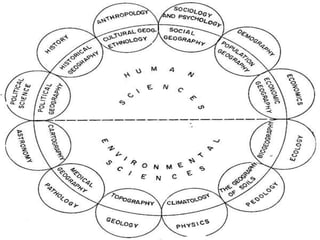
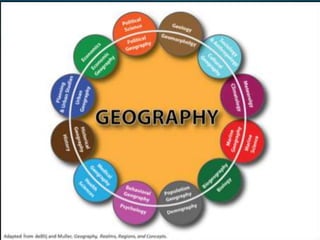
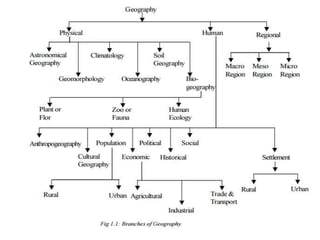
Geography is the study of the Earth's surface, focusing on the description and explanation of natural and cultural features, addressing ‘what,’ ‘where,’ and ‘why’ these features exist. It has systematic and regional approaches, with branches including physical, human, and biogeography, each subdivided into various fields such as climatology and social geography. Methods employed in geography include statistical techniques, field surveys, and remote sensing.