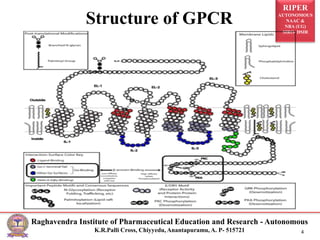
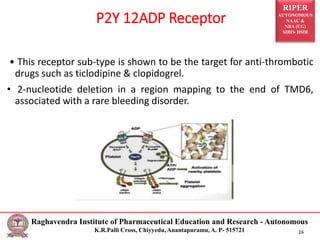
This document presents a seminar by R. Rekha on genetic variations in G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) and their implications in pharmacology and disease. It discusses the structure, function, and polymorphisms of GPCRs, emphasizing their role in signaling pathways and disease associations. Specific examples of genetic mutations affecting receptor functionality and related medical conditions are also provided.