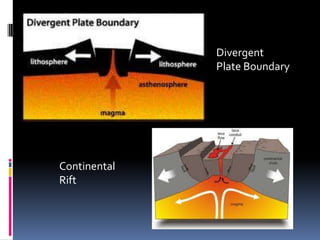
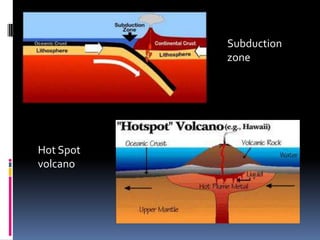
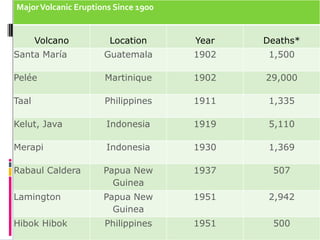
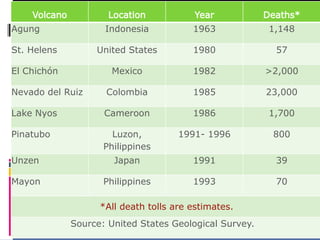
Volcanoes form at three main types of plate boundaries: divergent boundaries where plates split apart, convergent boundaries where one plate subducts beneath another, and at hotspots within plates. The type of boundary controls the composition of magma erupted - divergent boundaries produce basalt, convergent produce andesite, and hotspots can produce either depending on the plate composition. Major hazards from volcanoes include lava flows, explosive eruptions of ash and pyroclastic flows, lahars, and gas emissions. Large eruptions can impact global climate through atmospheric dust veiling sunlight. Volcanoes are monitored to determine activity levels and eruptions can be predicted based on increased seismicity, gas emissions,