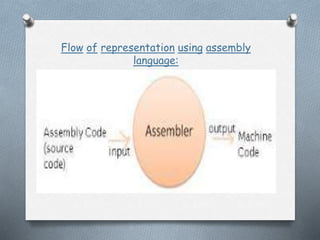
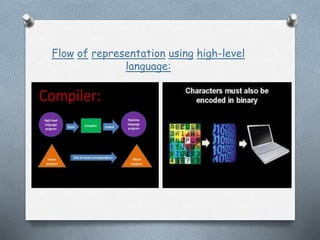
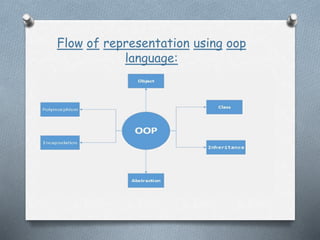
This document discusses the generations of programming languages from the 1940s to present and beyond. It covers machine languages from 1940-1956, assembly languages from 1956-1963, high-level languages from 1964-1971, object-oriented programming languages from 1971 to present, and artificial intelligence languages for the present and beyond. Each generation introduced languages that were more user-friendly and abstracted away from the underlying machine compared to previous generations.