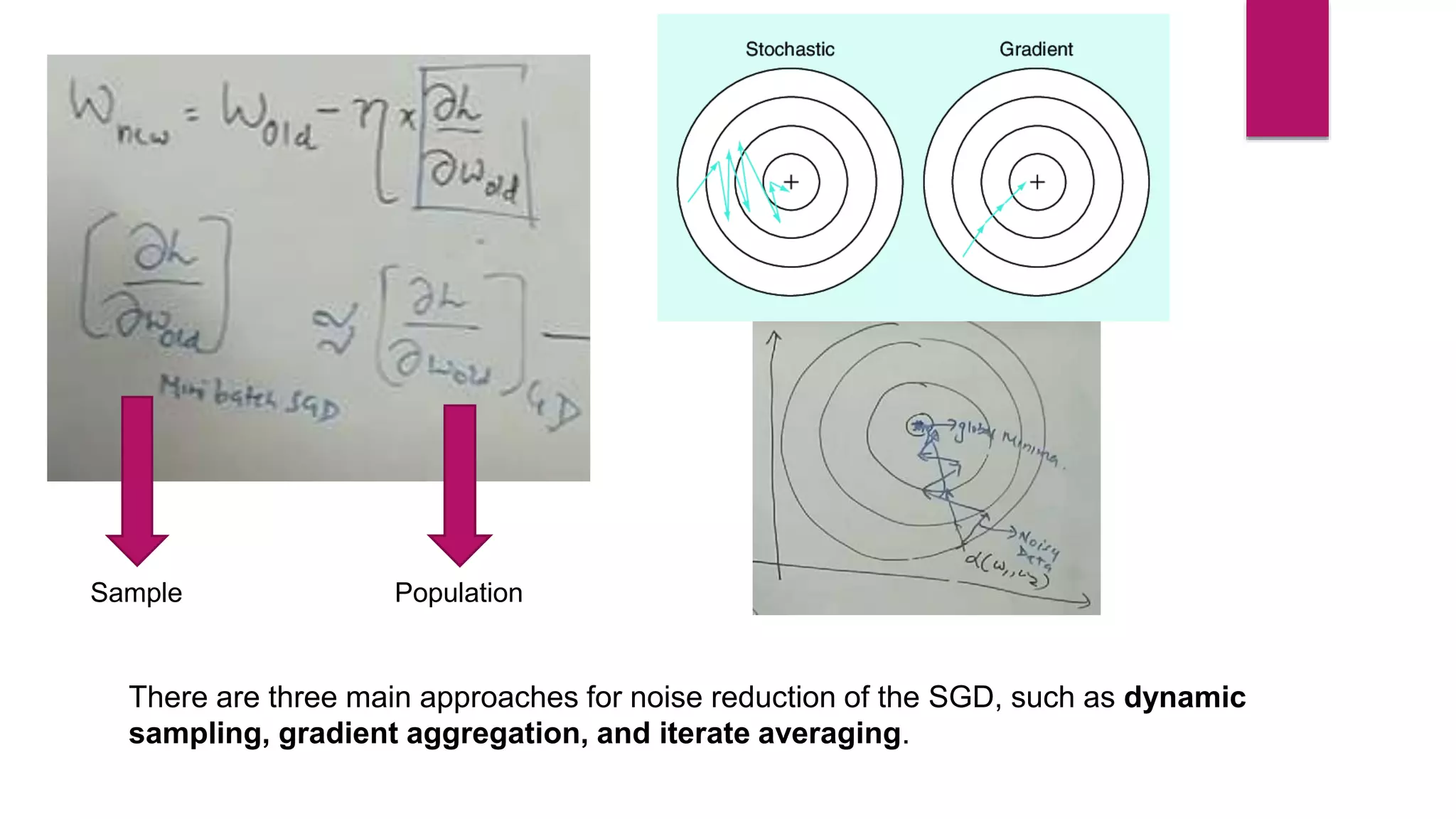
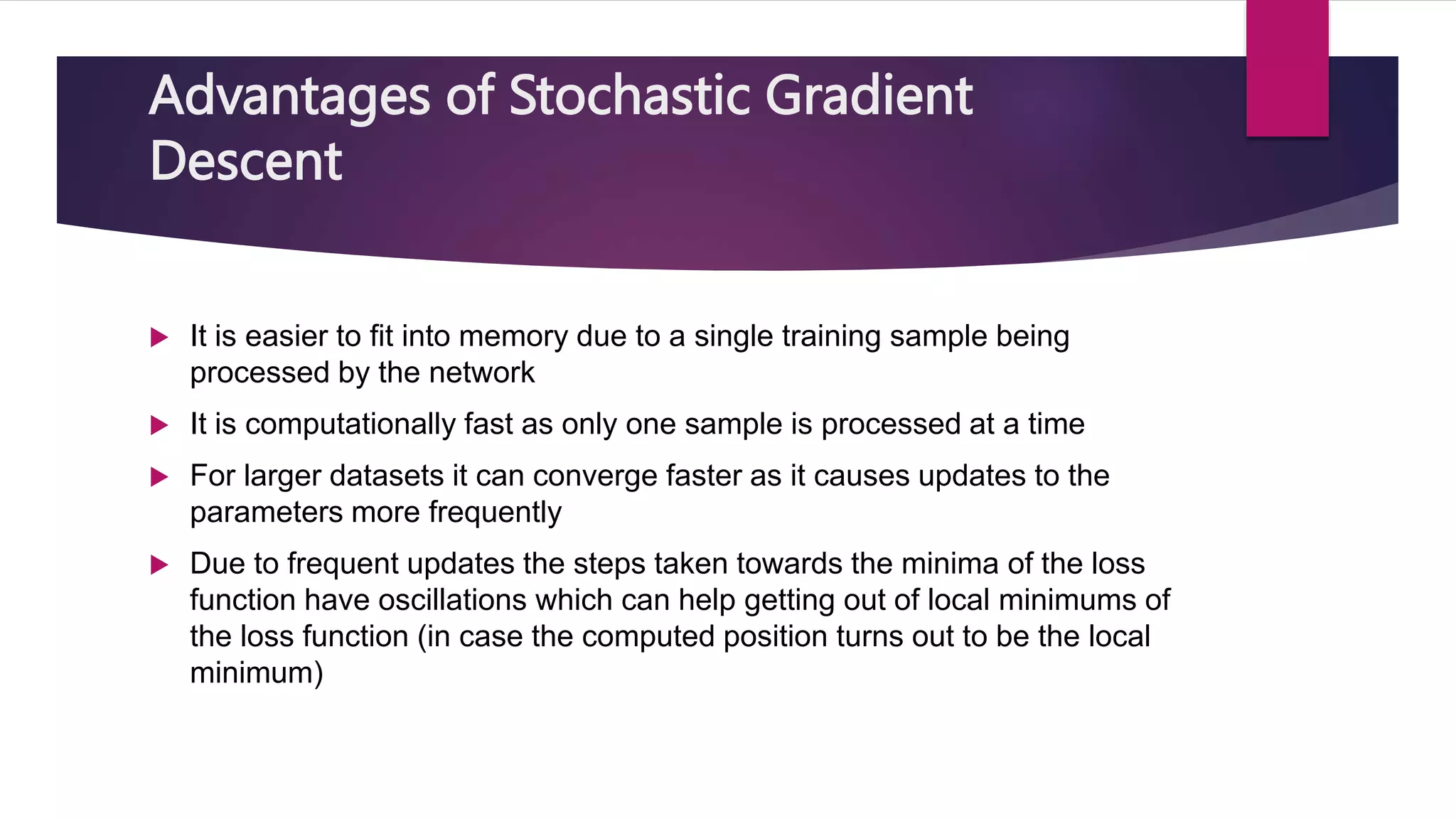
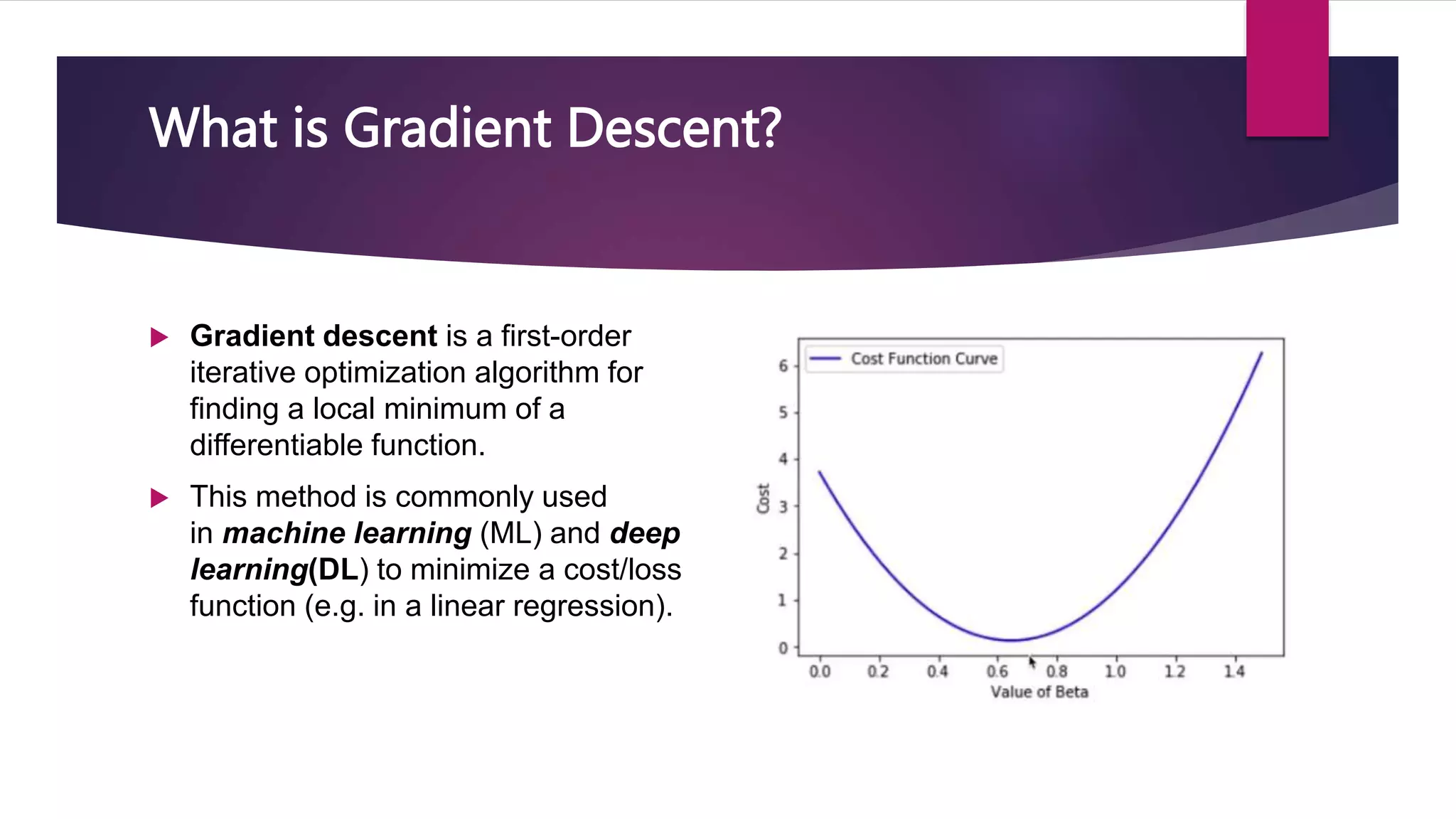
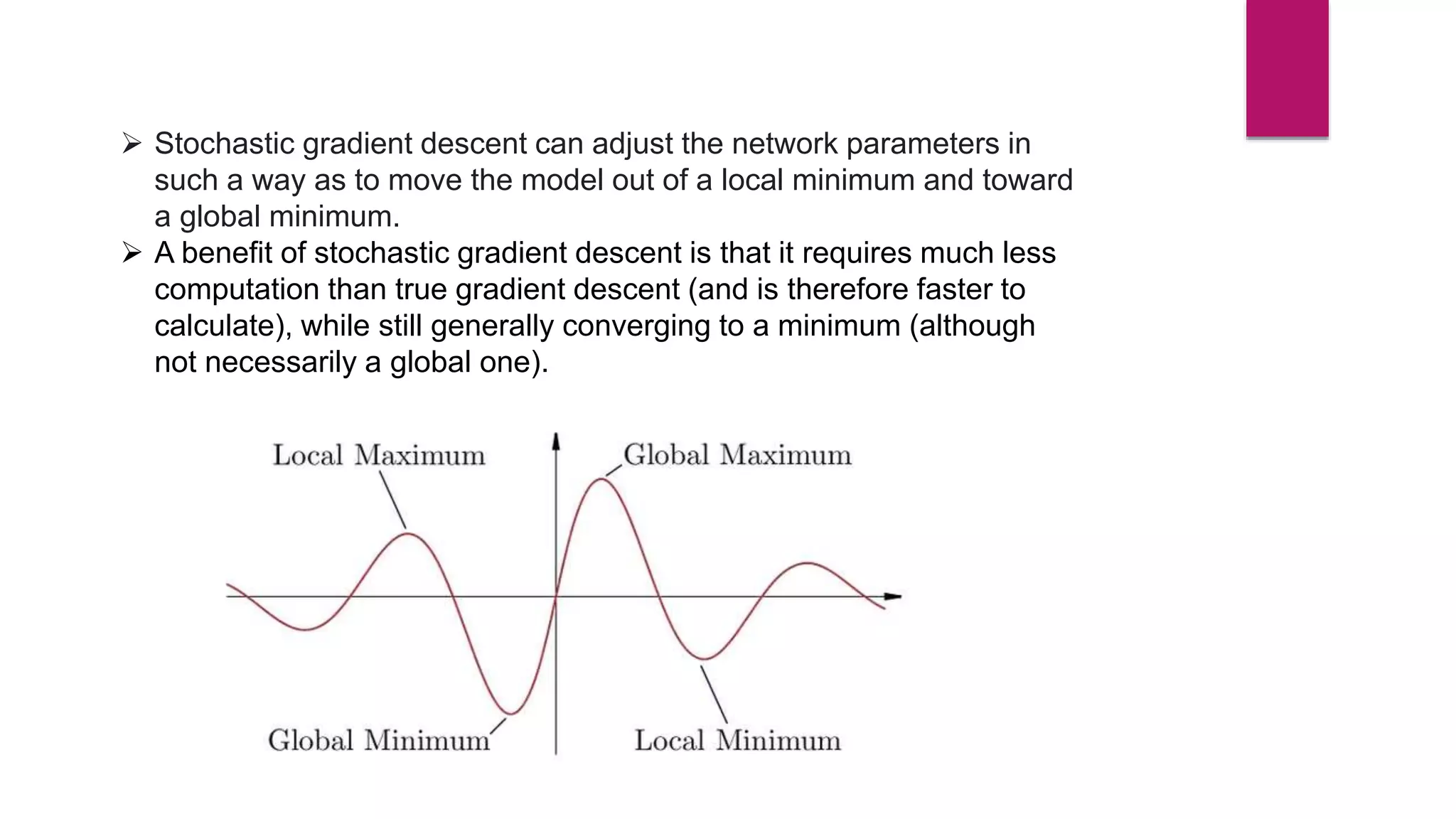
Stochastic gradient descent (SGD) is an iterative optimization algorithm used in machine learning to minimize a cost function by making adjustments to a model's parameters after each training sample, thereby facilitating convergence towards a global minimum. It is faster and requires less computational resources compared to traditional gradient descent methods, although it can be noisy and less stable due to frequent updates. Various approaches like dynamic sampling and gradient aggregation can help reduce noise in SGD.

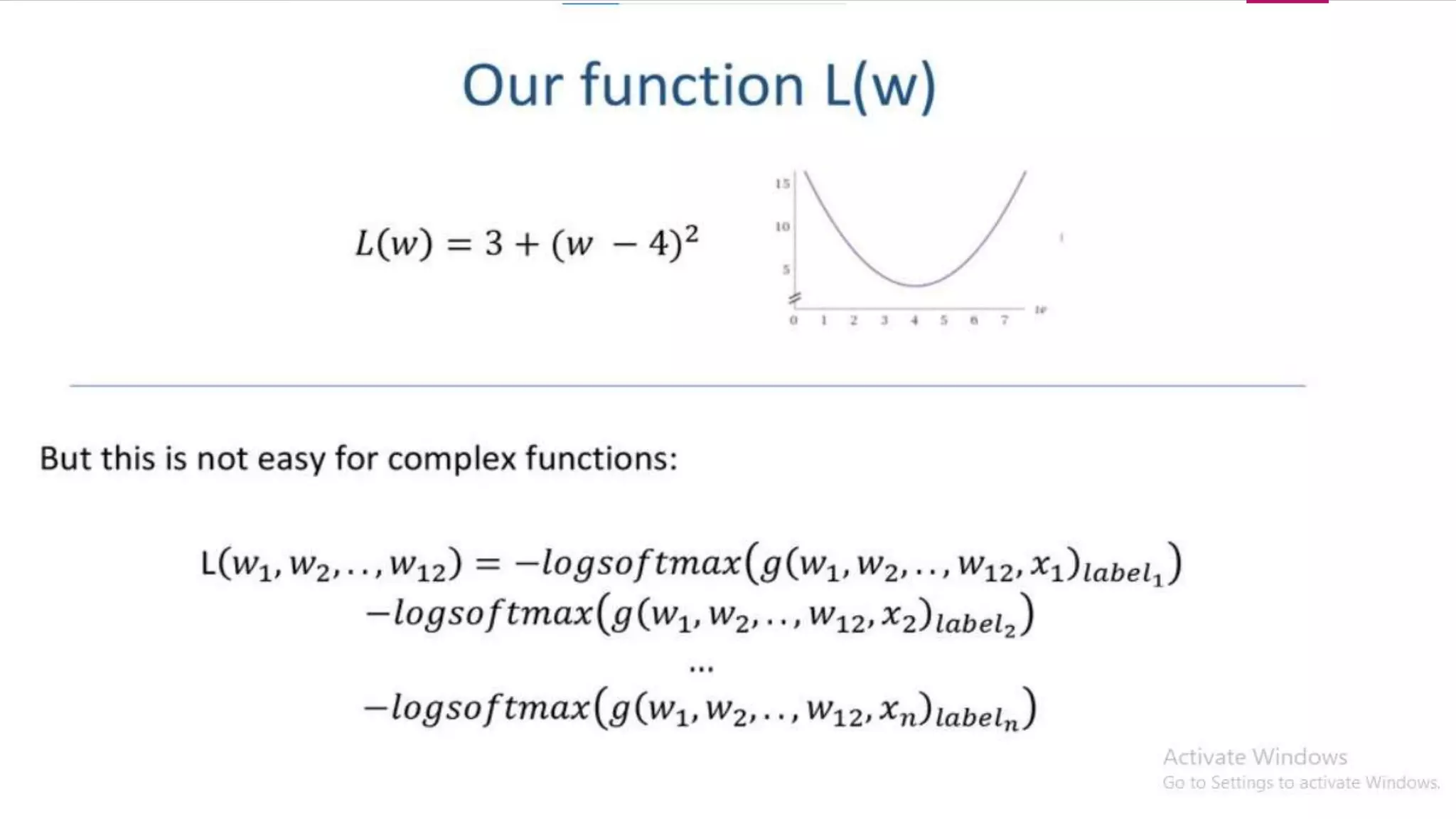
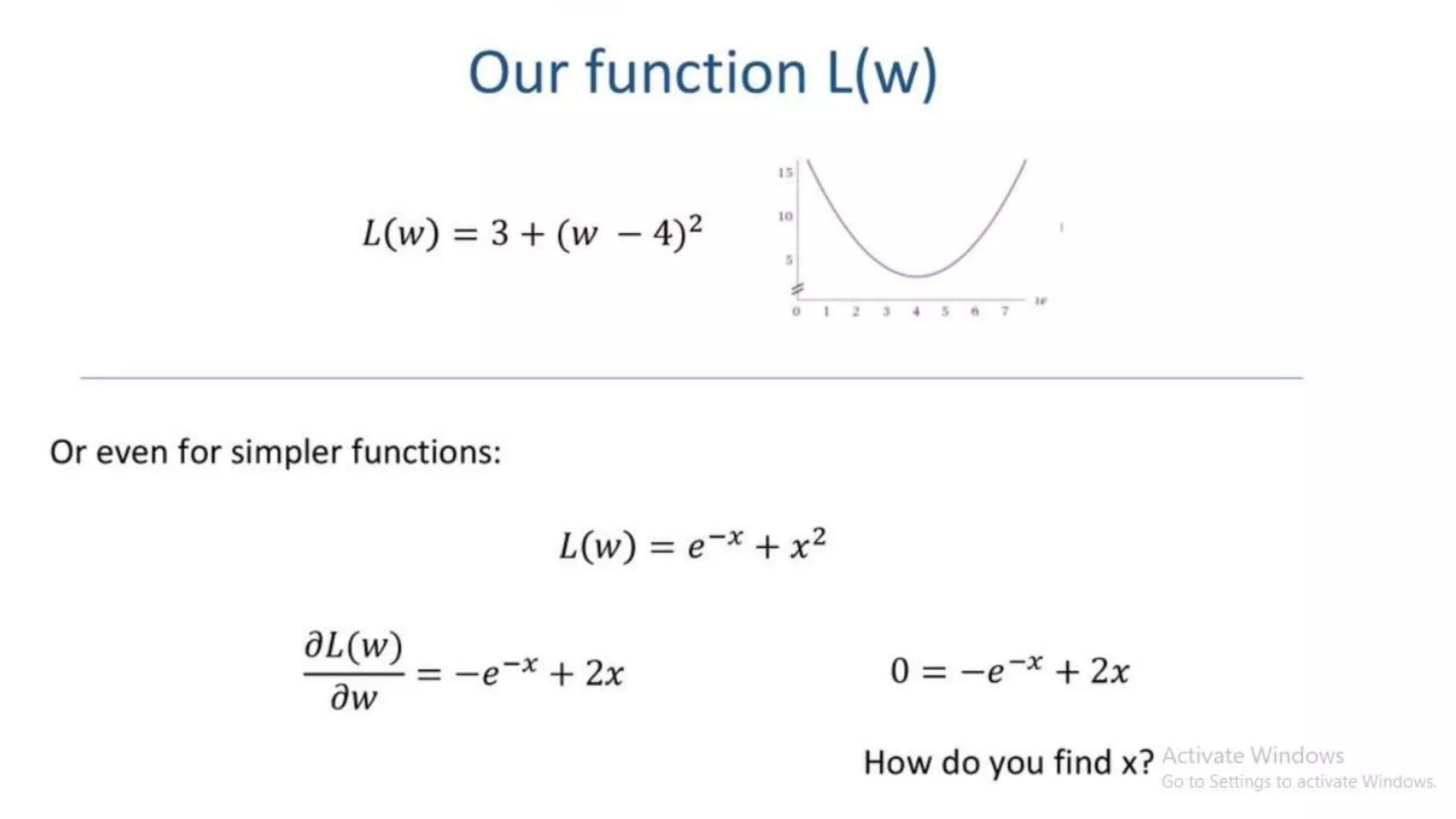

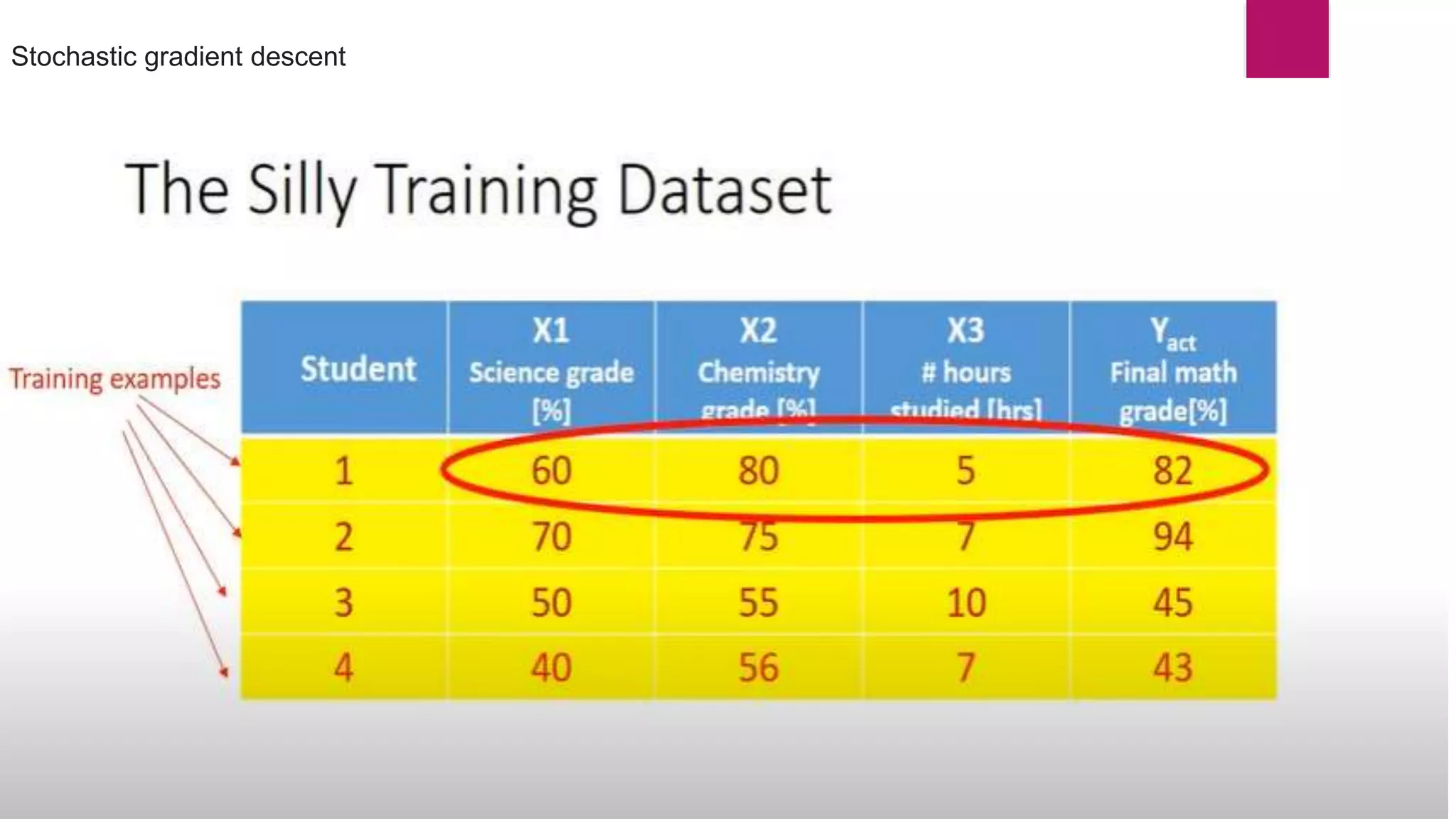
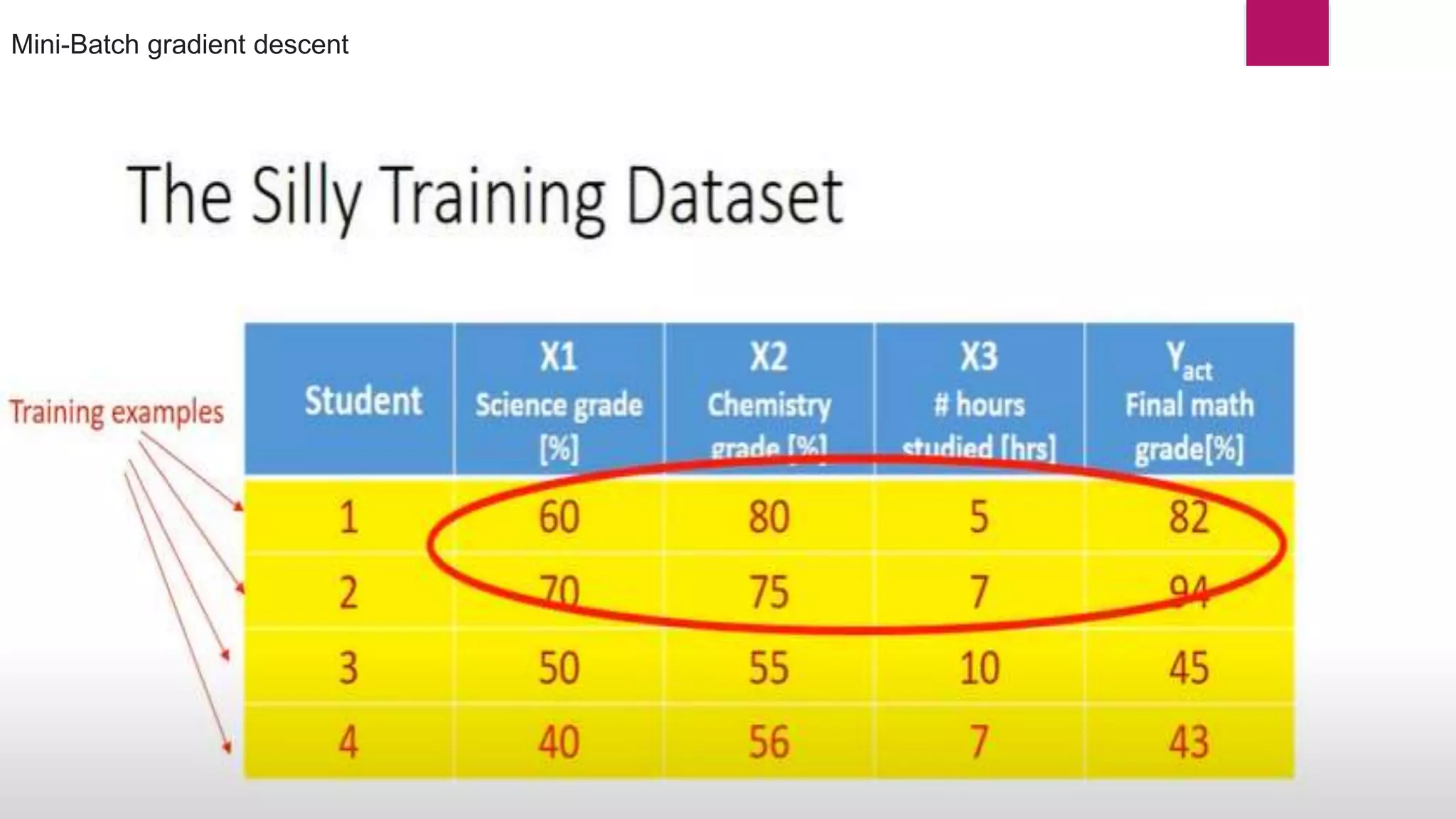
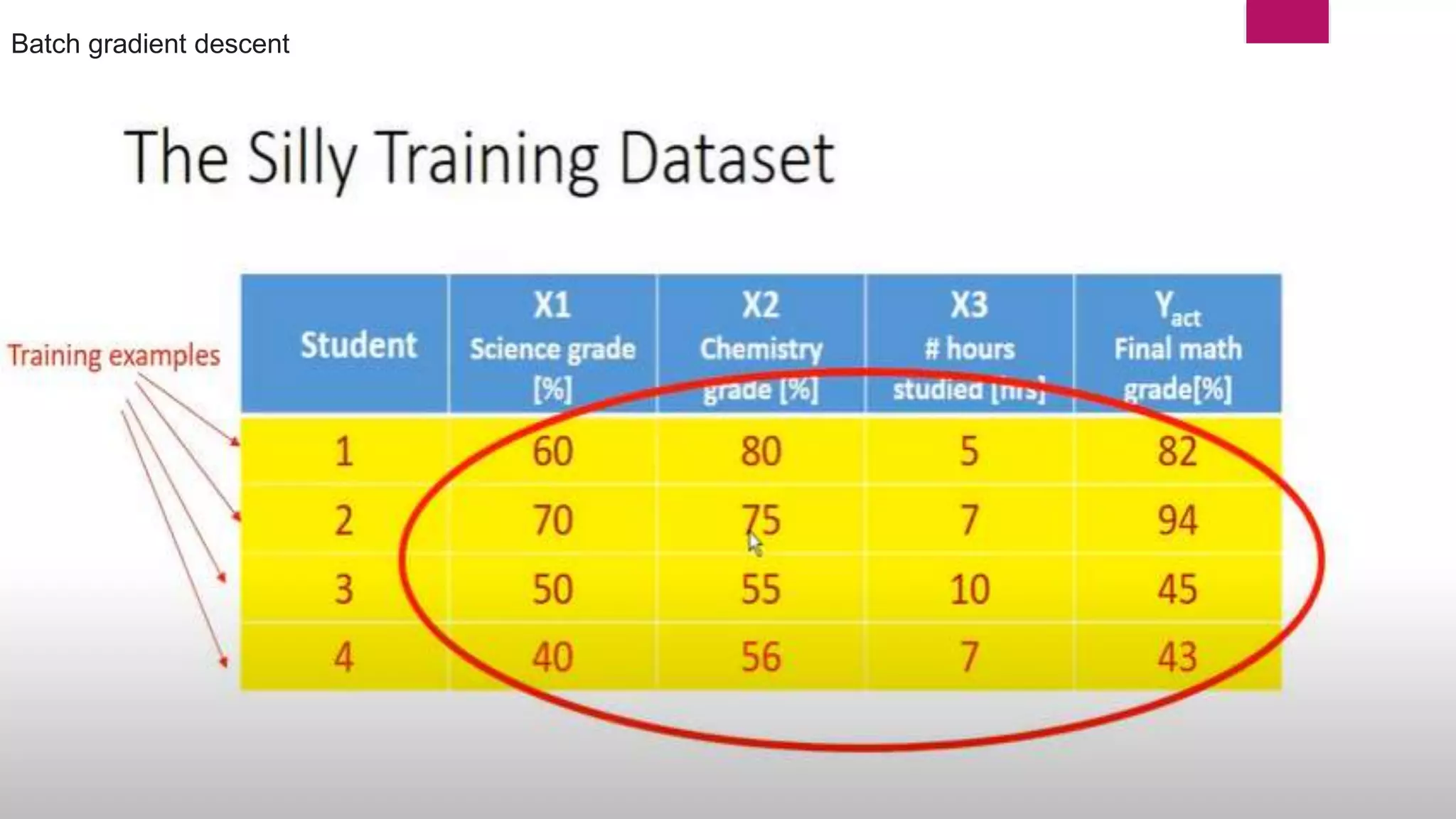

![ W(new) = W(old) - η * dL/dw(old) [Weight Updating formula]
Here dL/dw(old) n data point Batch gradient descent (gradient
descnet)
Here dL/dw(old) k data point Mini-Batch gradient descent
Here dL/dw(old) 1 data point Stochastic Gradient Descent](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/221121stochasticgradientdescentdl-221029081734-fbec6715/75/Stochastic-Gradient-Decent-SGD-pptx-14-2048.jpg)