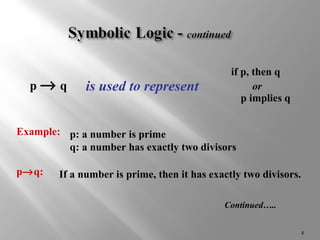
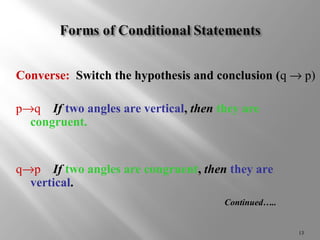
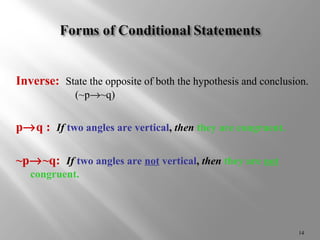
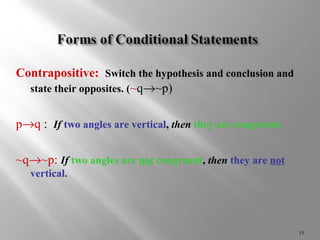
Conditional statements relate two parts, a hypothesis and conclusion, using "if-then" logic. The hypothesis follows "if" and is the given condition, while the conclusion follows "then" and is the result. Symbols like implies (®), not (~), and (Ù,Ú) can also represent conditional statements and connect multiple statements. A conditional statement is only false if the hypothesis is true but conclusion is false. Contrapositives and converses of conditional statements are also considered in determining logical equivalencies.