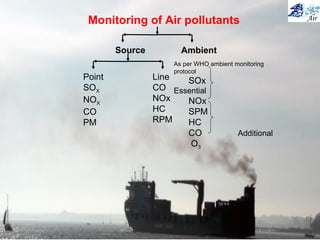
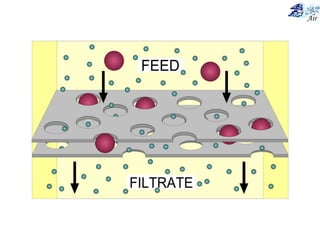
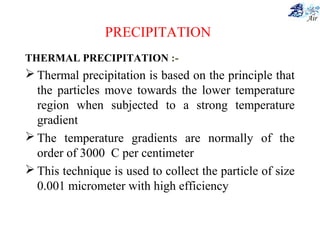
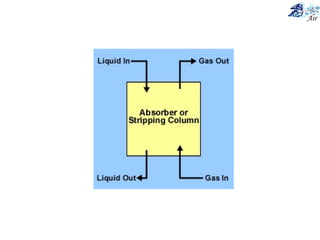
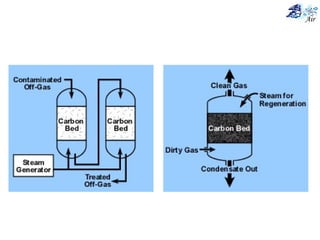
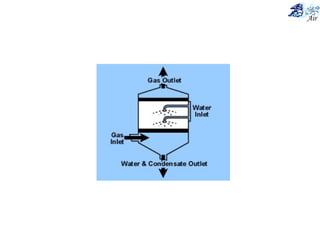
This document discusses various methods for sampling air pollutants. It describes techniques for sampling particulate pollutants such as sedimentation, filtration, impingement, and precipitation. For gaseous pollutants, techniques discussed include absorption sampling, adsorption sampling, and condensation sampling. New methods like bubble sampling and sorbent sampling are also summarized. The objectives of air sampling are to measure the quality, quantity, and variation of pollutants from emission sources to help determine control methods. Location selection aims to avoid disturbances and capture predominant wind directions.