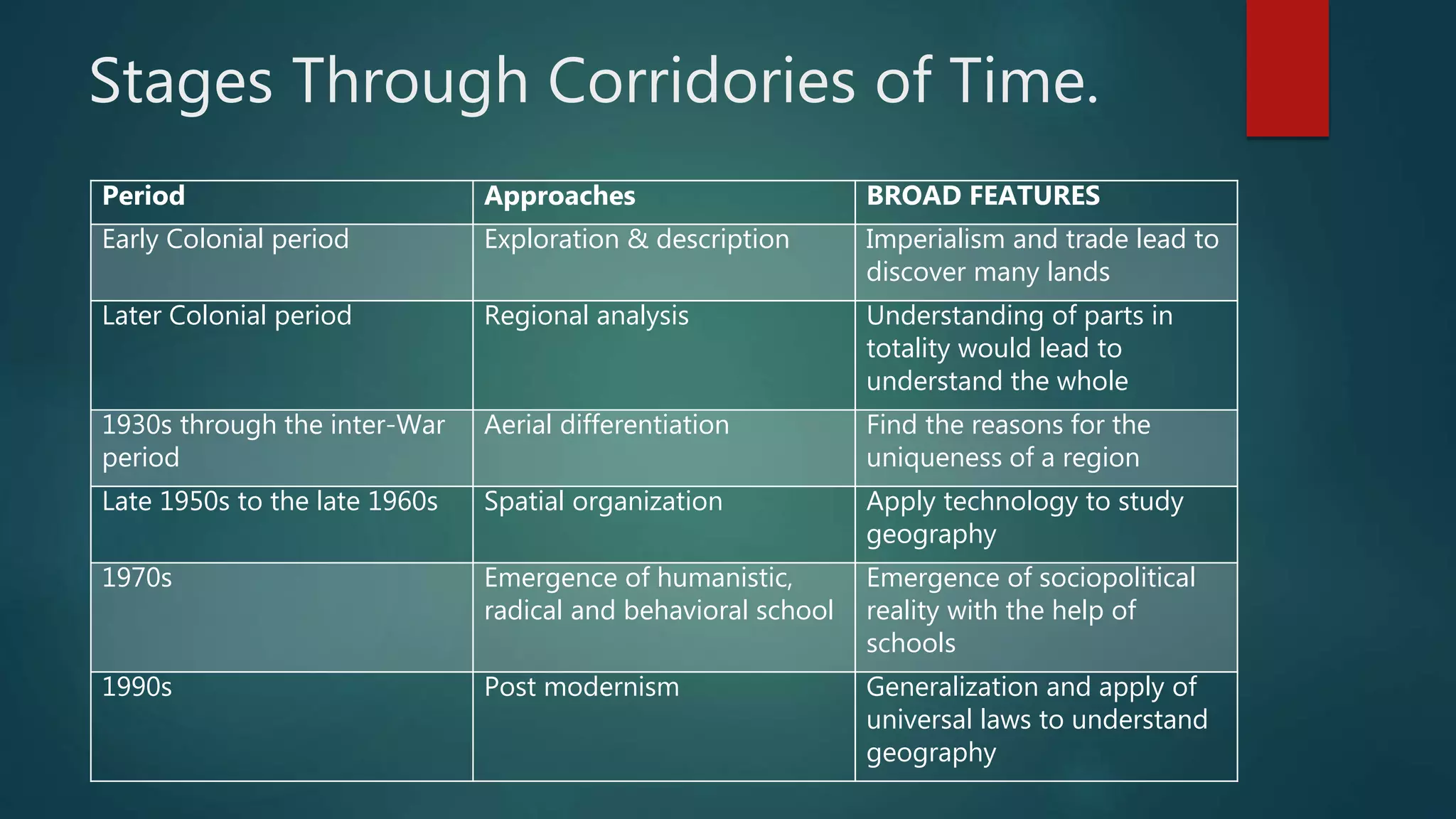
The document discusses human geography, emphasizing the study of relationships between human societies and the Earth's surface. It outlines various approaches and schools within human geography, including systematic and regional approaches, as well as concepts like environmental determinism and possibilism. Additionally, it highlights the importance of understanding the physical environment and the technological development that arises from this interaction.