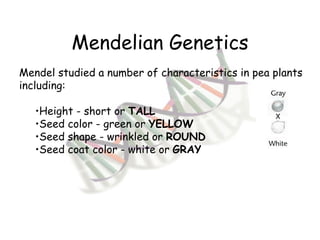
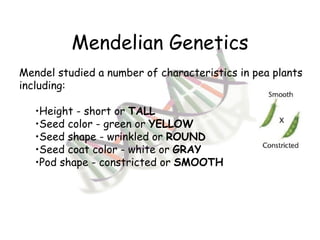
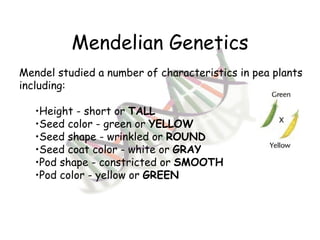
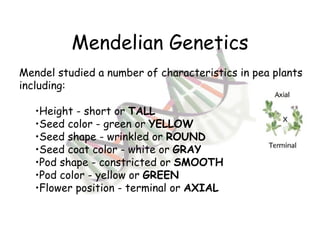
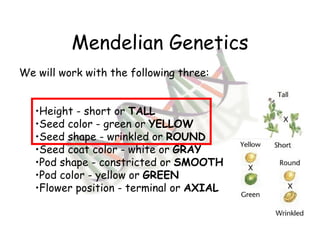
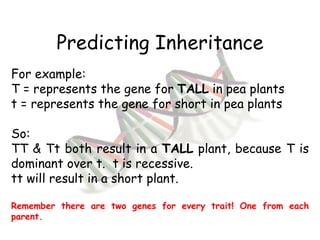
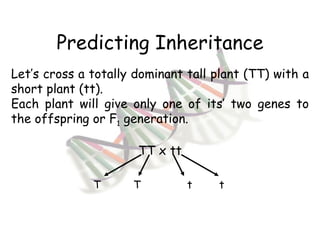
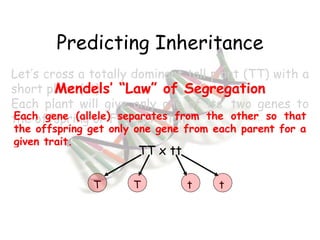
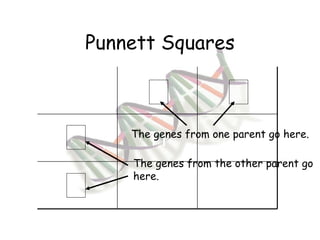
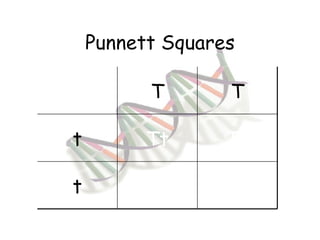
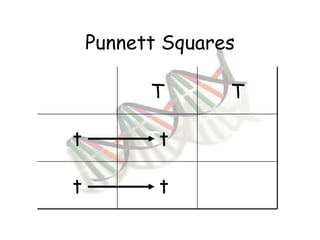
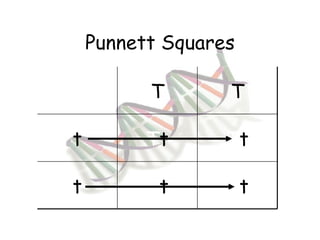
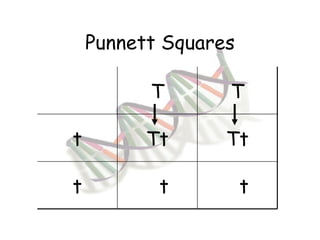
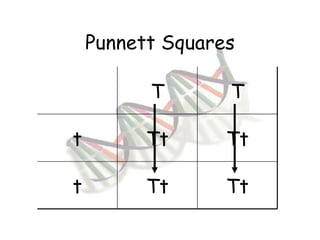
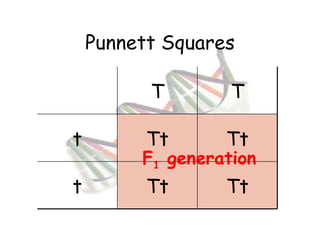
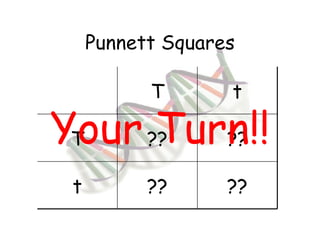
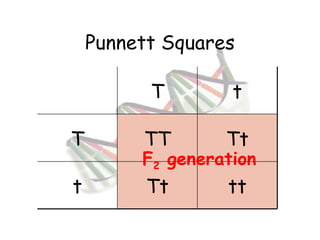
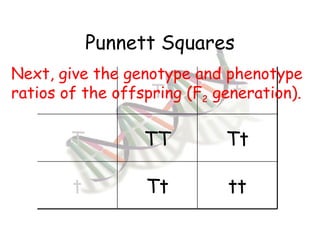
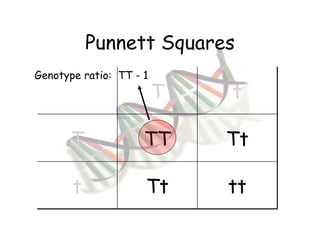
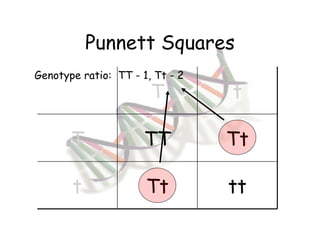
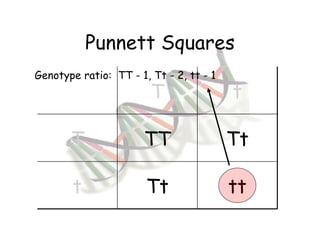
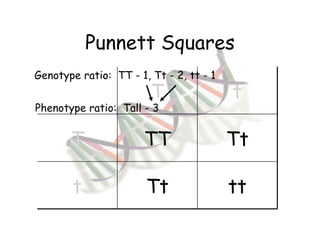
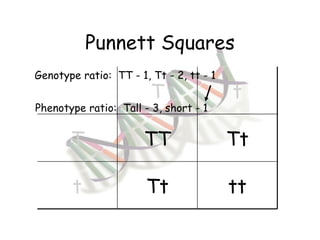
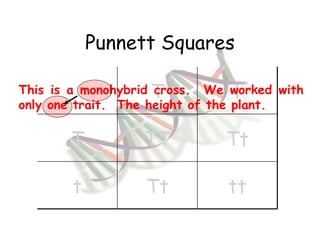
This document provides an overview of genetics and Mendelian inheritance. It discusses how Gregor Mendel pioneered the field of genetics through his experiments with pea plants in which he studied traits like height, seed color, and seed shape. The document explains key genetics concepts like phenotype, genotype, dominance, and segregation. It also demonstrates how to use a Punnett square to predict the genotype and phenotype ratios when crossing two parents for a given trait.