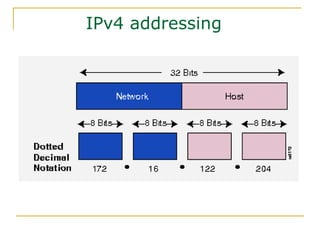
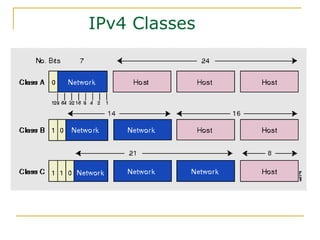
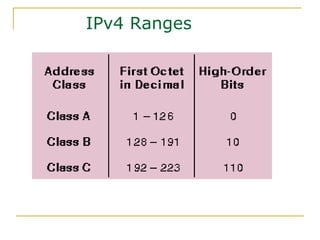
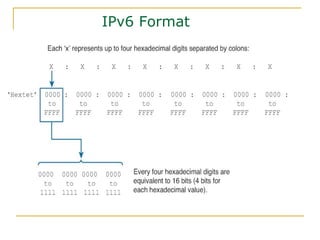
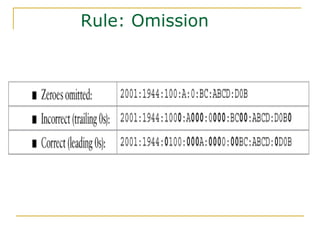
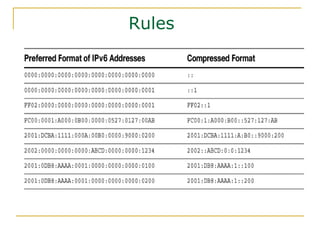
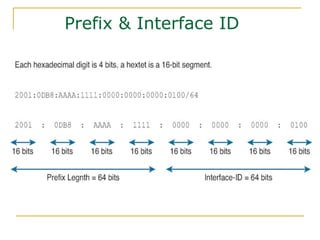
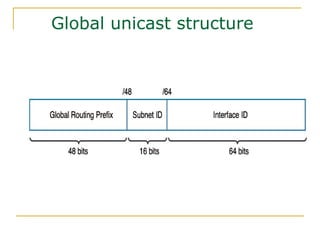
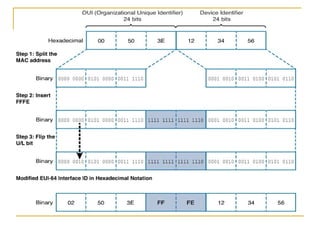
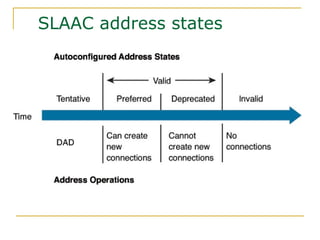
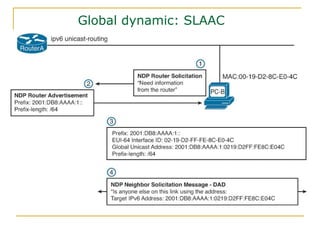
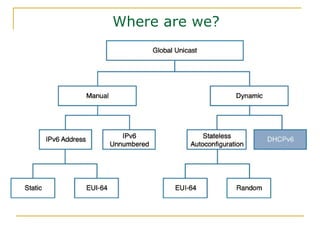
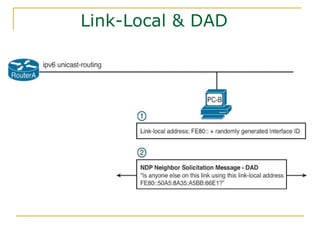
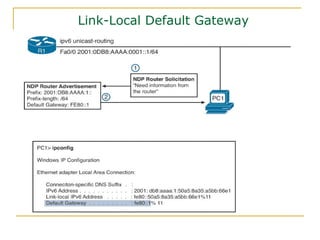
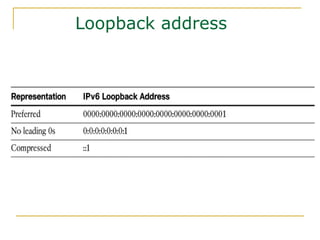
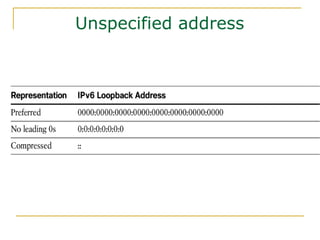
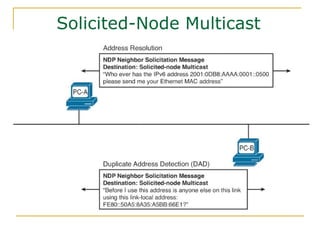
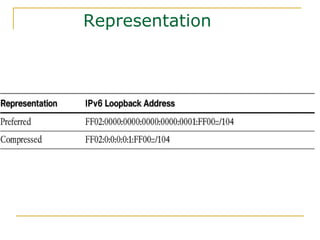
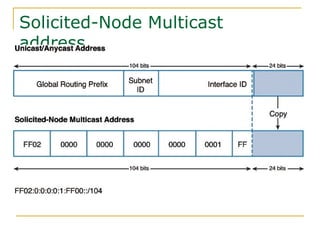
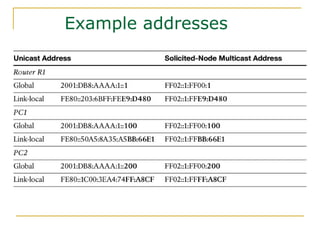
The document provides an overview of IPv6 including:
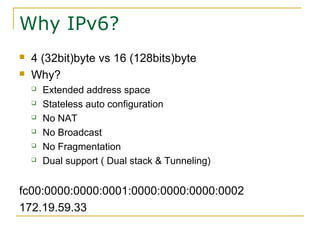
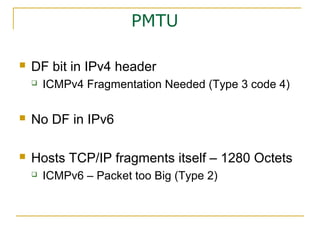
- Why IPv6 was created due to IPv4 address exhaustion and other limitations
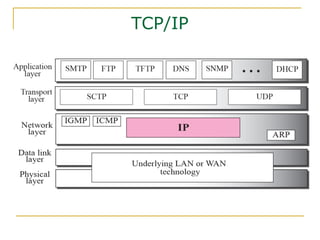
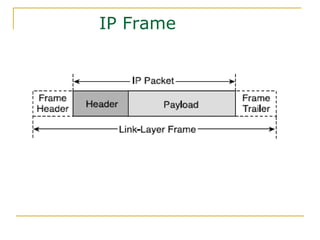
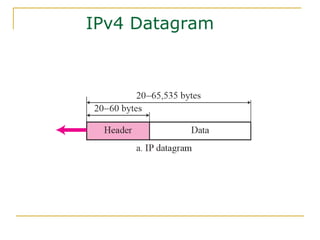
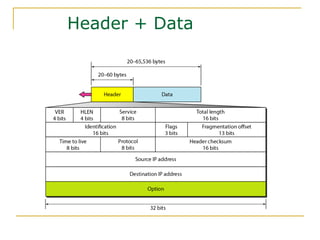
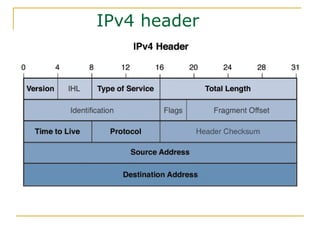
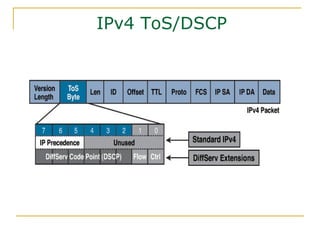
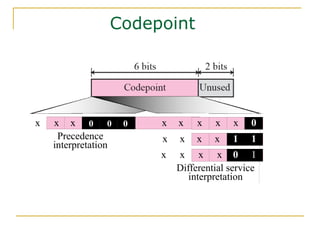
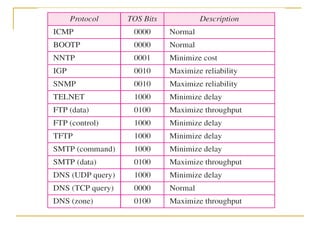
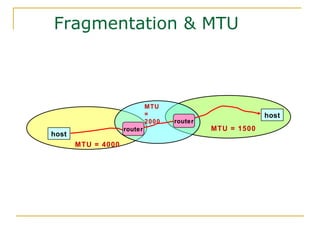
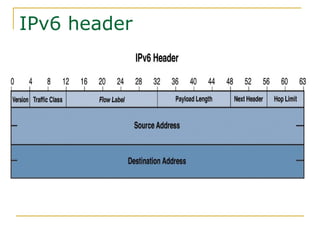
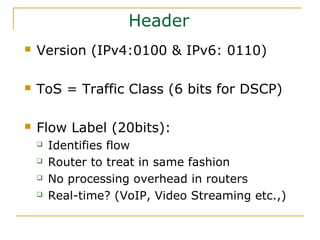
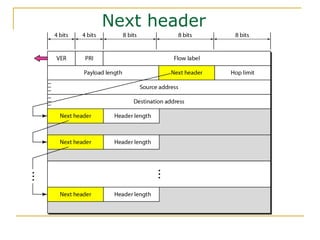
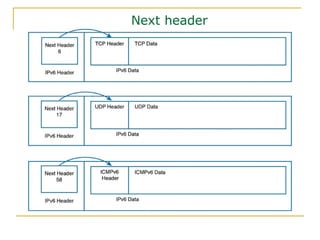
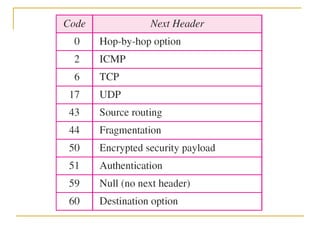
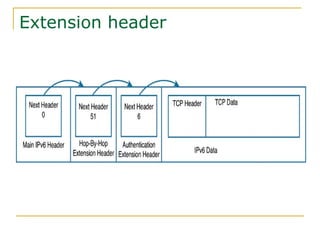
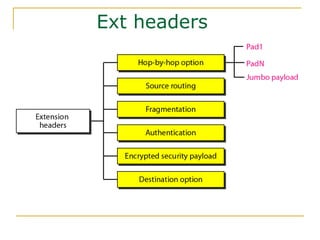
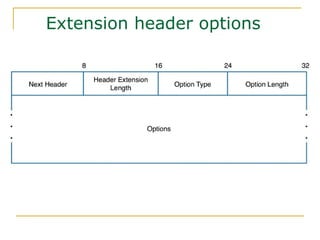
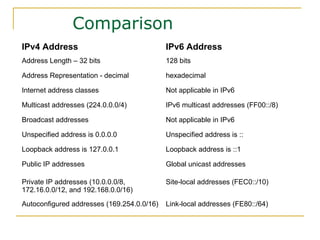
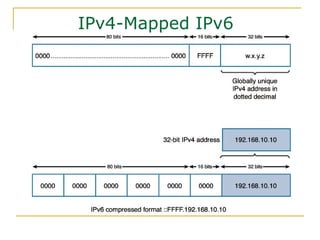
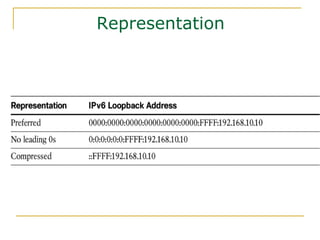
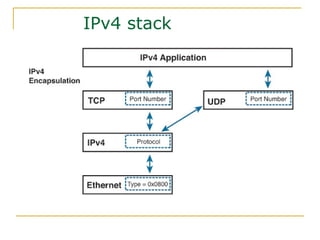
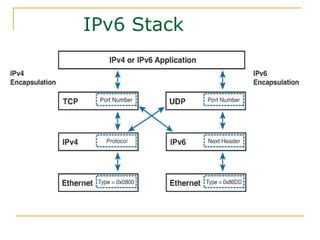
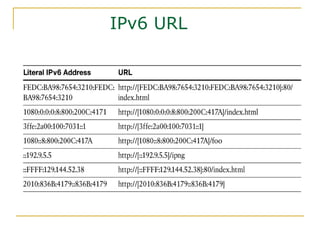
- Key aspects of the IPv6 protocol such as larger 128-bit addresses, simplified fixed-length header, and extension headers
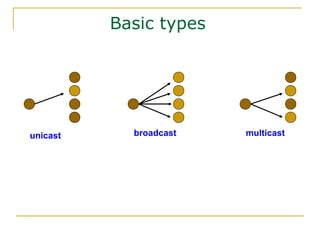
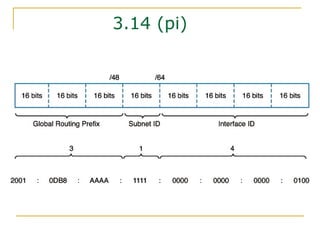
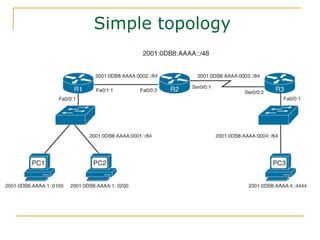
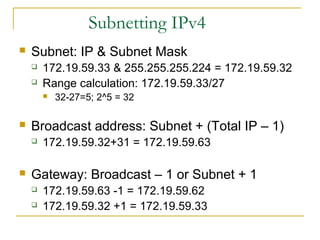
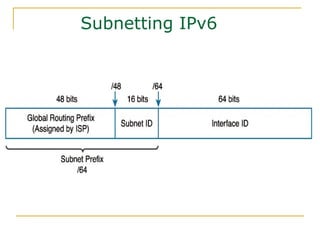
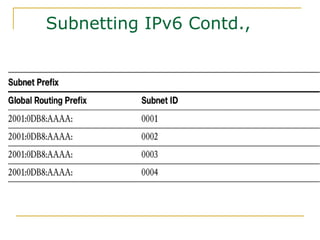
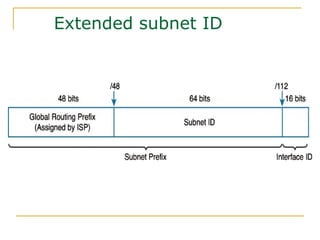
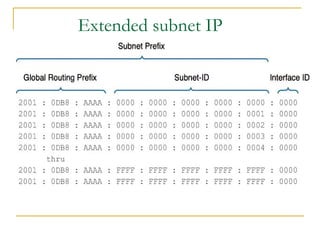
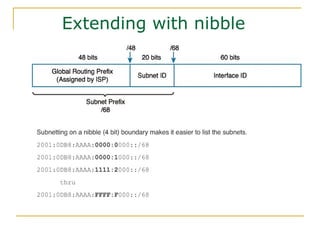
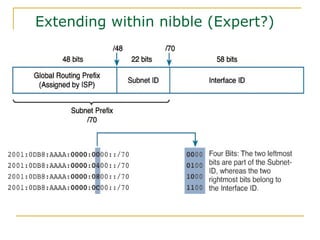
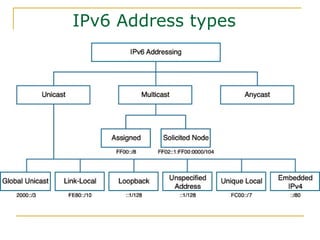
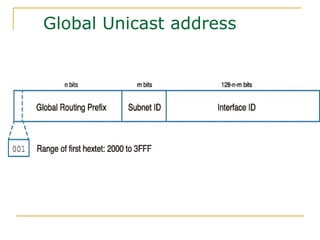
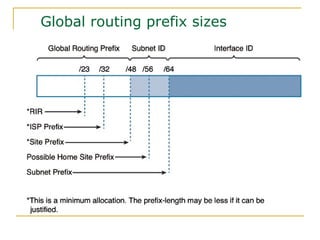
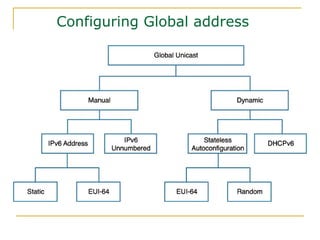
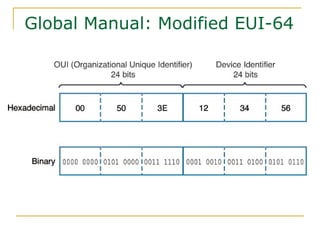
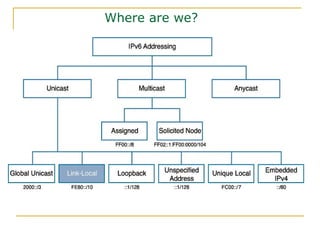
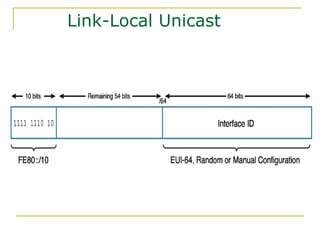
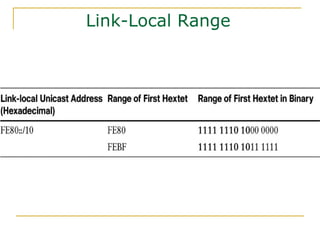
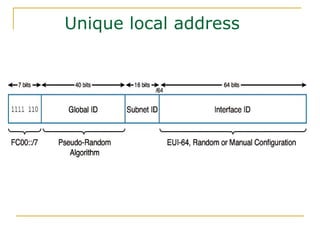
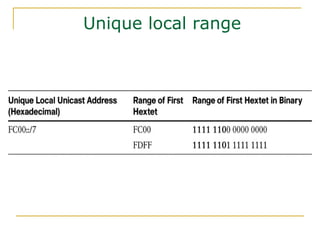
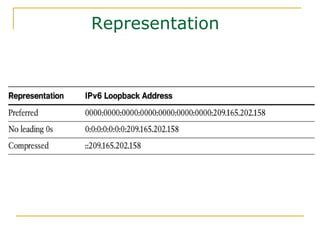
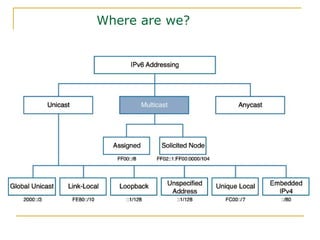
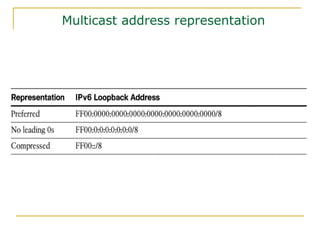
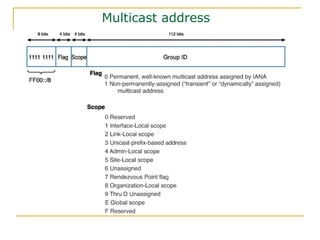
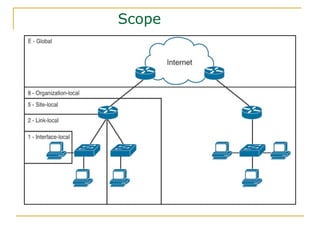
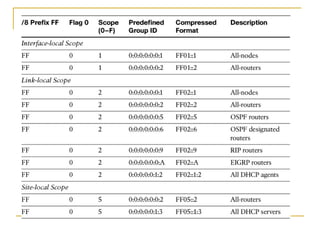
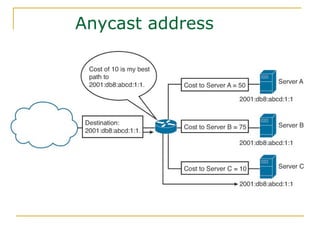
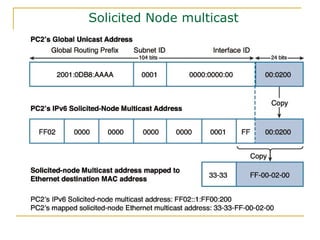
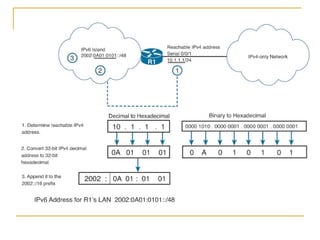
- Main IPv6 address types including global unicast, link-local, unique local, and multicast addresses
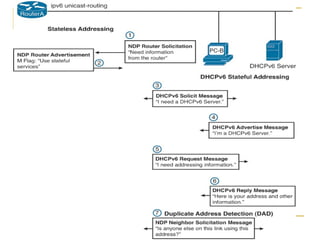
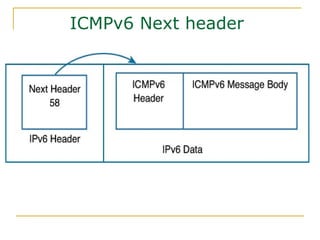
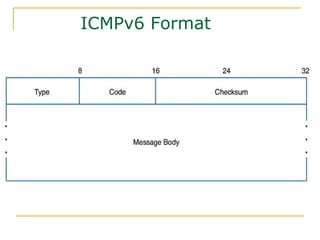
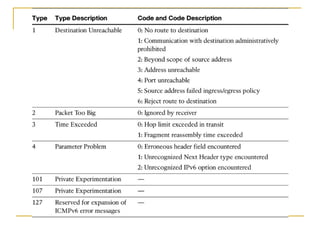
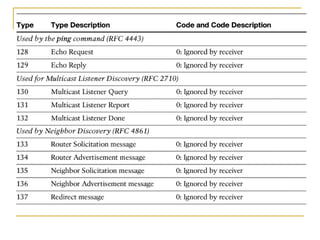
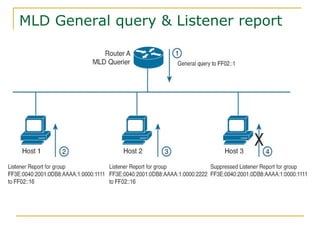
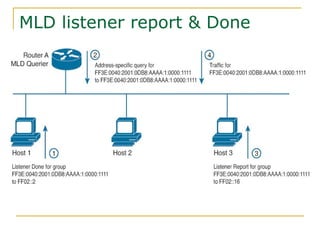
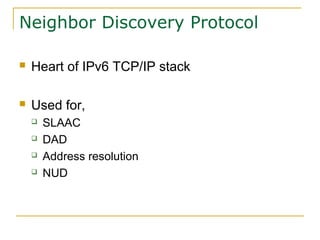
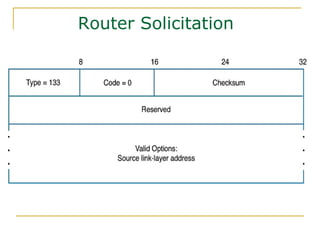
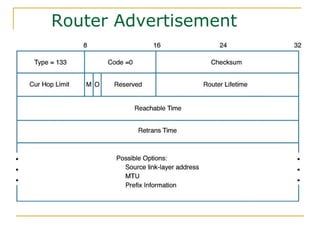
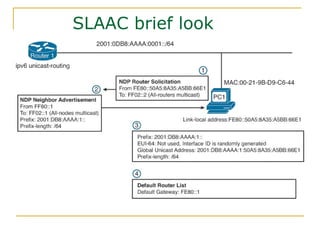
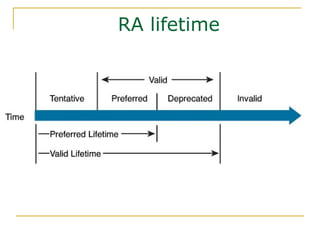
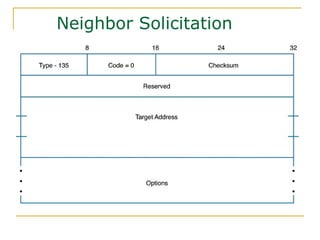
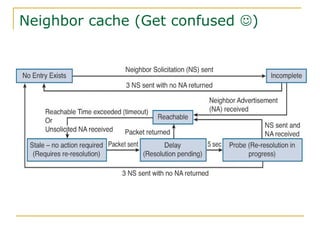
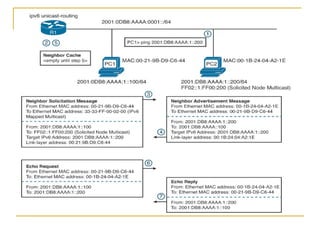
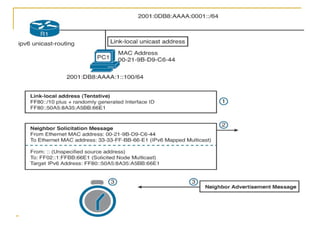
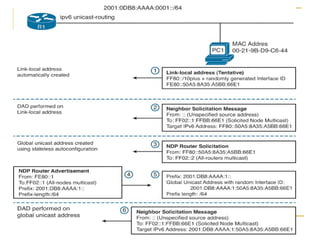
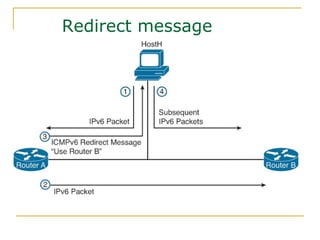
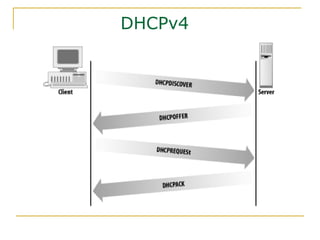
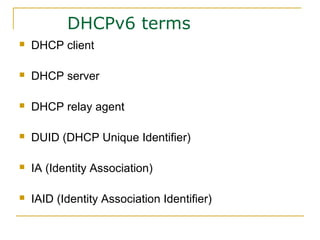
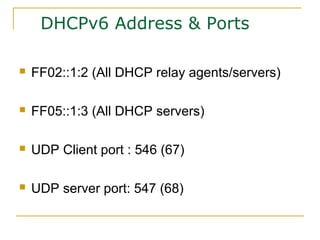
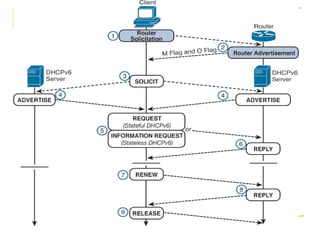
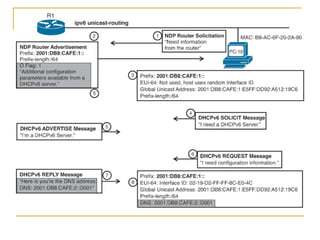
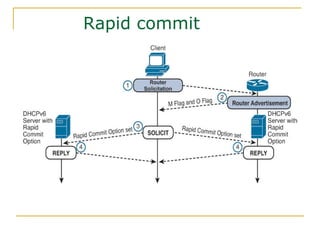
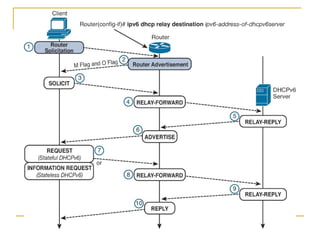
- Protocols that support IPv6 including Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP), ICMPv6, and DHCPv6
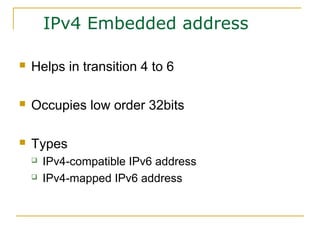
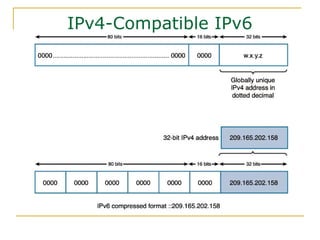
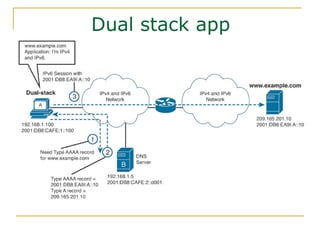
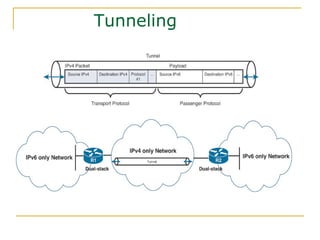
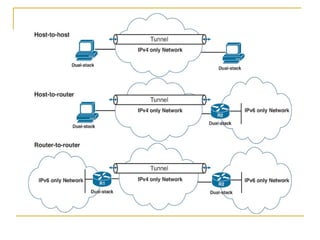
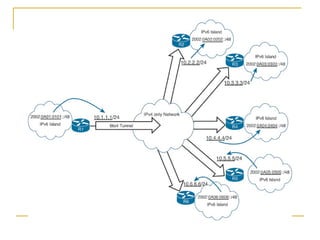
- Methods for transitioning from IPv4 to IPv6 including dual stack and tunneling technologies.