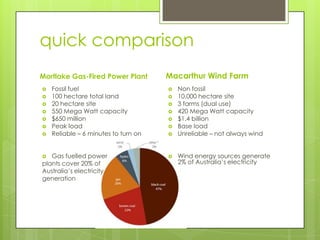
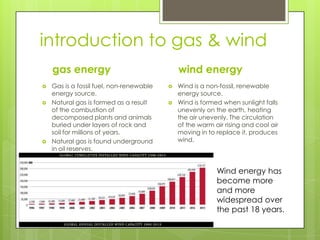
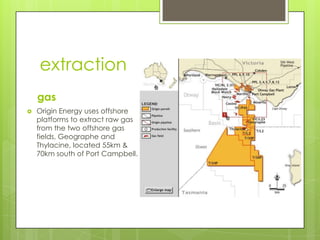
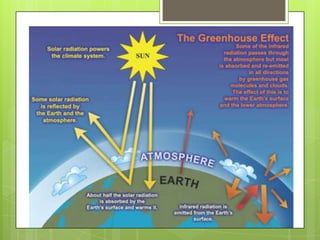
The document compares the environmental, economic, and social impacts of the Mortlake gas-fired power plant (fossil fuel) and the Macarthur wind farm (non-fossil energy source) in Australia. It discusses the principles of energy production, extraction methods, and the contribution of these energy sources to the enhanced greenhouse effect. The gas plant emits greenhouse gases due to combustion, while the wind farm has minimal emissions but can impact local wildlife.