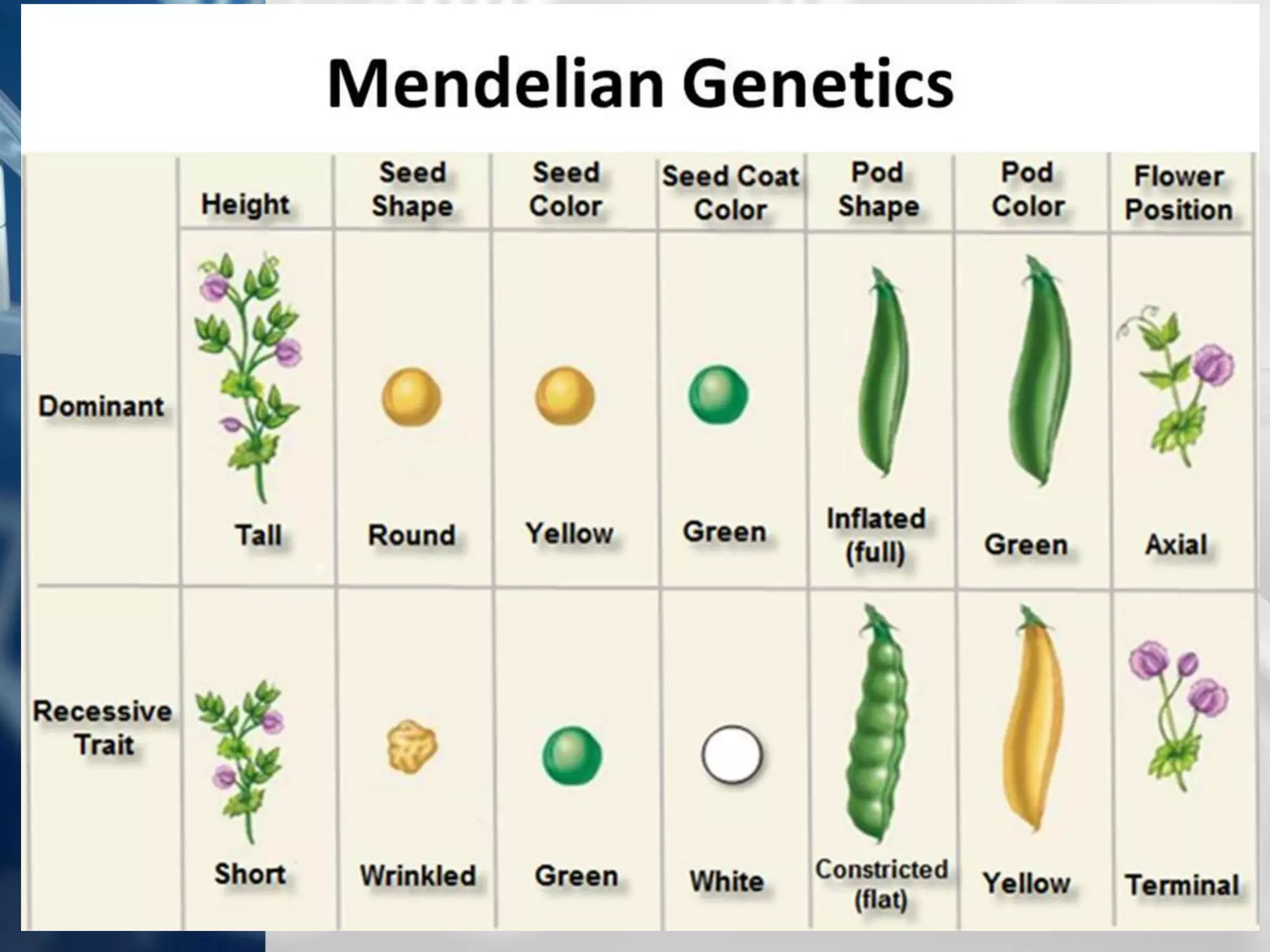
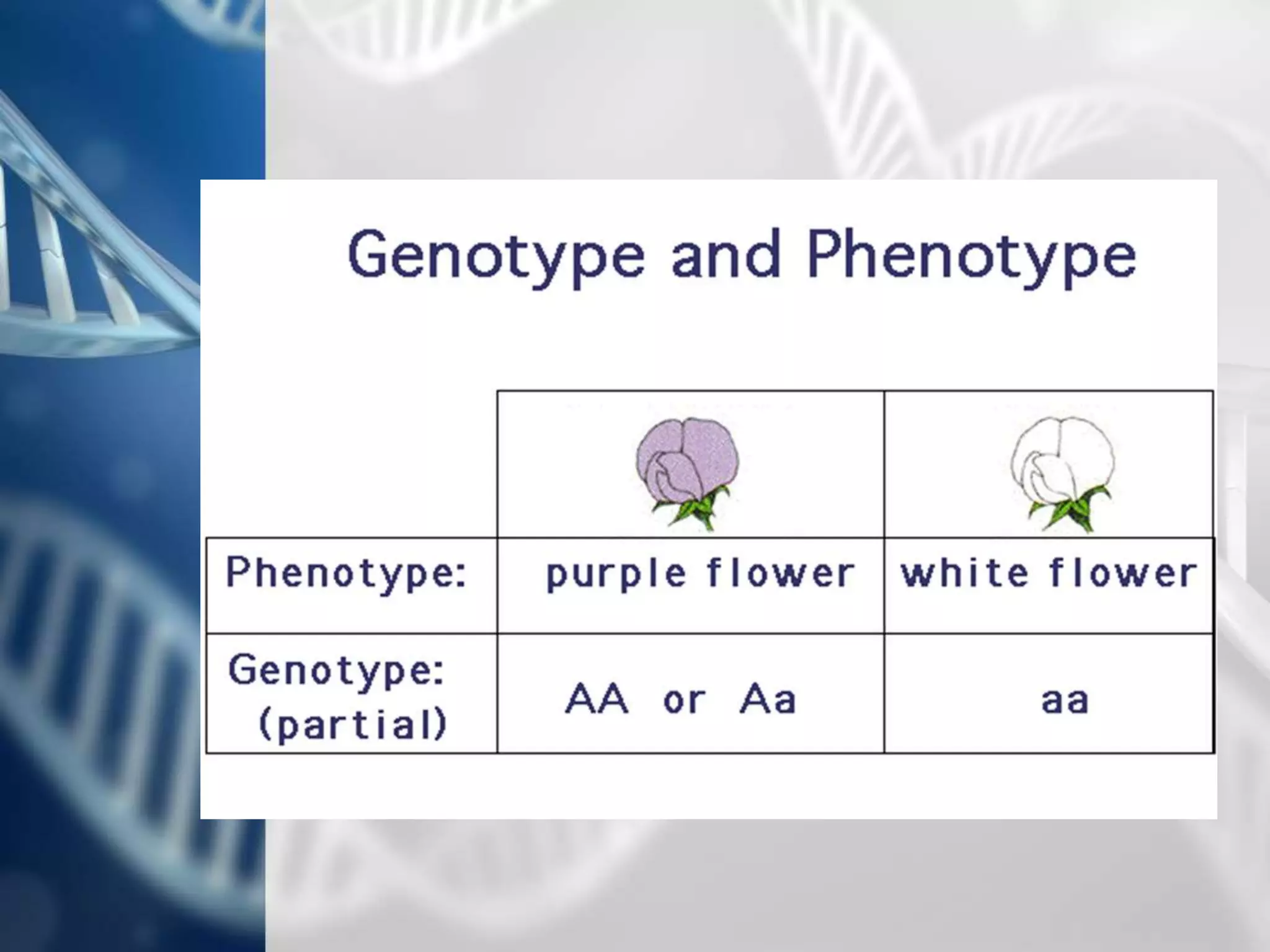
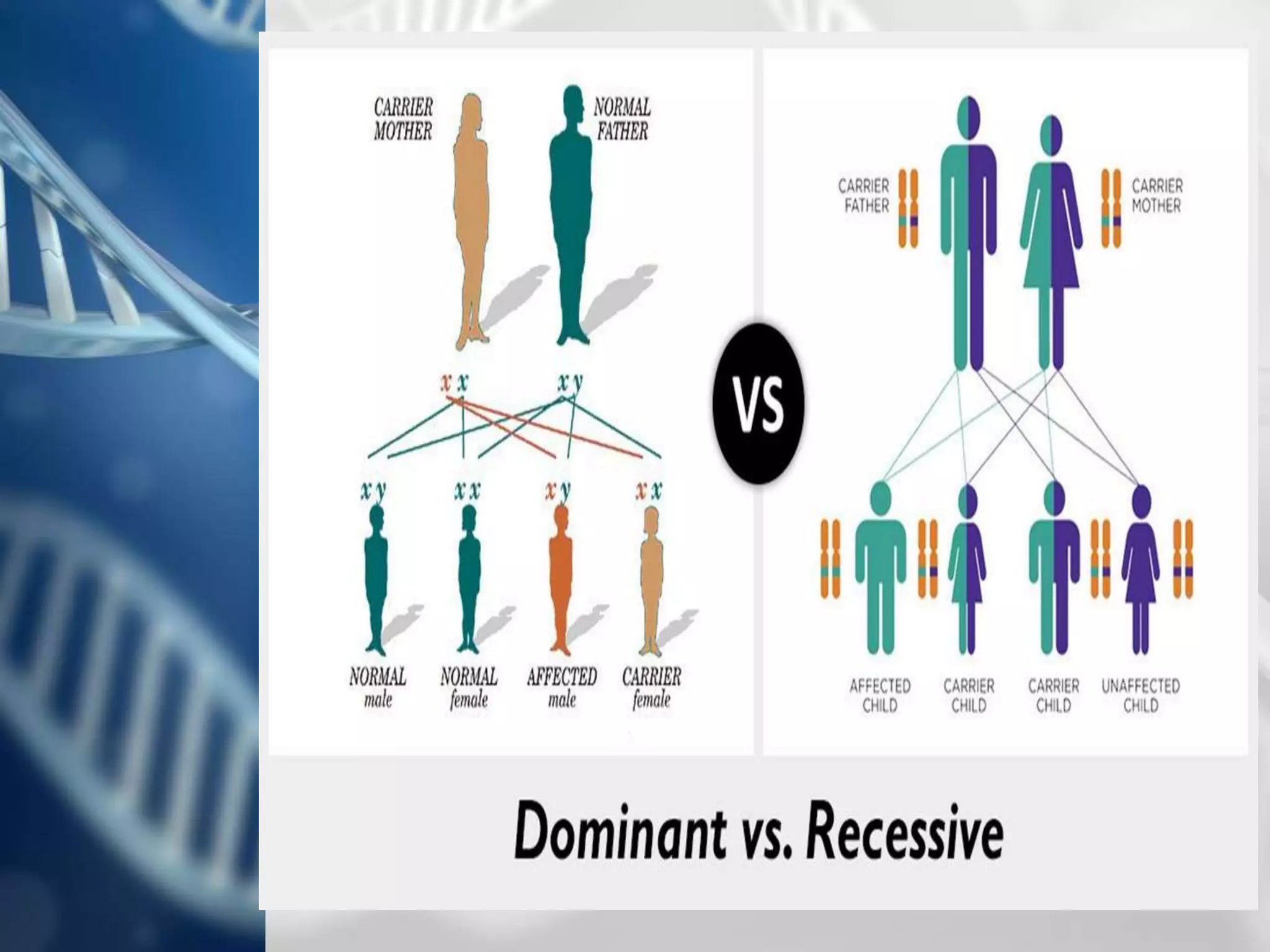
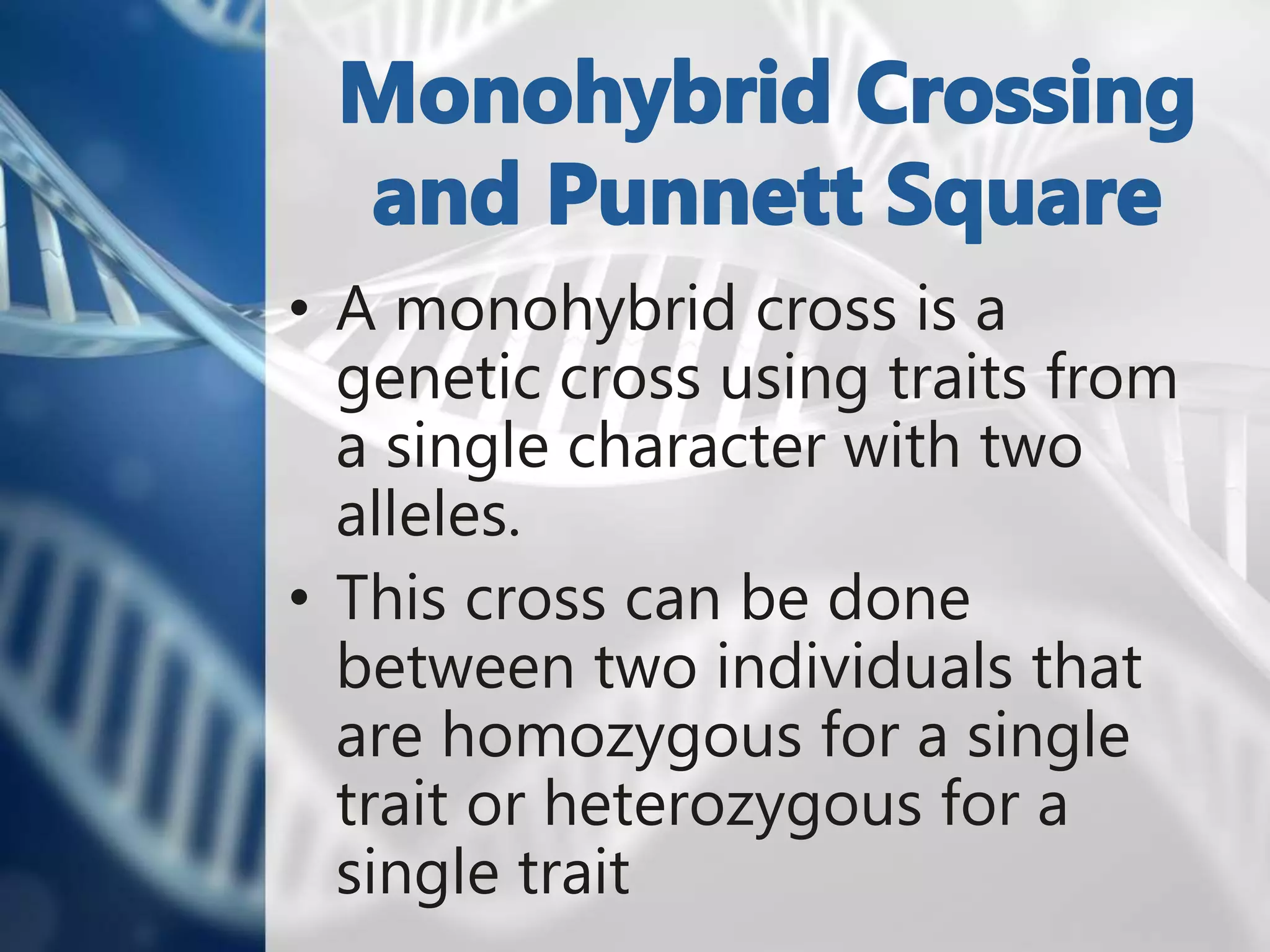
The document summarizes Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants and the principles of genetics that he discovered, including:
- Mendel was the first to study inheritance of traits through breeding experiments.
- He discovered the laws of segregation, independent assortment, dominance and recessiveness.
- Genes exist in pairs called alleles that determine traits, and can be dominant or recessive.
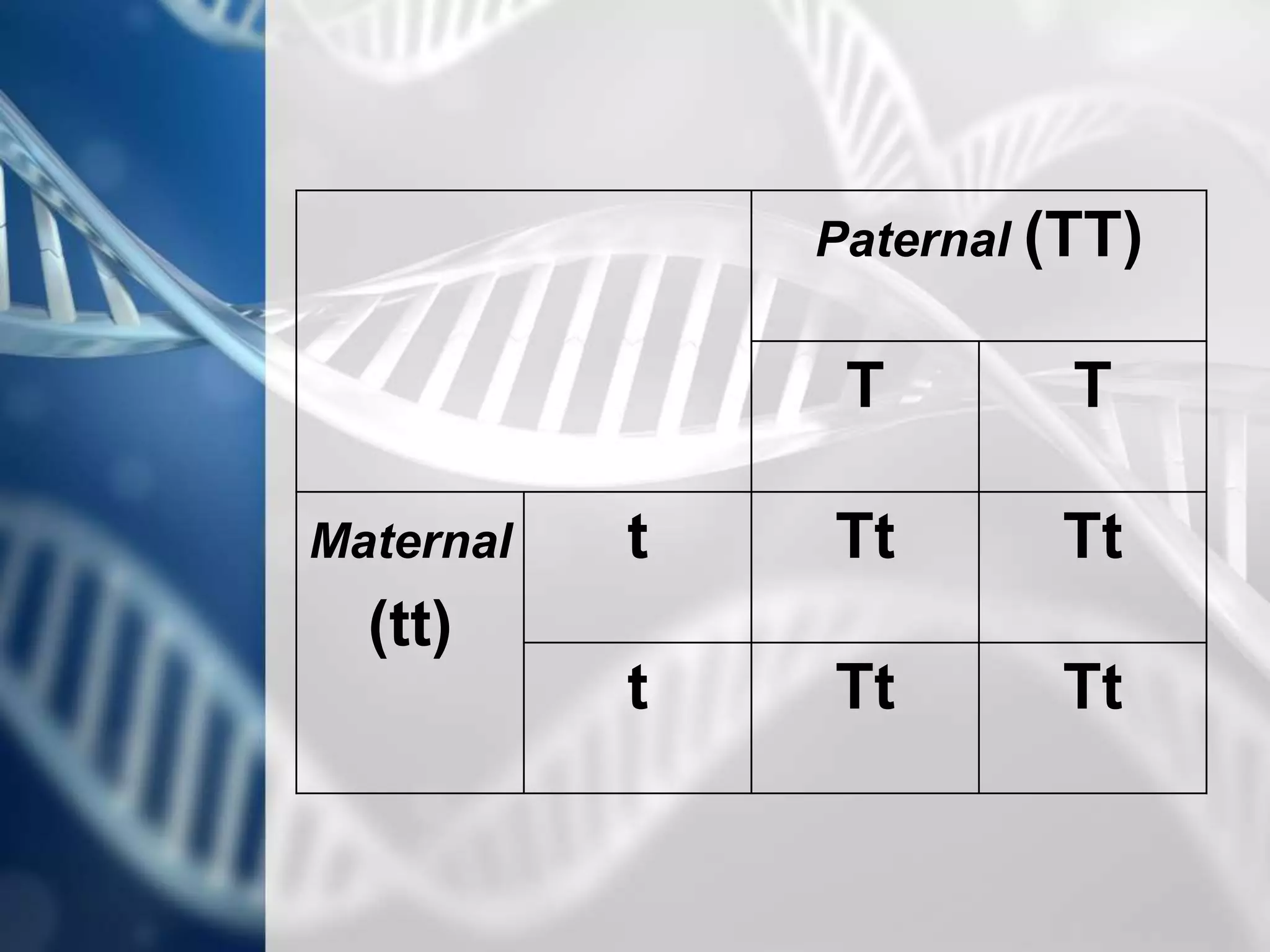
- Punnett squares can be used to predict the outcome of genetic crosses and determine probabilities.
- His work formed the basis of classical genetics and heredity.