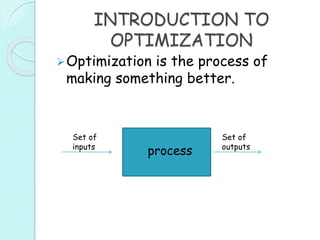
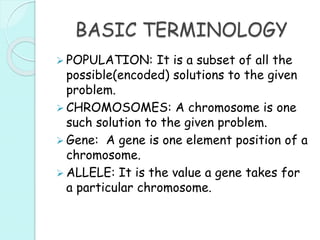
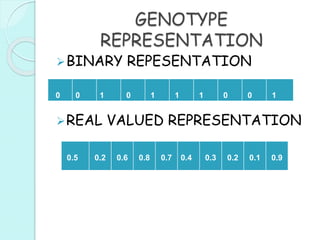
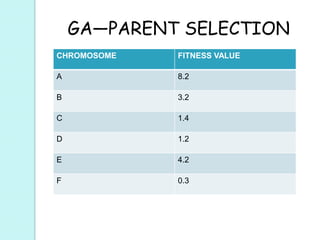
This document provides an introduction to genetic algorithms. It defines genetic algorithms as optimization techniques that are inspired by natural selection and genetics. Genetic algorithms are frequently used to find optimal or near-optimal solutions to complex problems. The document outlines the basic terminology used in genetic algorithms, including populations, chromosomes, genes, alleles, phenotypes, and genetic operations like crossover and mutation. It also describes the basic structure of a genetic algorithm, which involves initializing a population, calculating fitness, performing genetic operations, selecting survivors, and iterating until a termination condition is reached.