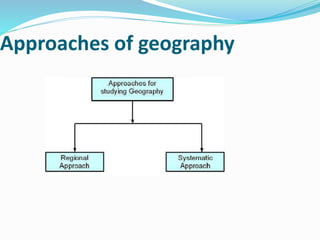
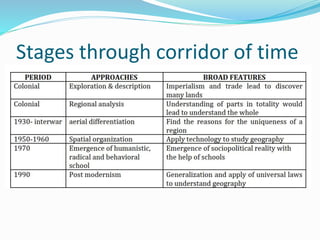
This document provides an overview of the nature and scope of human geography. It discusses how human geography studies the relationship between human societies and the earth's surface. Key points covered include the different approaches to geography like environmental determinism and possibilism. Environmental determinism suggests that the environment determines human activities, while possibilism argues that humans can modify their environment. The document also discusses new determinism as a middle path between these views. It outlines the different schools of thought in human geography like welfare, radical, and behavioral schools. Finally, it discusses how human geography relates to other social science disciplines through different time periods.