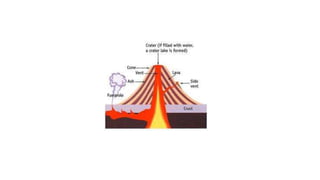
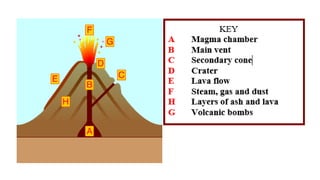
1) Volcanoes form at boundaries where tectonic plates meet, such as where plates are subducting or spreading apart.
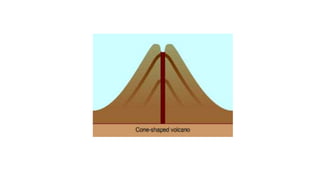
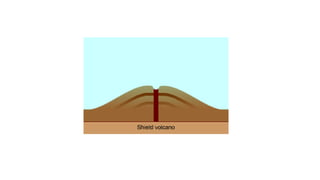
2) There are two main types of volcanoes - cone-shaped volcanoes which form from thick, slow-moving lava and shield volcanoes which have flatter slopes due to more fluid lava.
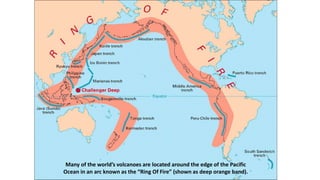
3) Examples of highly active volcanic regions include the Pacific Ring of Fire and areas around Alaska, Hawaii, and the Cascade Range in the western United States.