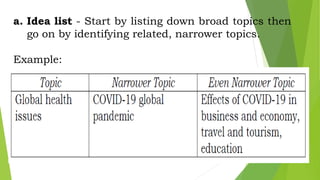
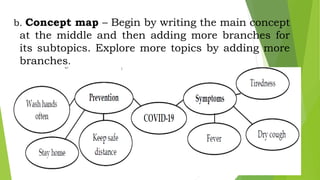
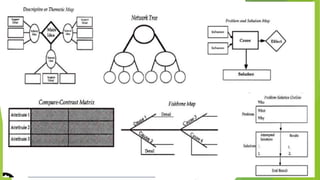
This document discusses techniques for selecting and organizing information, including brainstorming, outlining, and using graphic organizers. Brainstorming involves listing ideas to establish relationships between concepts. Outlining creates a hierarchical structure to organize writing in a topic or sentence outline. Graphic organizers visually display relationships among concepts using tools like Venn diagrams, charts, and diagrams. The techniques facilitate comprehension by breaking down information into simpler representations.