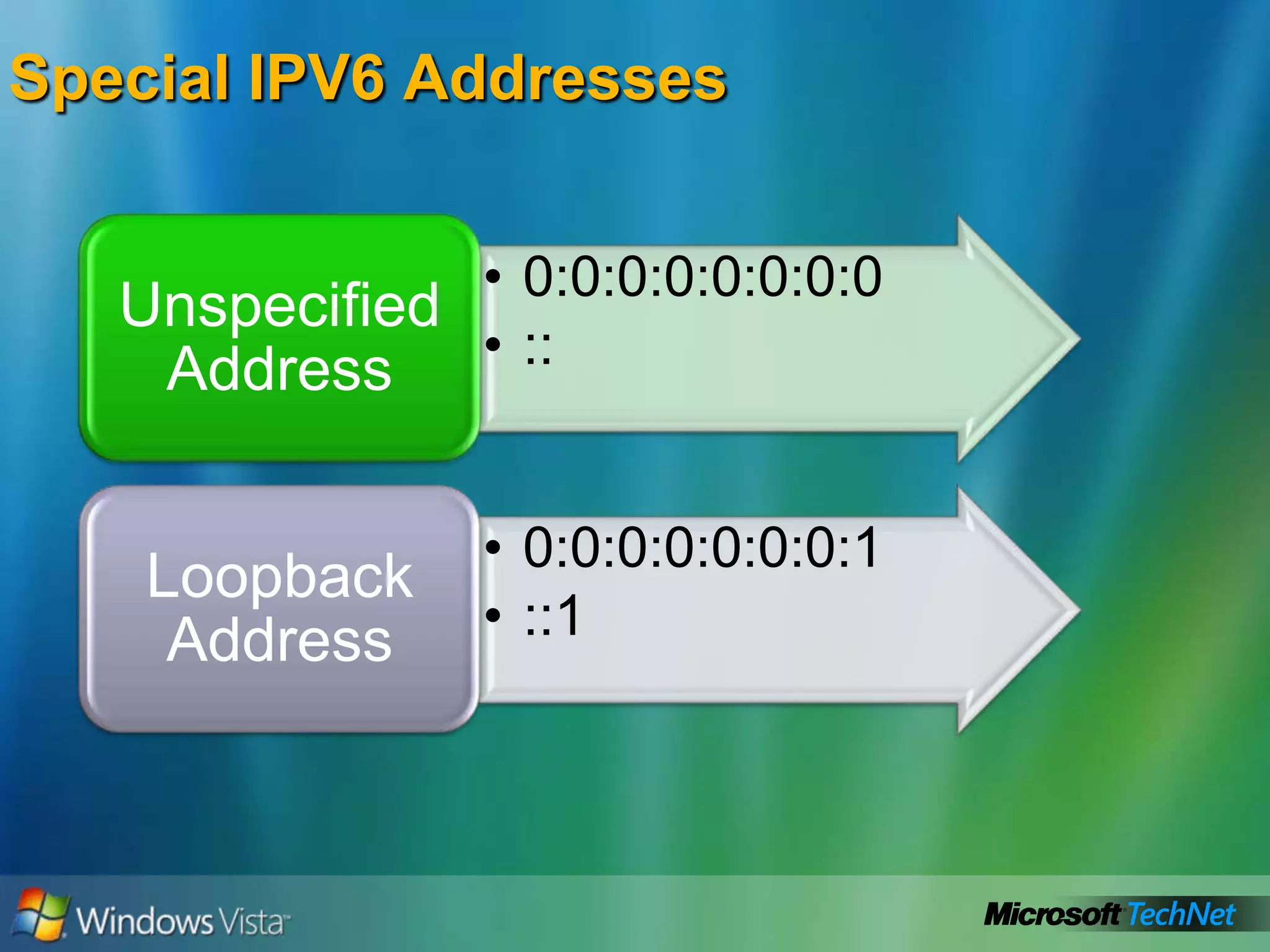
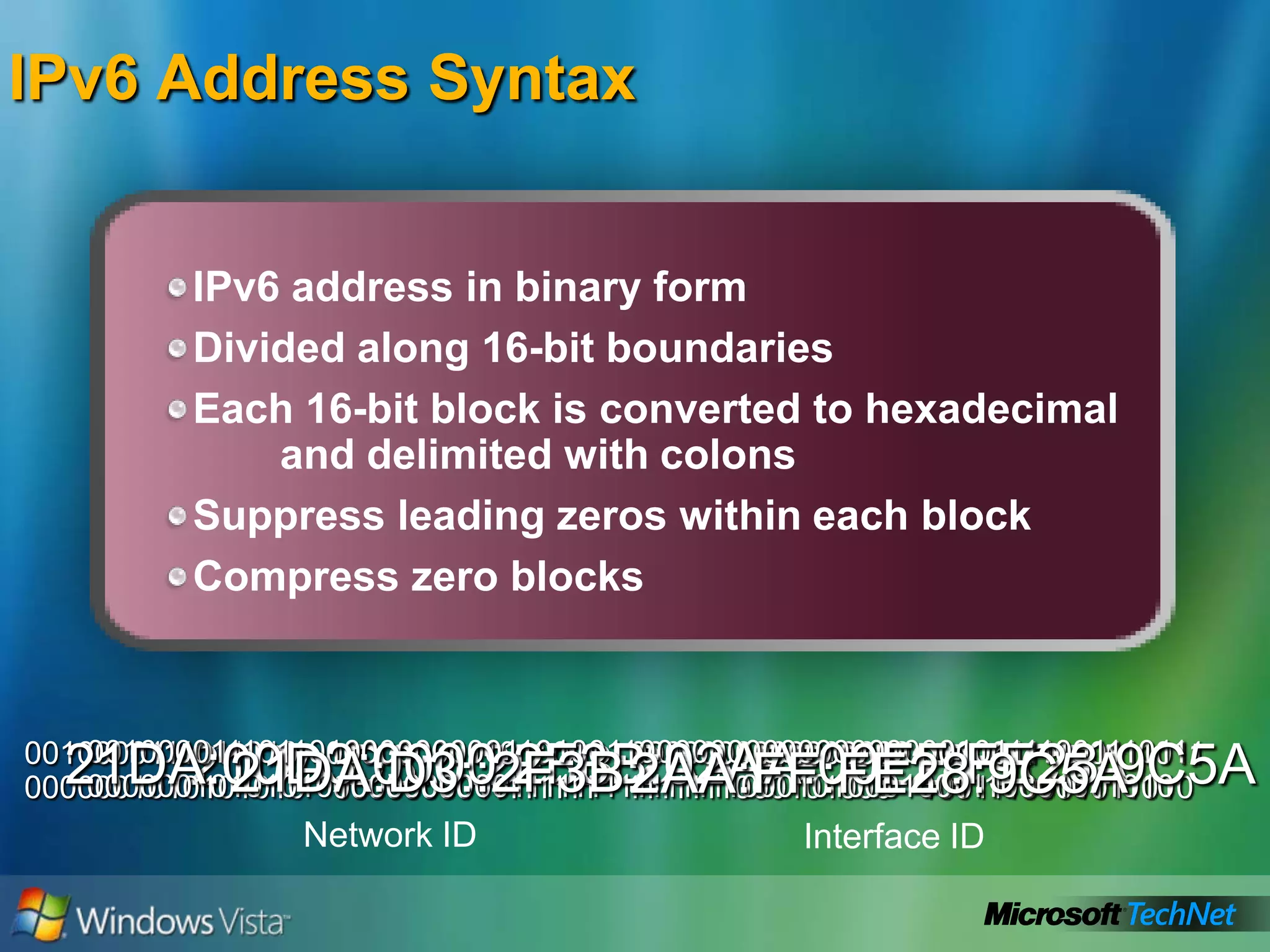
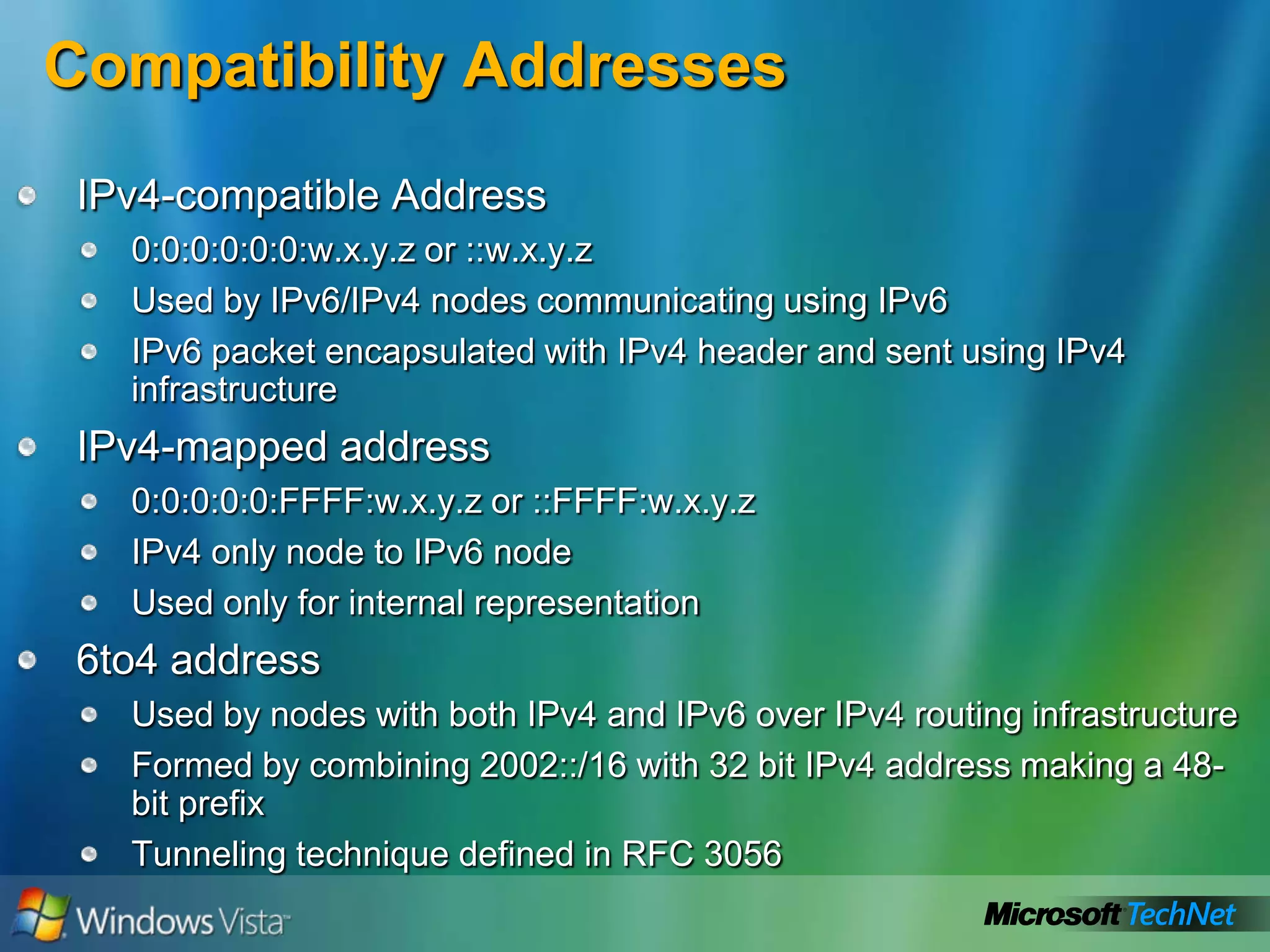
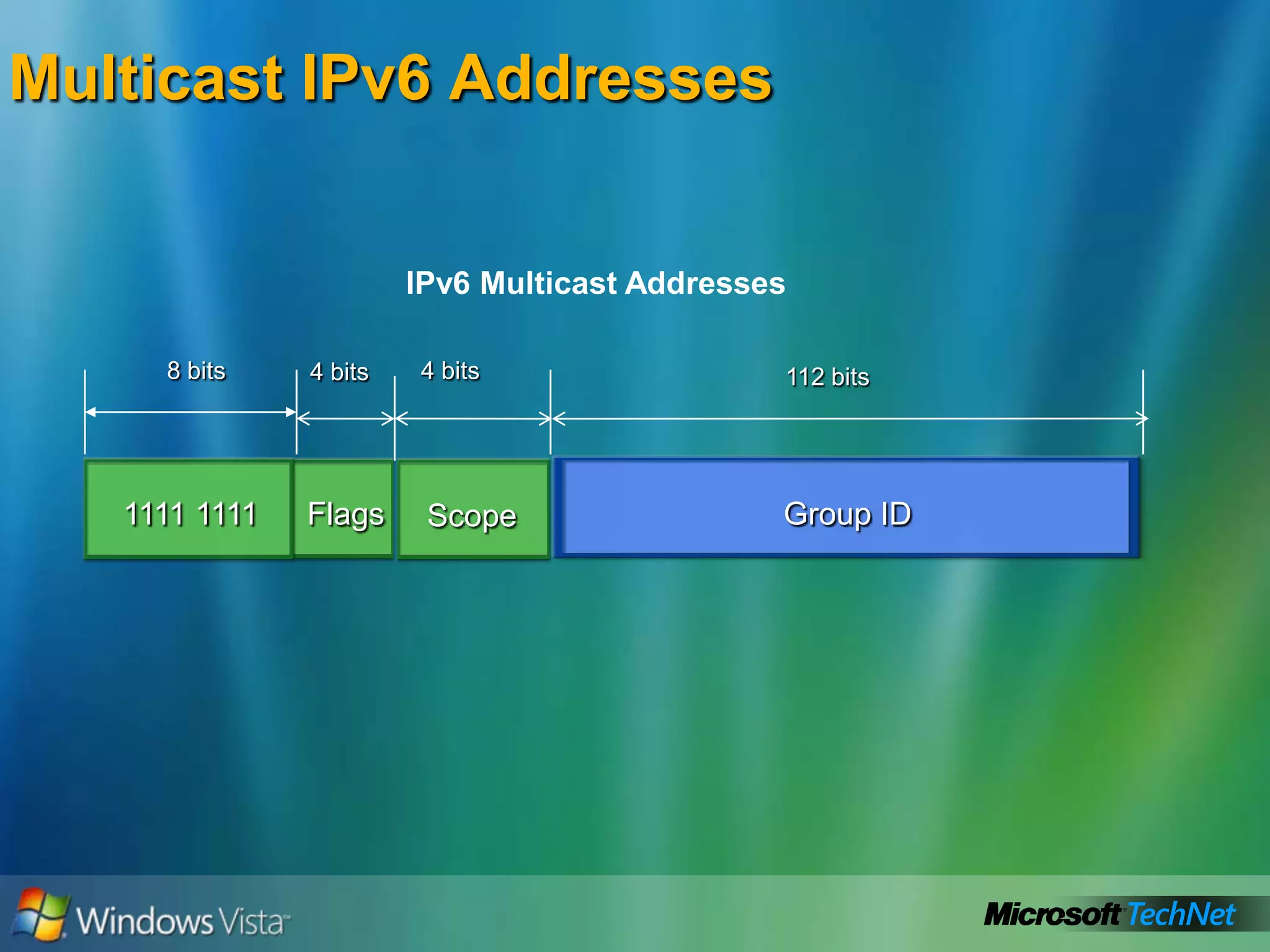
- How to summarize IPv6 addresses and the different types of IPv6 addresses
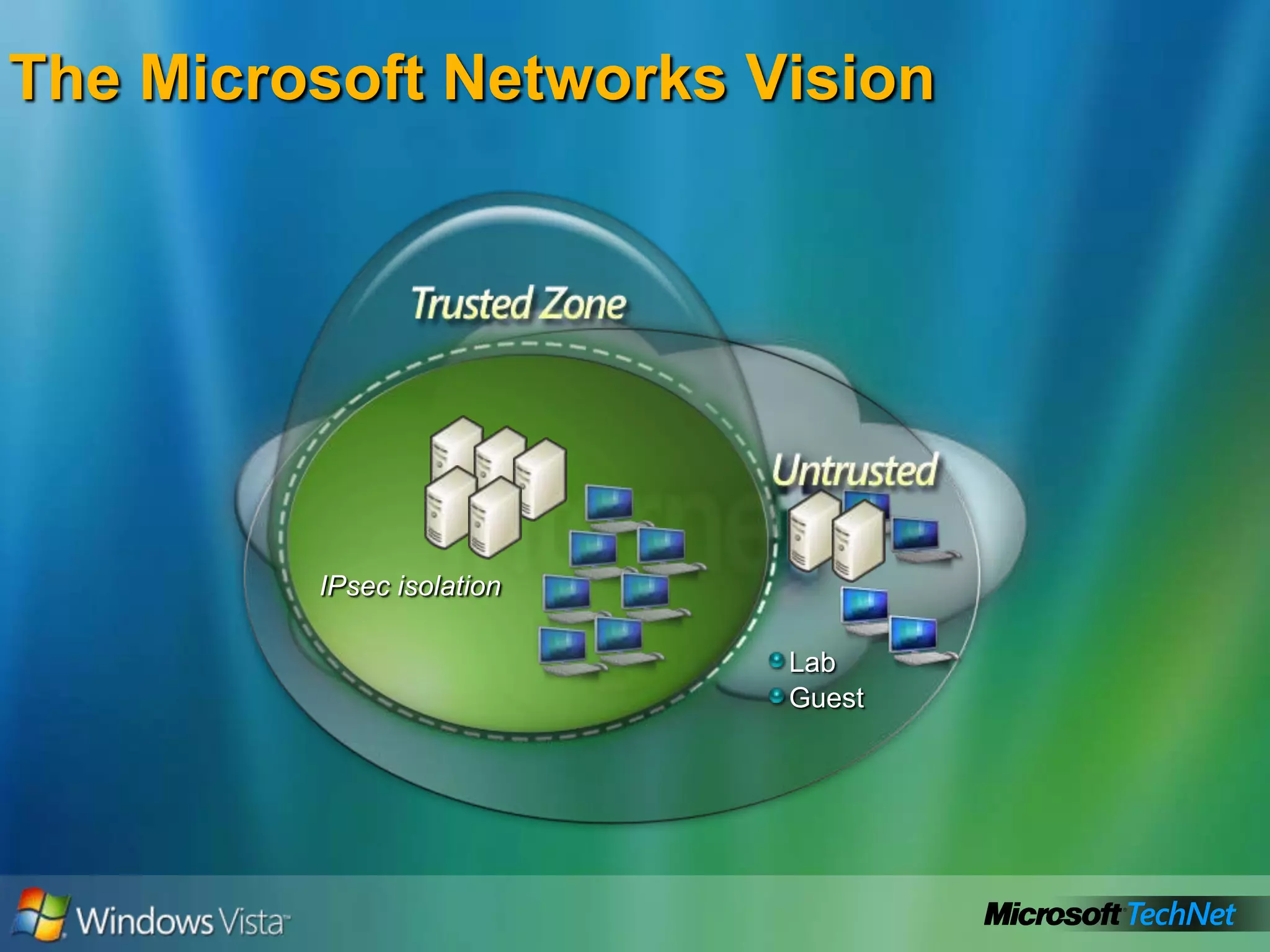
- IPv6 implementation in Windows Vista and transition solutions from Microsoft