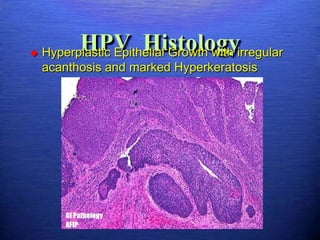
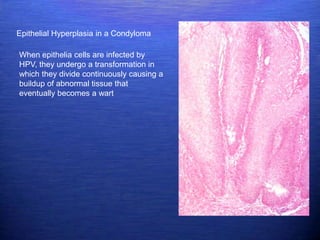
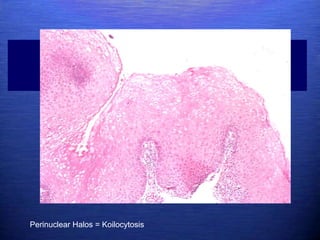
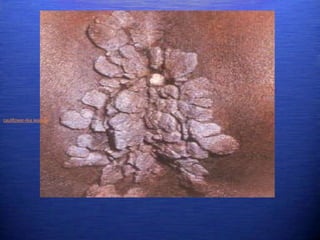
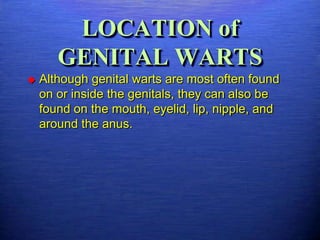
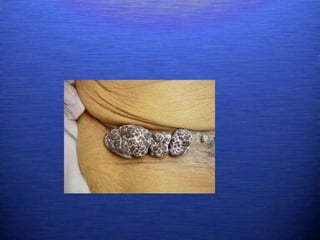
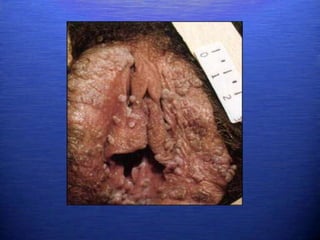
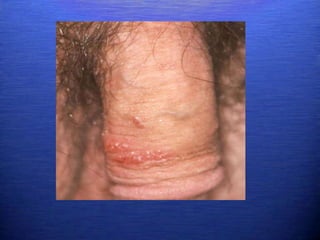
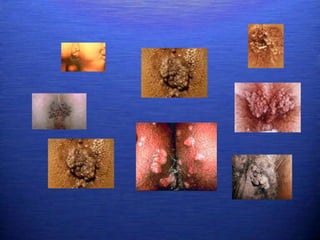
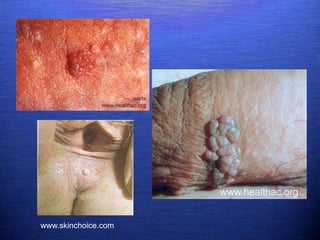
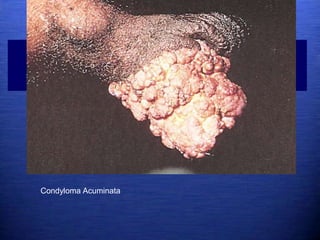
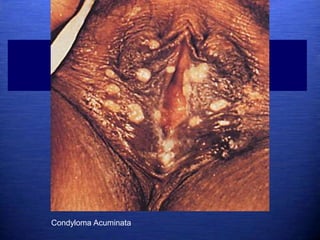
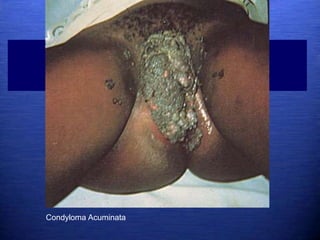
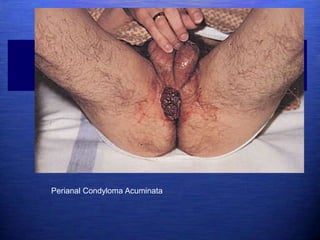
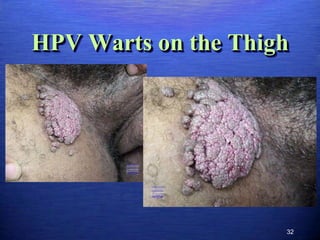
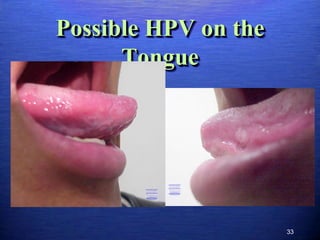
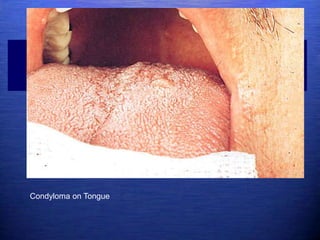
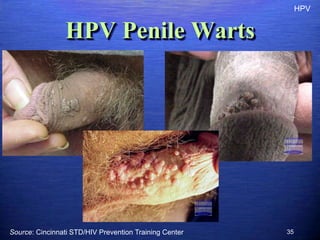
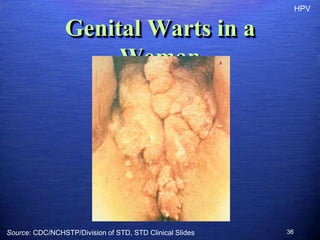
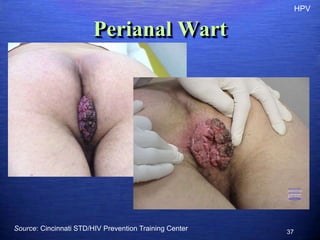
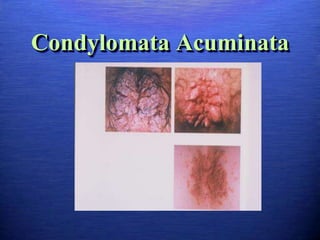
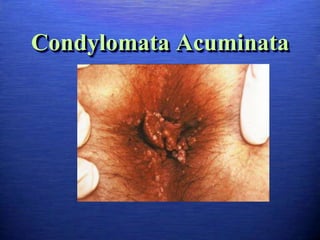
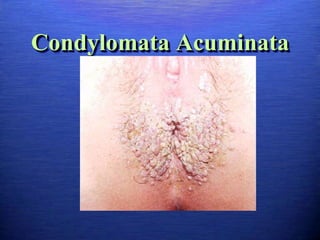
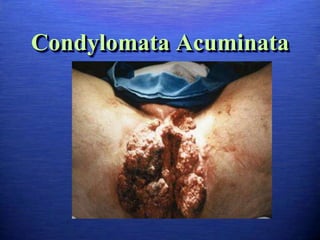
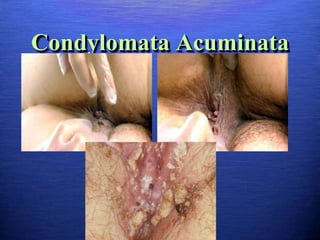
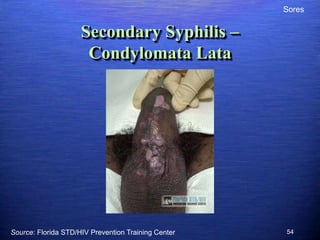
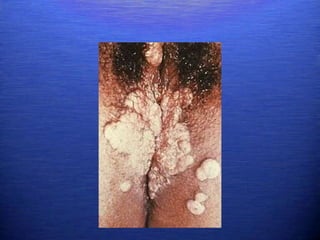
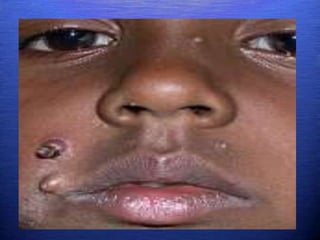
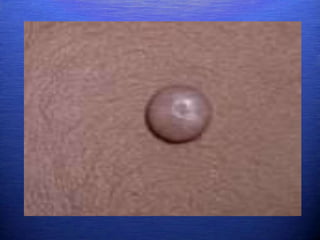
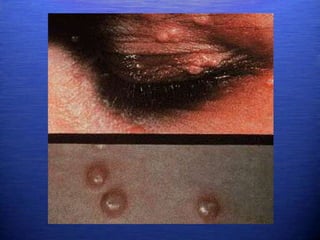
This document discusses genital warts (condyloma acuminata) caused by human papillomavirus (HPV). It notes that HPV is commonly seen in the homosexual male population and 19% of HIV patients have anal HPV. There is no cure for HPV and it can be transmitted even with condom use. Treatment options discussed include podophyllin, immunotherapy, imiquimod cream, cryotherapy, laser therapy, and electrocoagulation. Recurrence is common and regular screening is important due to HPV's link to cervical and other cancers.