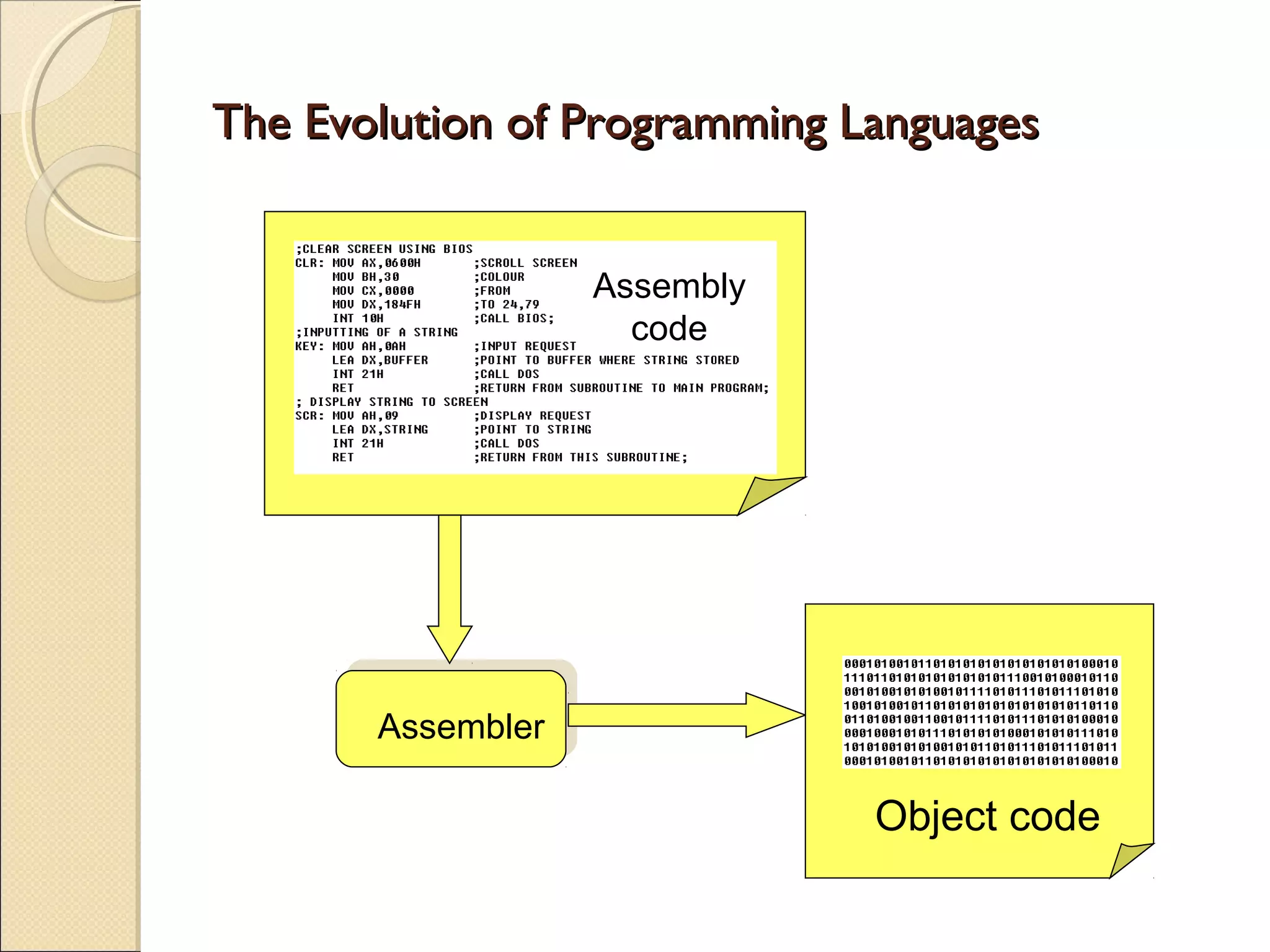
Three generations of computer languages are described:
1) Machine and assembly languages (1st and 2nd generation) which use cryptic codes that are translated to machine code.
2) Higher-level languages like FORTRAN, COBOL, BASIC (3rd generation) which use more English-like phrases.
3) Even higher-level languages like Visual Basic and Visual Age (4th generation) which may use graphical tools.
5th generation languages are designed for artificial intelligence problems.