Genetic variations in gpcr
- 1. Genetic variations In GPCR By: Meenakshi Gupta (M.Pharm. 2nd sem)
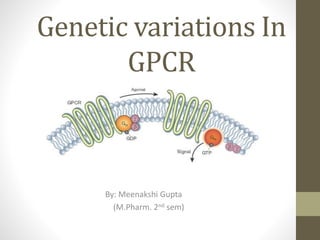
- 2. What is G-protein?? • also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins. • family of protein that act as a molecular switches inside the cell. • Activity regulated by factors that controls their ability to bind to and hydrolyze GTP into GDP. • When they are bound to GTP, they are 'on', and, when they are bound to GDP, they are 'off'. G proteins belong to the larger group of enzymes called GTPase. • There are two classes of G proteins: a. monomeric small GTPase b. heterotrimeric G protein complexes (alpha (α), beta (β) and gamma (γ) subunit)
- 3. G-Protein Coupled Receptor 7 trans membrane helices connected by alternating cytosolic and extra cellular loop C terminal: inside the cell N terminal : extra cellular region Extra cellular portion has unique messenger binding site Cytosolic loop allow receptor to interact with G protein. The eventual effect of agonist -induced activation is a change in the relative orientations of the TM helices (likened to a twisting motion) leading to a wider intracellular surface and "revelation" of residues of the intracellular helices and TM domains crucial to signal transduction function (i.e., G-protein coupling). Inverse agonists and antagonists may also bind to a number of different sites, but the eventual effect must be prevention of this TM helix reorientation
- 5. Genetic variations may be due to 1.Sequence variations of the human genome • Introduces variability in genetic make-up • Suspected to play a main role in diseases & variable response in drug therapy • Polymorphism- refers to sequence variation leading to occurrence of two or more clearly different forms. • Single nucleotide polymorphism accounts for approx. 80% of all sequence variations.
- 6. 2. Structure & function of GPCRs • Comprises a large class of membrane proteins – encoded by approx. 600 human genes. • Molecular architecture might permit the prediction of functionally relevant domains where sequence variations are more likely to alter receptor function. • Normally, TM domains are highly conserved, the loops are variable in sequence & length, &the C- and N-terminals tails represents the most diverse elements.
- 7. 3. GPCR coupling to G proteins and other signaling pathways • GPCR thought to be couple to heterotrimeric G proteins composed of α, β and γ subunits. It display considerable heterogenecity, with a predicted number of 27 different α, 5 β and 13 γ subunits. • Main sites of contact between receptor and G proteins include the third intracellular loop, but i1, i2 and the C- terminus have also been reported to contribute G protein coupling • Proteins like protein kinases, arrestin & phosphatases modulates receptor functions at distinct domains that are possible targets for polymorphic effects.
- 8. 4. GPCR binding pockets • Ca++, acetyl choline, glutamate, bradykinin, prostaglandins, & the large polypeptide FSH bind to the same site. • Distinct binding sites appear to exist, either embedded within the pocket formed by the 7- TMD bundle within the membrane, at pockets formed by the extracellular loops, or in the N- terminus. • The thrombin receptor family represents a special case whereas the protease activity of the ligand thrombin cleaves a portion of the N- terminus. The newly generated N-terminus then serves as a tethered ligand.
- 9. • GPCRs appear to be activated by ligand binding to many different sites of the protein . At the opioid receptors, peptide endorphins bind primarily to the extracellular loops, whereas opioid alkaloids dock deep into the 7-TMD core. Human μ opioid receptor
- 10. • Sequence variation in the receptor protein can affect ligand binding or the structural integrity of the receptor , indirectly changing ligand binding . 5. Spontaneous GPCR signalling • Exchange of single amino acid residues can lead to constitutive receptor activation. • Considerable number of human polymorphisms enhance signalling (gain of function) or even activate the receptor constitutively, causing serious genetic disorders.
- 11. 6. Multiple receptor conformations with distinct functions • GPCRs are flexible structures and may accommodate ligands in various ways. It exists in multiple conformations. Discrete signalling pathways are triggered by discrete conformational states of GPCR
- 12. Sequence variations of GPCRs and associated diseases
- 13. Impaired or enhanced agonist signalling efficacy Several inactivating sequence variants of peptide receptors have been associated with congenital disorders. For example, 1. A point mutation causing truncation of thyrotropin stimulating hormone receptor leads to leydig’s cell hyperplasia.(activating mutation) Truncated TM5, D578G, T398M
- 14. 2. Inactivating mutations of the ACTH receptor are associated with familial glucocorticoid deficiency . The mutation occurs in the large N-terminus , the binding site for glycoprotein hormone receptor, leading to toxic multinodular goiter. S120R, R201Stop, S74I, V254C
- 15. V2 vasopressin recptors • A number of mutations in the gene encoding the V2 vasopressin receptor leads to functionally inactive receptor protein and are causative for nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.(missense mutations) • This a clear indication that receptor activity depends on intact signalling pathways. (multiple SNPs; decreased ligand binding; R113W; R137H)
- 17. Thromboxane A2 Receptor • This receptor performs an essential role in haemostasis by inducing platelet aggregation. An R60L amino acid substitution in the first cytoplasmic loop of TBXA2 receptor causes a dominantly inherited bleeding disorder characterised by defective platelet response to TBXA2. This leads to decreased agonist-induced second messenger formation.
- 19. P2Y 12ADP Receptor • This receptor sub-type is shown to be the target for anti-thrombotic drugs such as ticlodipine & clopidogrel. 2-nucleotide deletion in a region mapping to the end of TMD6, associated with a rare bleeding disorder.
- 20. Chemokine reeptors • Fusin and CKR5 have been identified as a co- receptors for the cellular entry of HIV. Similarly , certain chemokines were found to block HIV entry into cells. • Natural resistance can be either by high endogenous levels of chemokines or by mutations of the receptors. • A 32 bp deletion in CKR5 leading to a frame shift and a non functional protein appeared to protect homozygous carriers against HIV infection & blocking its entry.
- 21. • Val 64 substitution with Ile was shown to result in heterodimerisation of CCR2 with CCR5 or CXCR4, thereby promoting resistance to AIDS.
- 22. Biogenic amine receptors • The R16G substitution in the β2 adrenoreceptors has been associated with nocturnal asthma whereas W64R in the β3 receptor expressed in adipocytes are involved in energy metabolism – is linked with obesity.
- 23. Sequence variants of human G coupled receptors
- 24. receptors Variant/Allele Disease/ Phenotype cellular mechanism/ Event Β1 adrenergic receptor R16G Nocturnal asthma; Enhanced agonist promoted down regulation of receptor Β3 adrenergic receptors W64R Obesity Luteinising hormone Truncated TM5 D578G Leydig’s cell hyperplasia; Precocious puberty in male children FSH A189V Ovarian dysgenesis; Altered protein folding; inactivation of receptor Thyrotropin (TSH) S120R, R201Stop, S74I, V254C Glucocorticoid deficiency; altered/ loss of receptor function/ reduced expression ACTH D727E Altered receptor function/conformation; Toxic multinodular goiter Vasopressin V2 receptor Multiple SNPs Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus;
- 25. Decreased ligand binding; reduced expression of receptor Chemokine receptors CCR2 CCR3 CCR5 V64I R275Q,L351P CCR5P1 alleles Delayed progression of AIDS Unknown functional change or influence on disease Increased progression of AIDS Thromboxane A2 R60L Bleeding disorder ADP receptor P2Y12 Del of 2 nt (TTCATT) in coding region (end of TMD6) Bleeding disorder
- 26. THANK YOU
