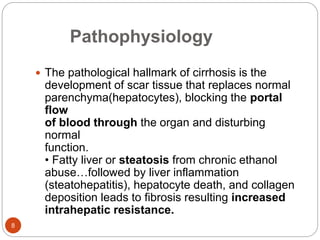
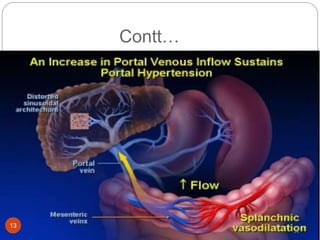
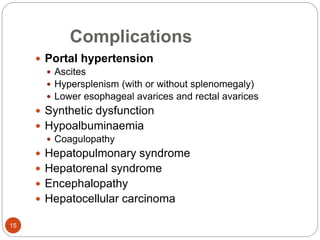
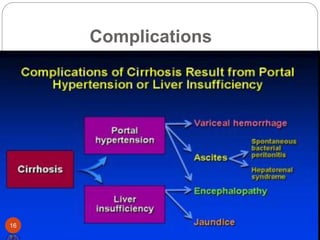
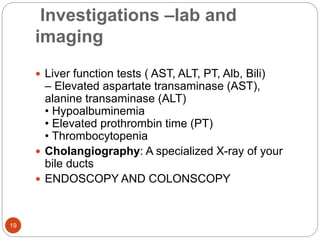
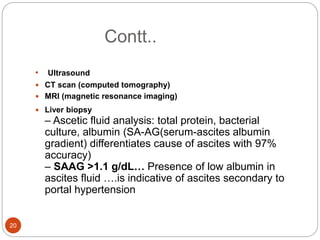
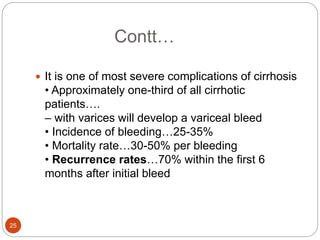
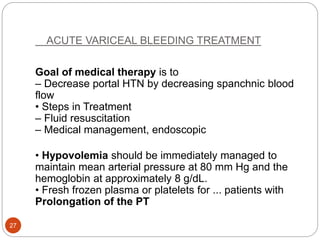
This document provides an outline and details regarding chronic liver disease. It begins with an introduction defining chronic liver disease and its causes. Key points include that chronic liver disease lasts over 6 months and can result from viral infections, autoimmune conditions, inherited diseases, cancer or toxin consumption. The document then covers the epidemiology, etiology, pathophysiology, risk factors, complications, signs and symptoms, investigations and treatments of chronic liver disease in greater detail over multiple pages.




![Etiology
Result of chronic, long-term insult to liver
• Most common causes
– Chronic alcohol abuse
• Ethanol and metabolites are direct hepato toxins
– Hepatitis
• Hep C and Hep B
• Other causes
– Immunological disease[autoimmune hepatitis]
– Drugs: isoniazid, methotrexate, methyldopa,
Tamoxifen, propylthiouracil
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cld-230521170747-aed12a50/85/cld-pptx-7-320.jpg)