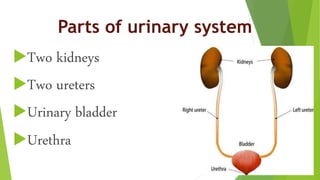
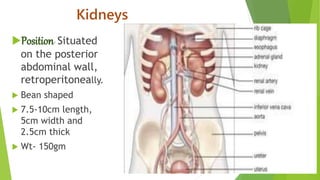
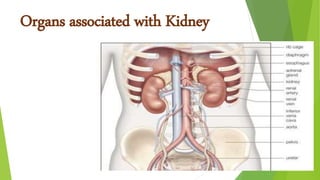
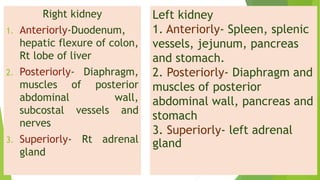
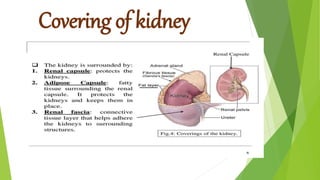
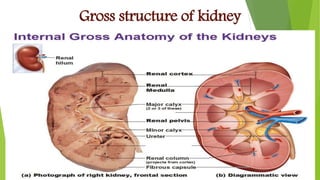
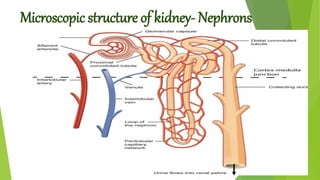
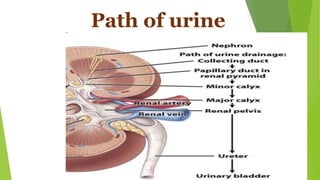
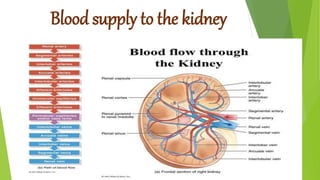
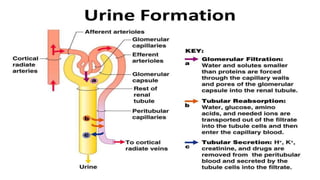
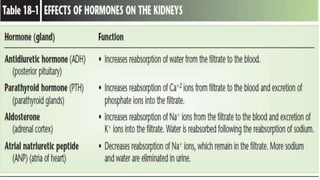
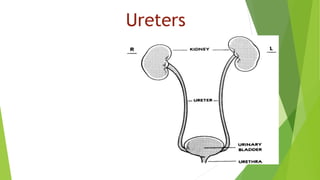
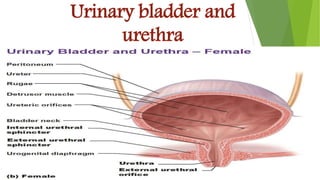
The urinary system functions to excrete waste from the body and regulate fluid balance, electrolytes, and acid-base levels. It consists of two kidneys, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra. The kidneys filter blood to form urine and are located retroperitoneally in the abdominal cavity. They contain microscopic filtration units called nephrons that filter blood to form urine, which travels through the ureters to the bladder and then exits through the urethra. Hormones regulate fluid balance and the reabsorption of water and electrolytes during urine formation.