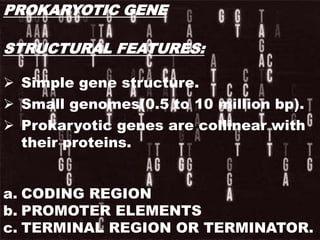
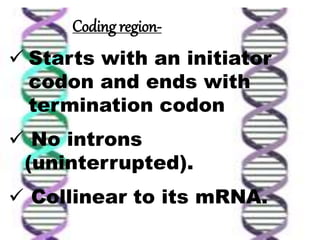
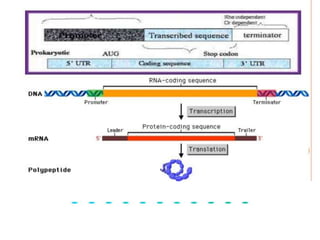
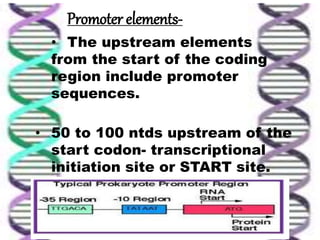
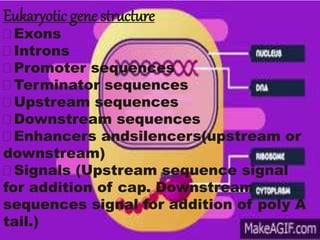
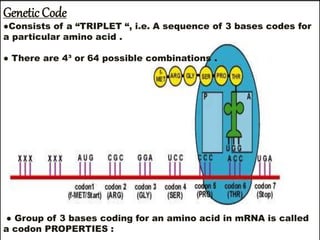
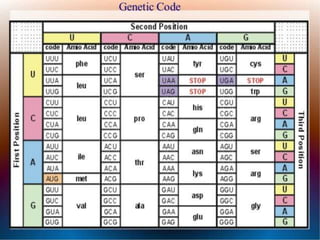
The document discusses the structure of genes and the genetic code, detailing differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic genes, including concepts like exons, introns, and various gene unit definitions. It explains the structural features of prokaryotic genes, the role of promoter elements, and the termination of transcription in both types of organisms. Additionally, the genetic code is described as based on triplets of bases, with properties like degeneracy and unambiguity.