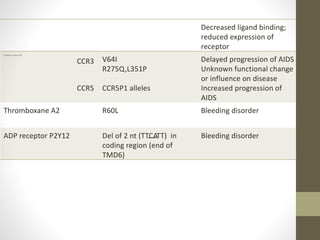
G-proteins are molecular switches that regulate various cellular activities. They exist in two classes: monomeric small GTPases and heterotrimeric complexes consisting of α, β, and γ subunits. G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) have seven transmembrane domains and interact with G-proteins via intracellular loops to transmit extracellular signals within the cell. Genetic variations in GPCRs can affect receptor functions like ligand binding and G-protein coupling, potentially causing diseases. Many single nucleotide polymorphisms and mutations have been linked to impaired or enhanced receptor signaling and diseases ranging from bleeding disorders to asthma, obesity, and immune deficiencies.