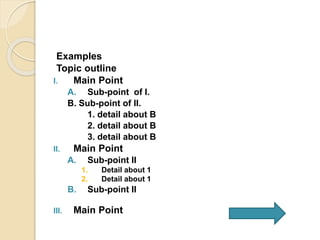
This document provides guidance on gathering, organizing, and summarizing information. It discusses note-taking, outlining, summarizing, and categorizing/classifying. Note-taking involves recording important information for future use in as brief a form as possible. Outlining involves organizing information into a hierarchical structure with main ideas, sub-points, and details. Summarizing extracts the key ideas and restates them briefly, while omitting unnecessary details. Categorizing/classifying involves grouping related concepts and information.