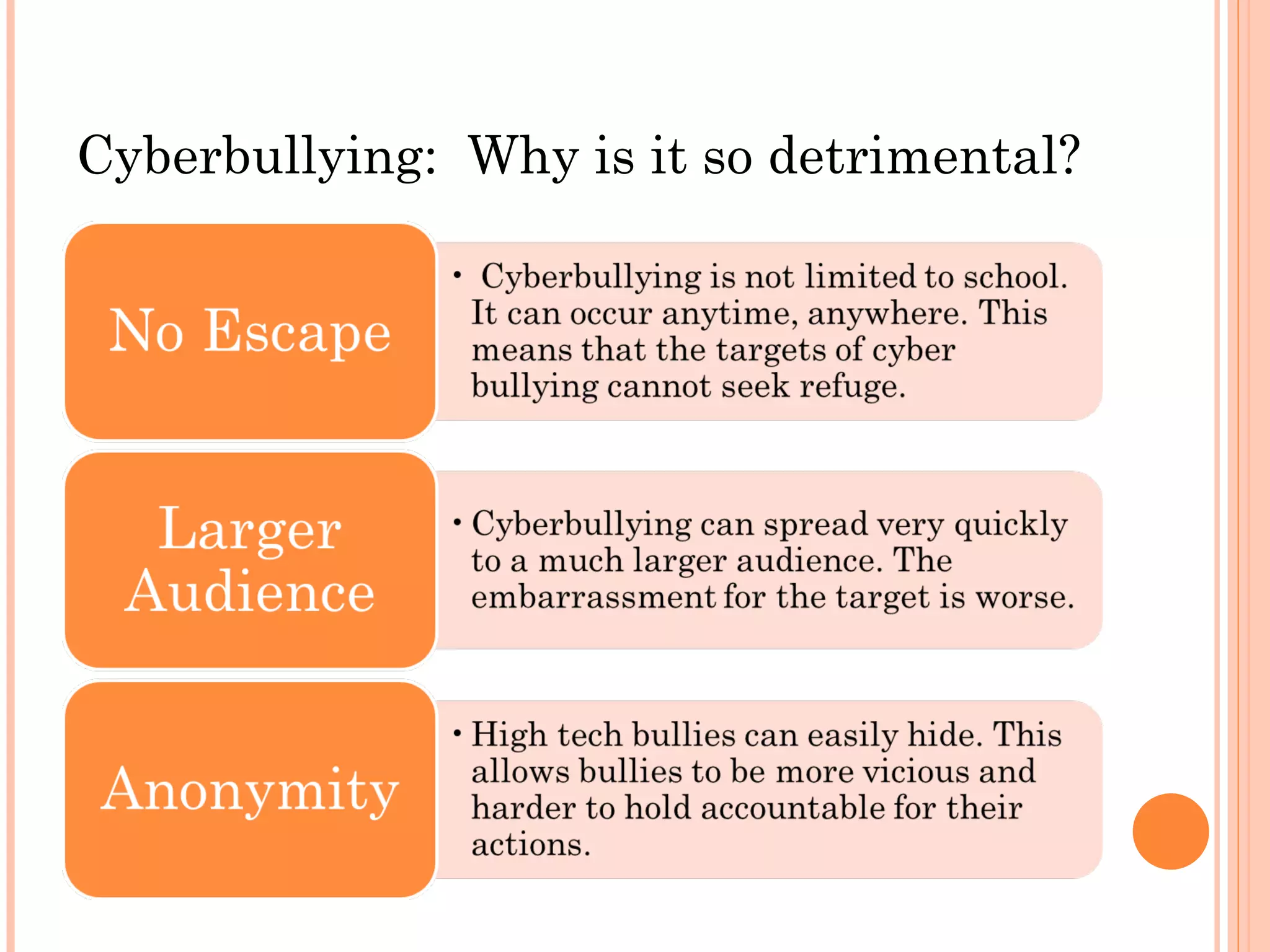
This document discusses strategies for preventing cyberbullying in schools. It begins by defining bullying as repeated harmful acts with an imbalance of power. It then notes that verbal abuse is the most common form of bullying. The document discusses how bullying peaks in 6th grade and 9th graders do the most bullying. It also notes that conflict resolution and zero tolerance policies are ineffective at addressing the root causes of bullying. The document advocates approaches that address all parties involved. It discusses why cyberbullying is particularly detrimental and notes cell phones are a common tool for elementary school bullying. It provides examples of effective school and peer responses to cyberbullying.