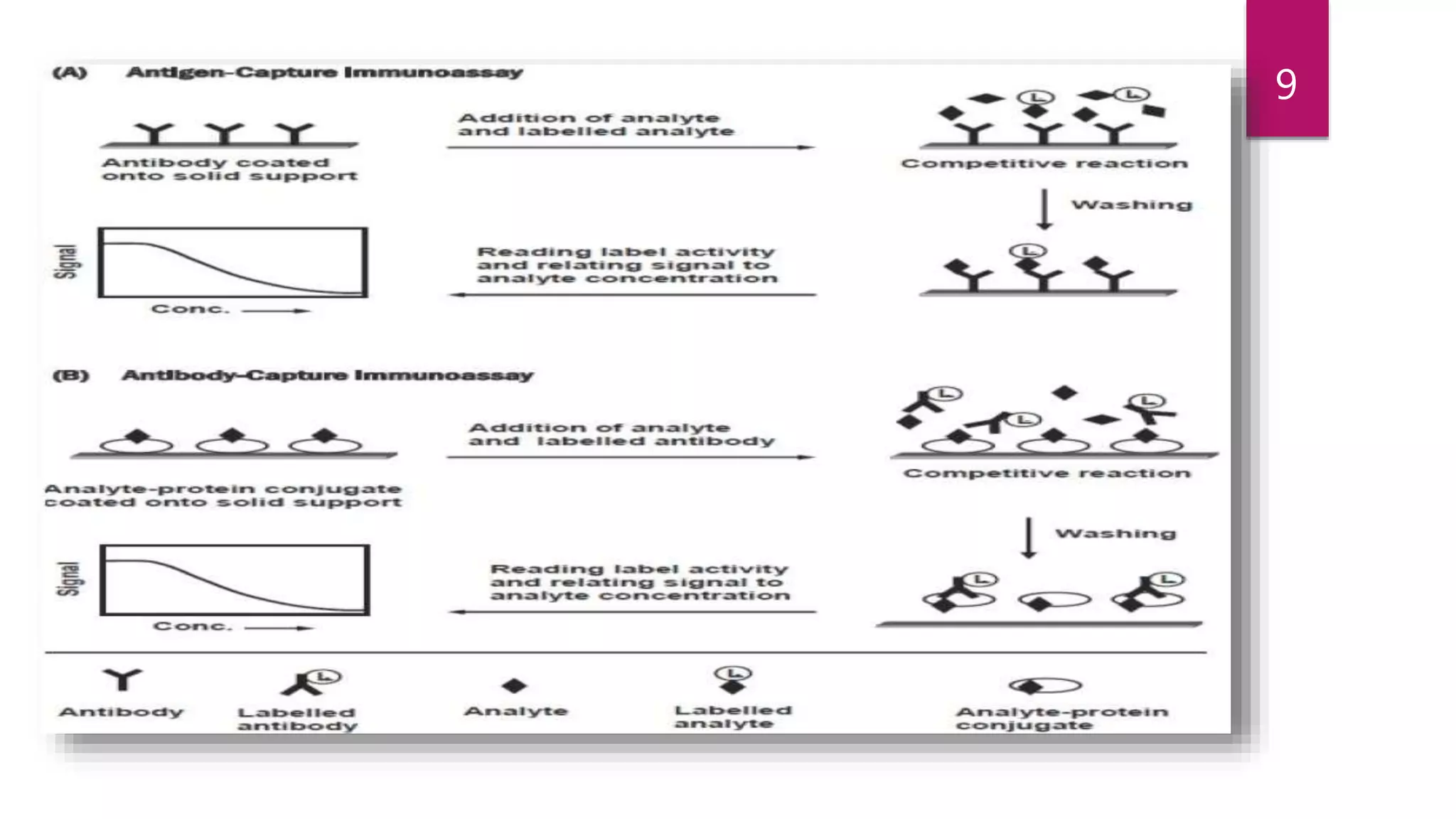
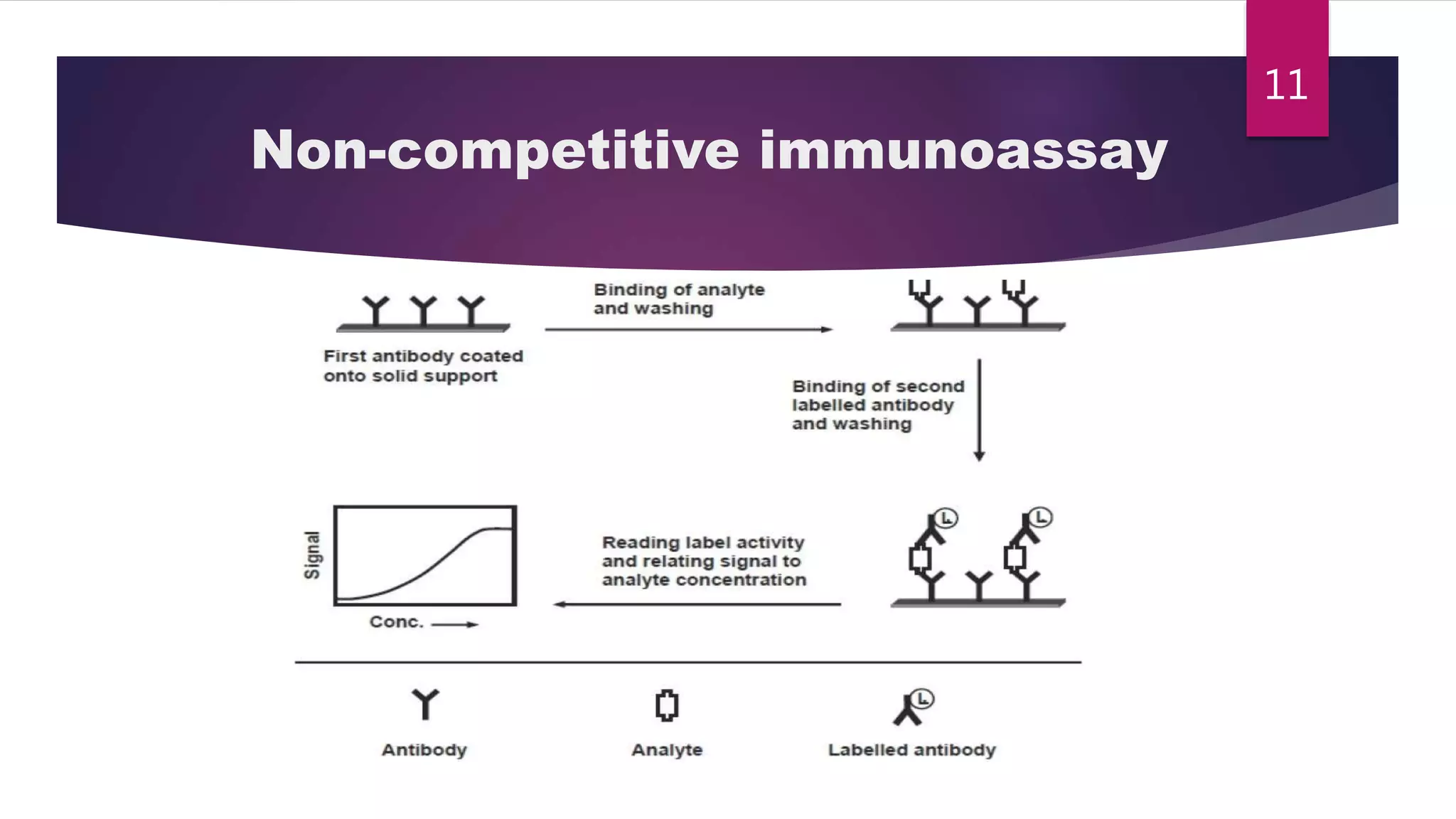
This document discusses the theoretical basis and optimization of immunoassays. It begins by introducing immunoassays and their importance in pharmaceutical analysis due to their specificity and sensitivity. It then describes the basic principles of immunoassays, including the competitive binding reaction between labeled and unlabeled analyte for antibody binding sites. The document categorizes different types of immunoassays and provides examples of their use. It also discusses optimization of immunoassays through techniques like minimizing background signals, improving precision and reproducibility, stabilizing conjugates, and increasing shelf-life. A key immunoassay method discussed is ELISA.