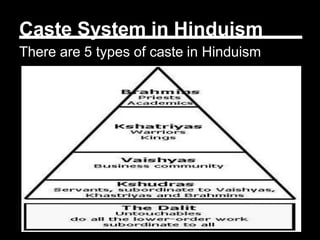
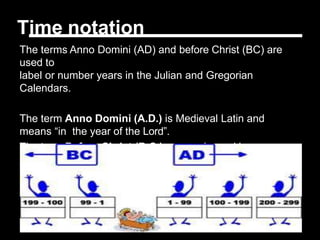
The document provides an overview of Indian history from ancient to modern times, including how it is studied and categorized. It discusses key figures like James Rennel and Warren Hastings, and the East India Company's role in British imperialism in India. The criteria used to divide Indian history into periods is also explained, from the initial Hindu and Muslim rulers classification to the later categorization of ancient, medieval, and modern/colonial periods based on British documentation.