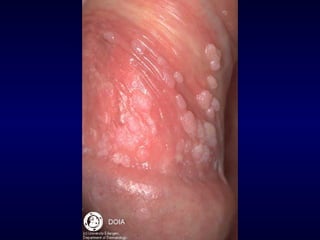
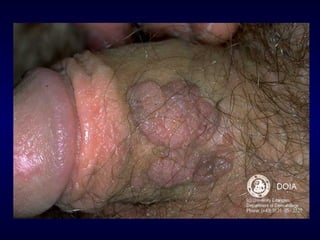
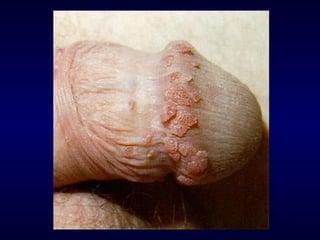
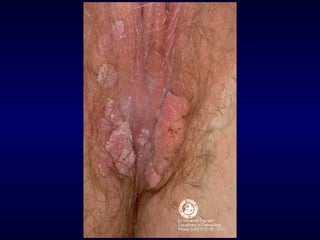
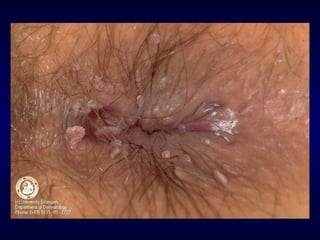
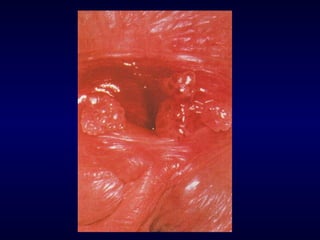
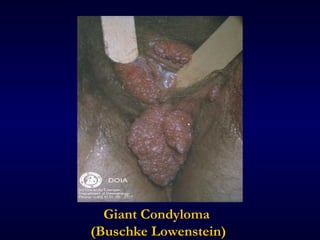
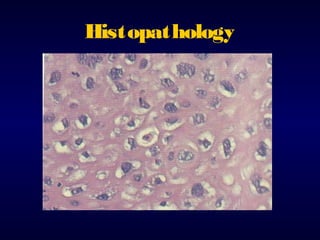
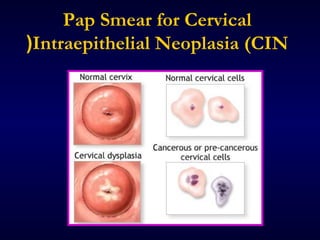
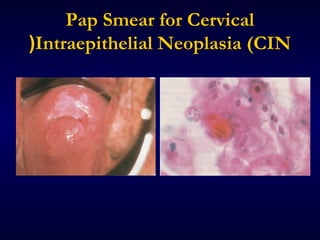
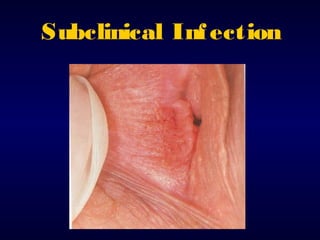
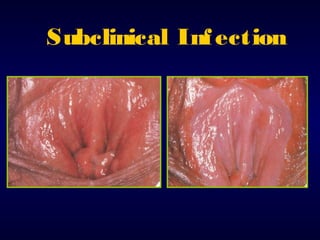
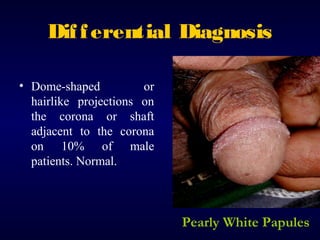
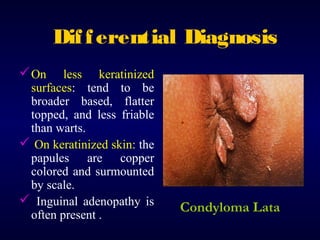
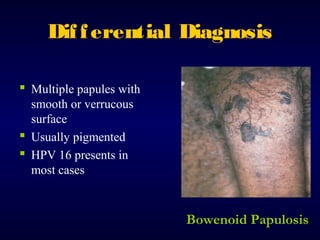
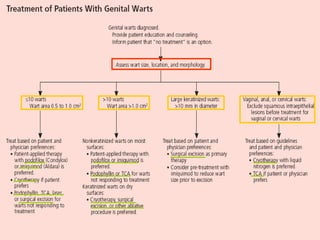
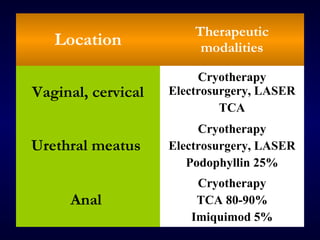
This document provides information on the management of anogenital warts (condyloma acuminata). It discusses that human papillomavirus (HPV) causes anogenital warts, which can be transmitted sexually or through non-sexual contact. Treatment options for external genital warts include patient-applied therapies like podofilox and imiquimod cream, as well as provider-administered cryotherapy, podophyllin, and surgical removal. The choice of treatment depends on factors like wart size, number and location. Patient education emphasizes that HPV is common, warts may recur, and treatment aims to remove visible warts, not eliminate the virus.