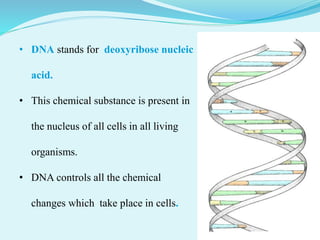
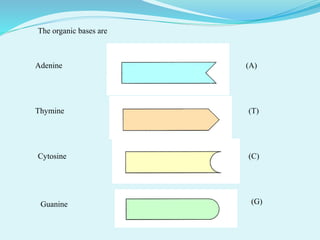
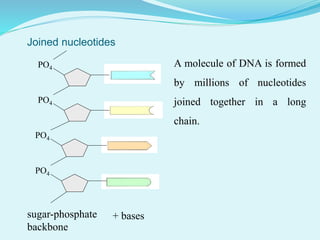
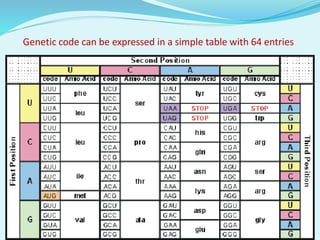
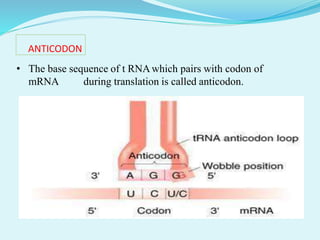
This document provides information about genetic code. It defines genetic code as the set of rules by which DNA and RNA sequences are translated into proteins. The genetic code is made up of 64 codons consisting of three nucleotides each. 61 codons code for 20 amino acids while 3 are termination codons. The genetic code is expressed in a table mapping the 64 codons to their corresponding amino acids or termination signal. The document also discusses anticodons, which are sequences in tRNA that pair with mRNA codons during protein translation.