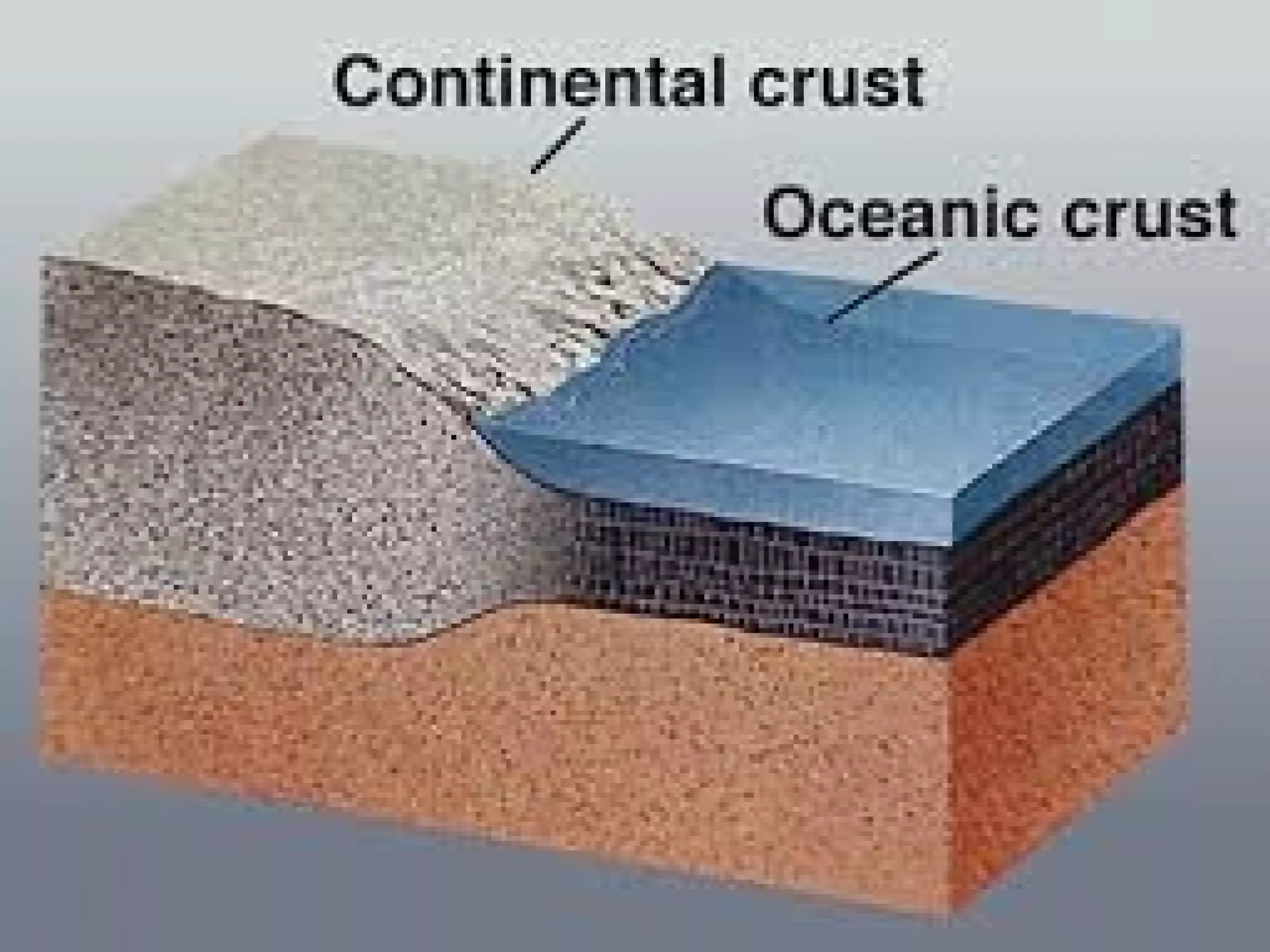
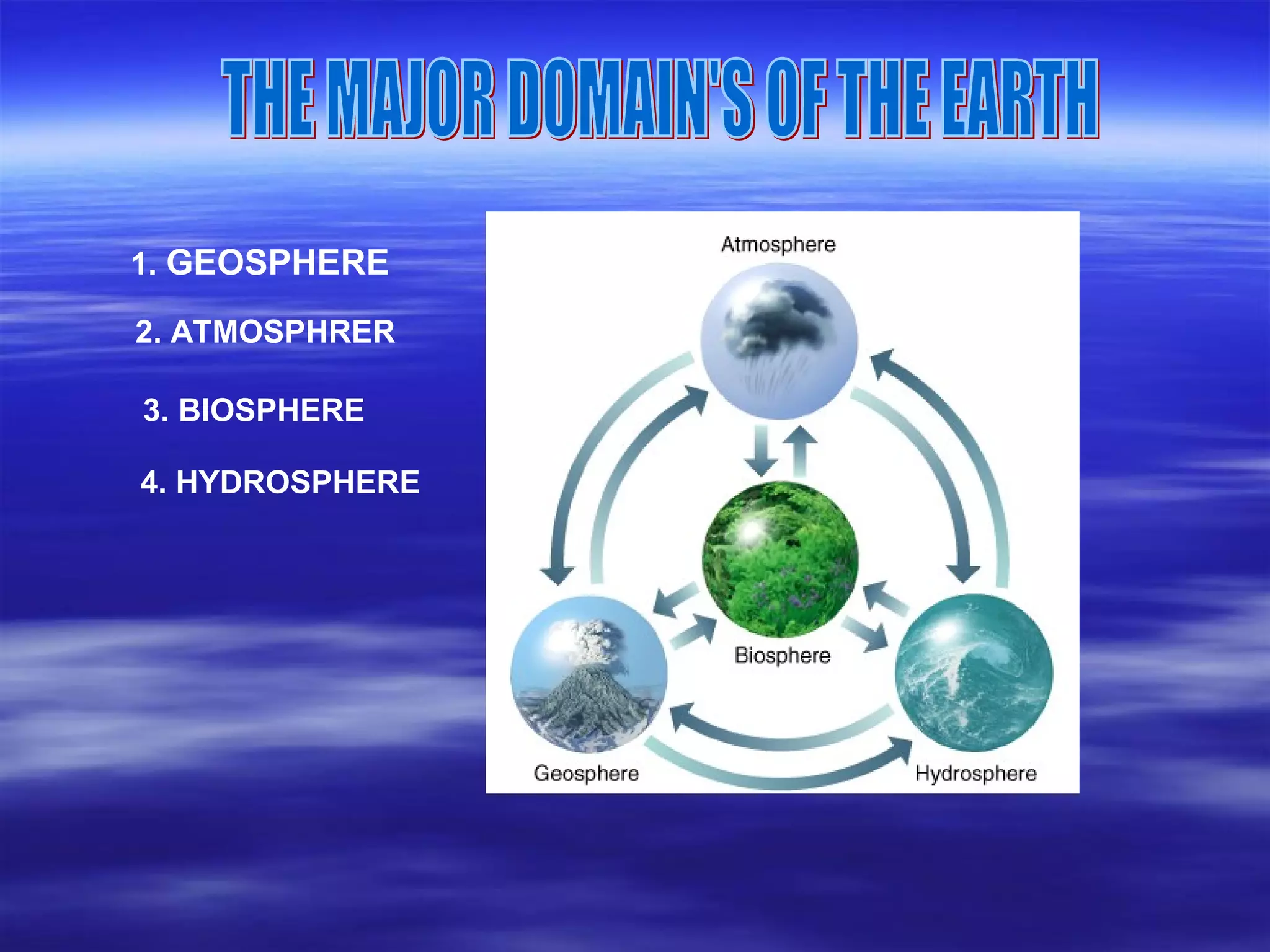
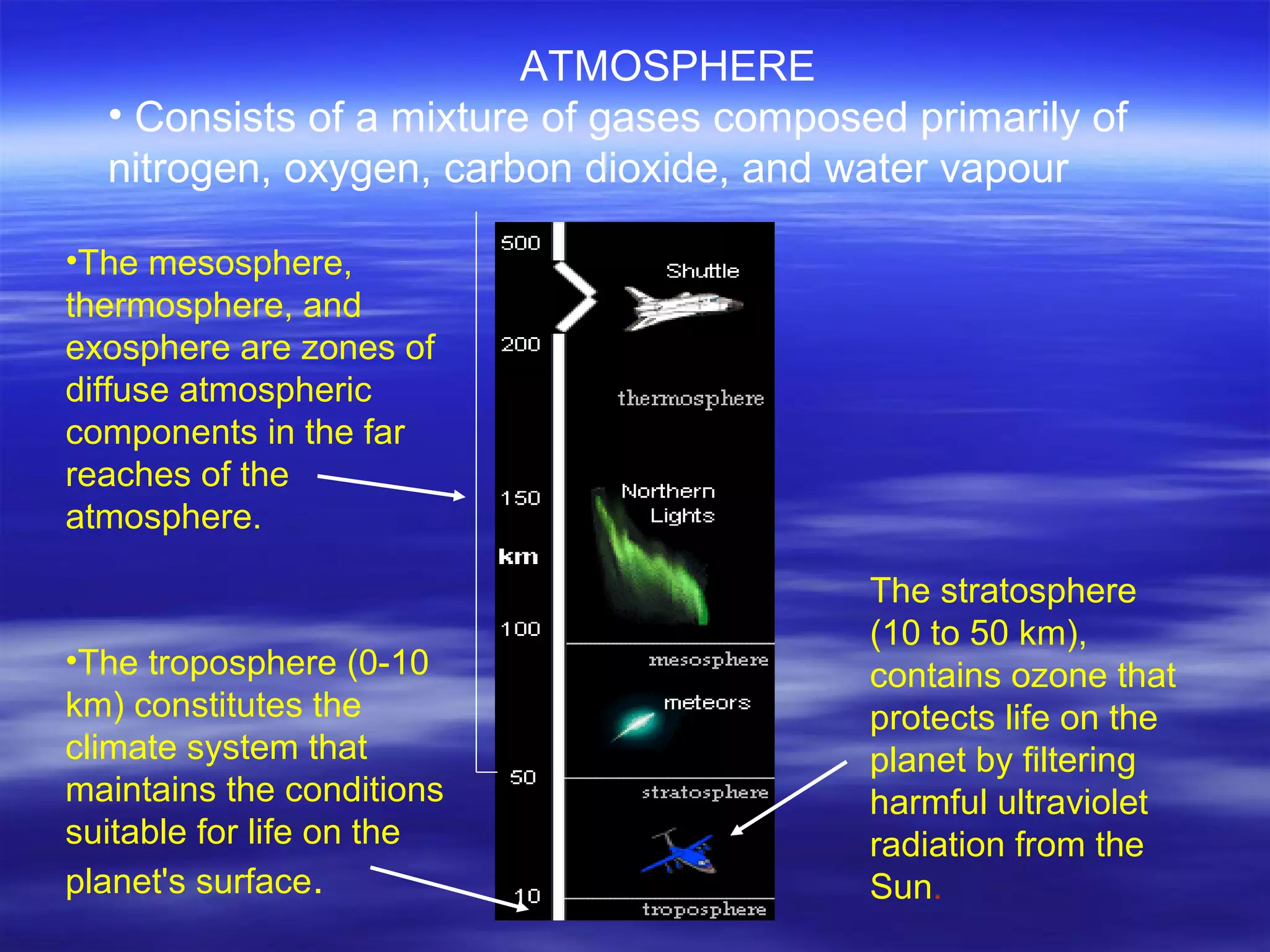
The document discusses the four major spheres of Earth - the geosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere. It describes the composition and layers of the geosphere, including the crust, mantle, and core. The crust consists of different rock types and divides into continental and oceanic plates. The mantle is the largest layer and flows due to temperature differences. The core has an outer liquid layer and inner solid layer with extreme heat and pressure. The atmosphere surrounds Earth and consists of nitrogen, oxygen and other gases. The hydrosphere includes all water on the planet across oceans, ice, underground, and vapor in the air. The biosphere encompasses all living things and organic matter on the planet.