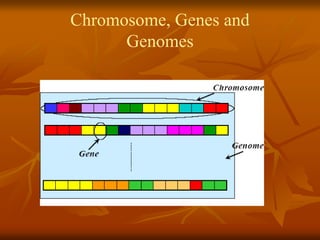
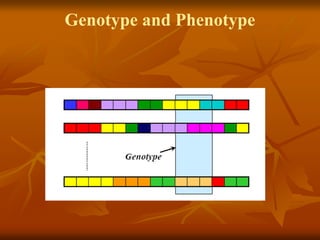
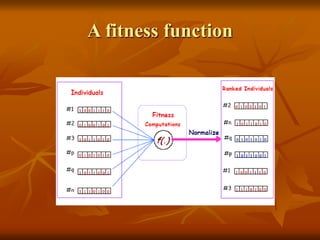
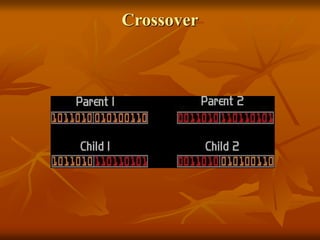
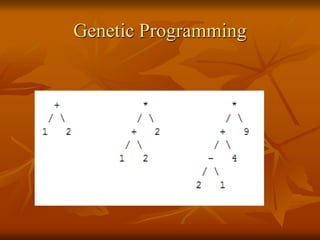
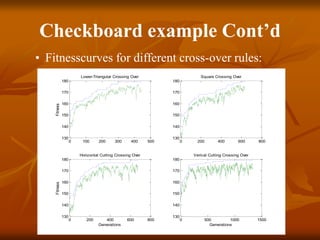
Genetic algorithms are a class of evolutionary algorithms that use techniques inspired by evolutionary biology such as inheritance, mutation, selection, and crossover. They work by generating a population of candidate solutions and evolving them toward increasingly better solutions over multiple generations. Each individual in the population is evaluated to determine its fitness, with more fit solutions being more likely to reproduce and pass on their traits. Offspring are produced through crossover and mutation operations, creating a new population that is used in the next iteration of the algorithm. The process terminates when a satisfactory solution has been found or a maximum number of generations has been produced.