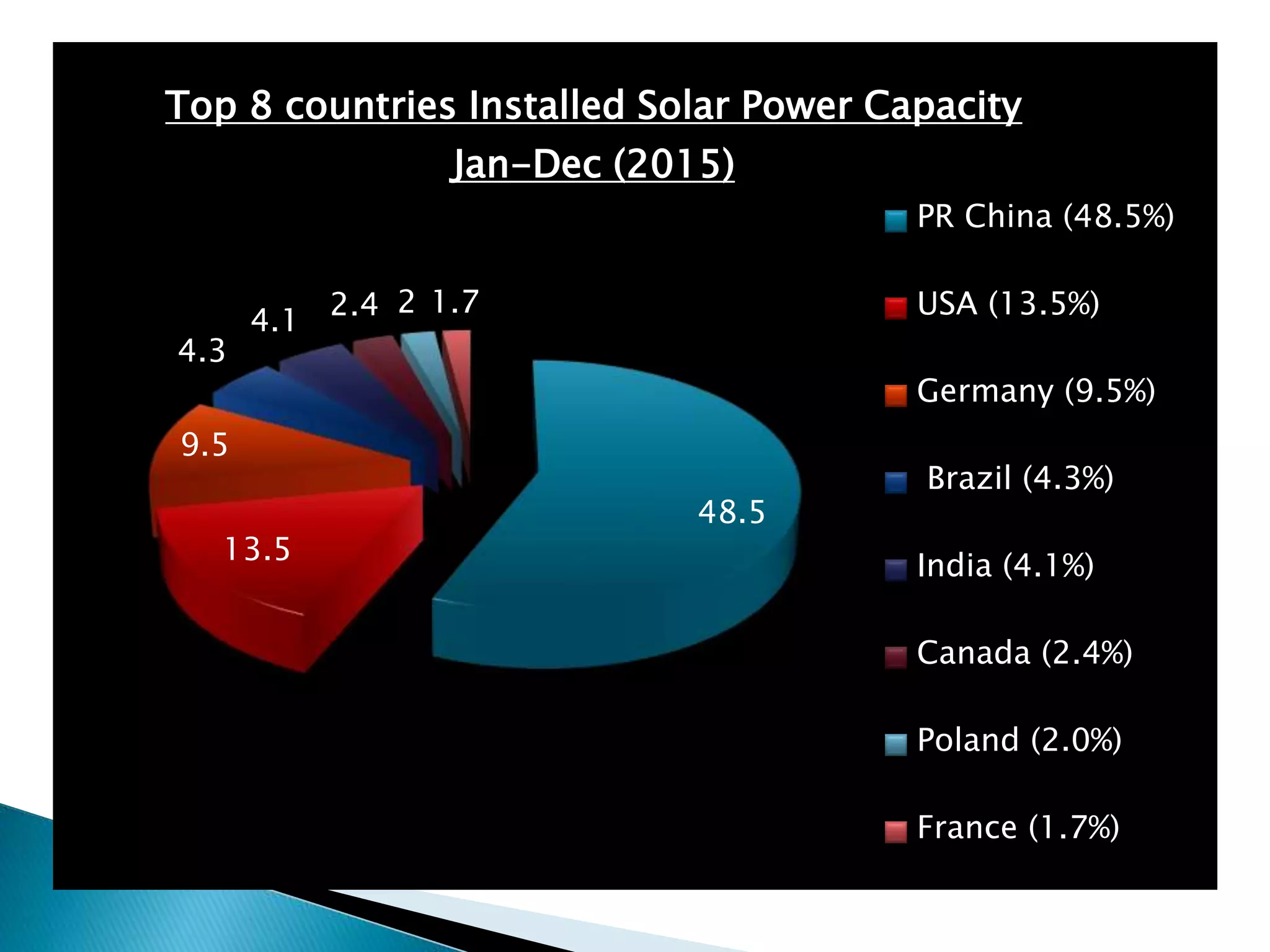
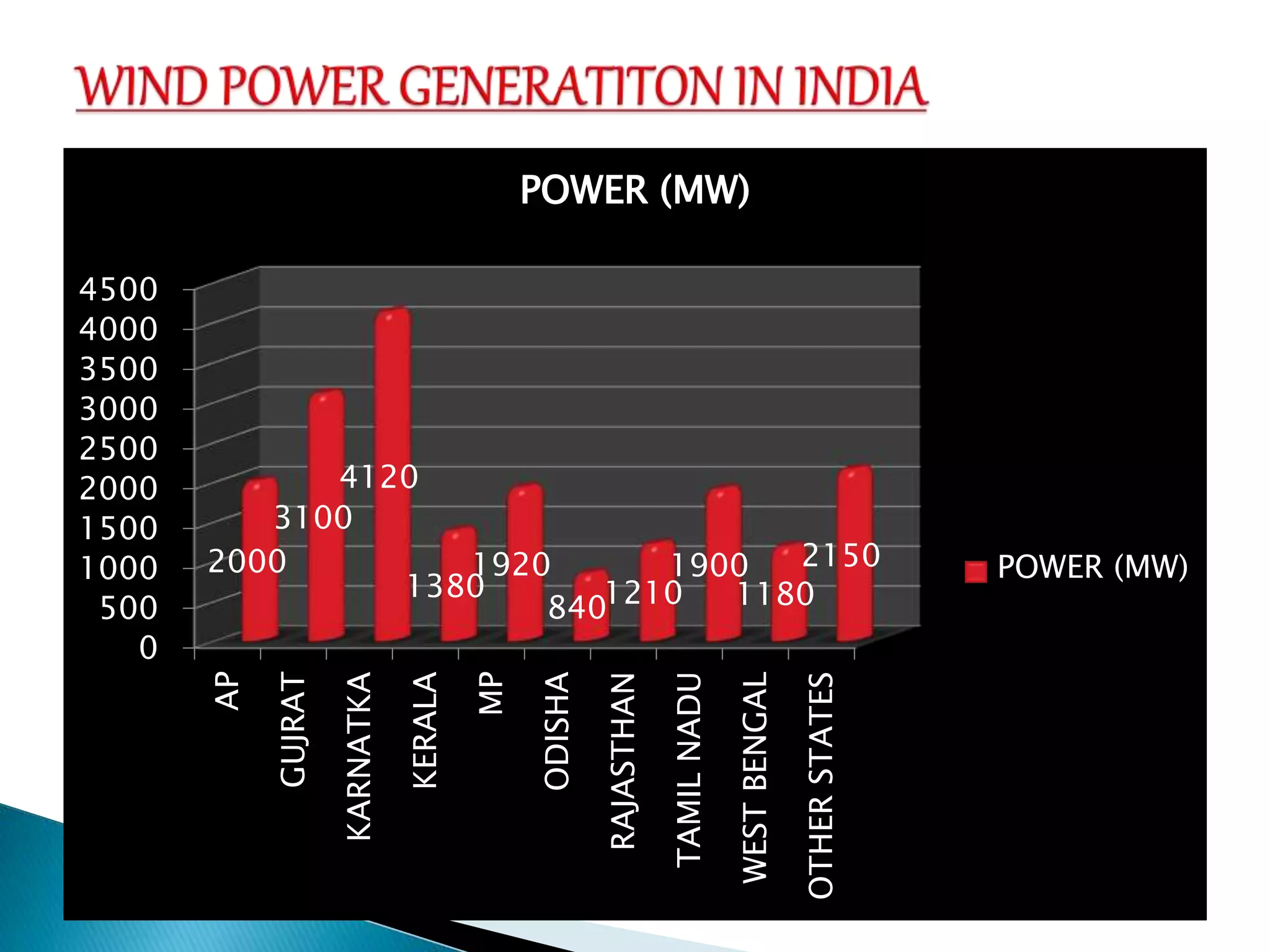
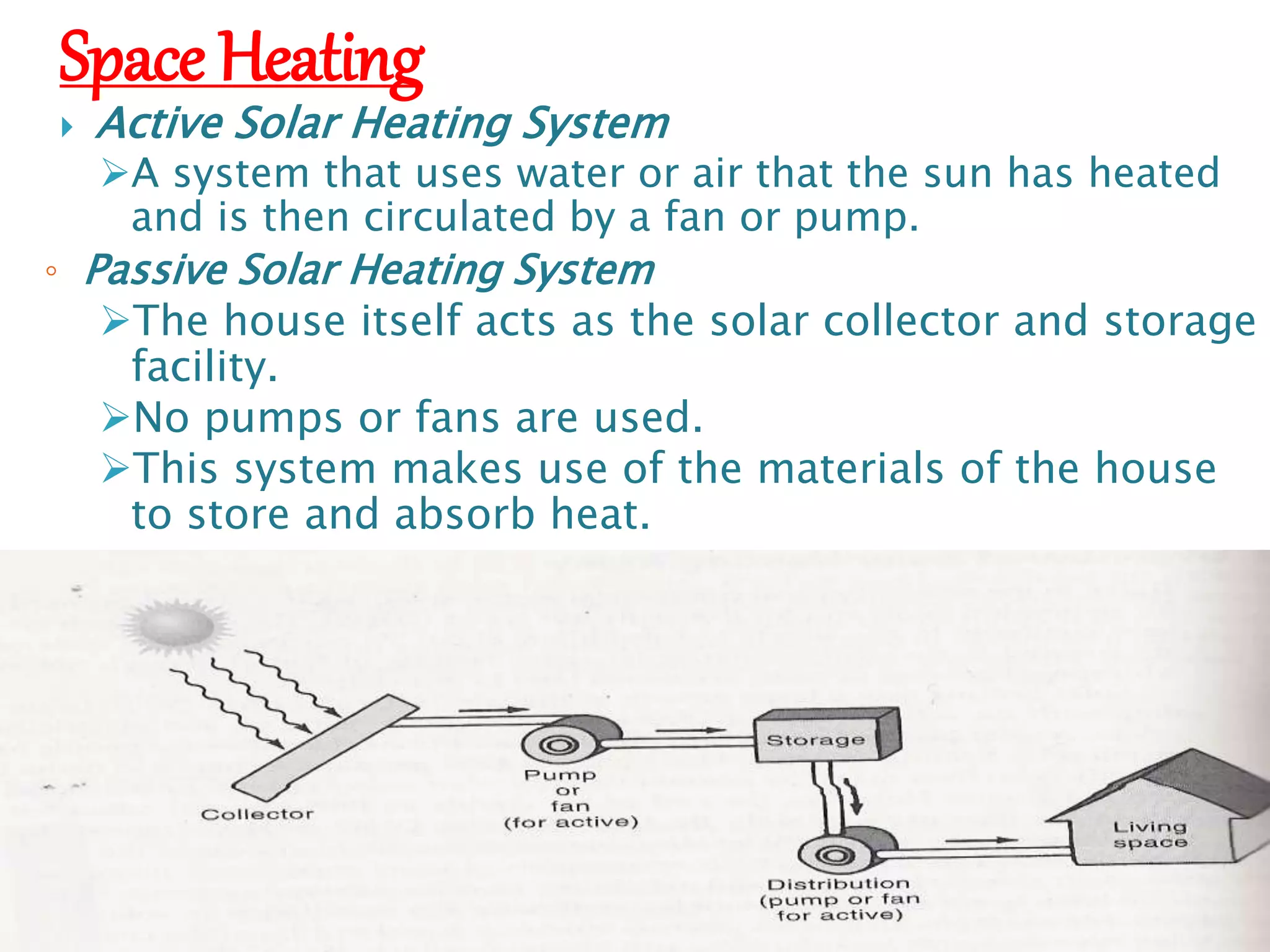
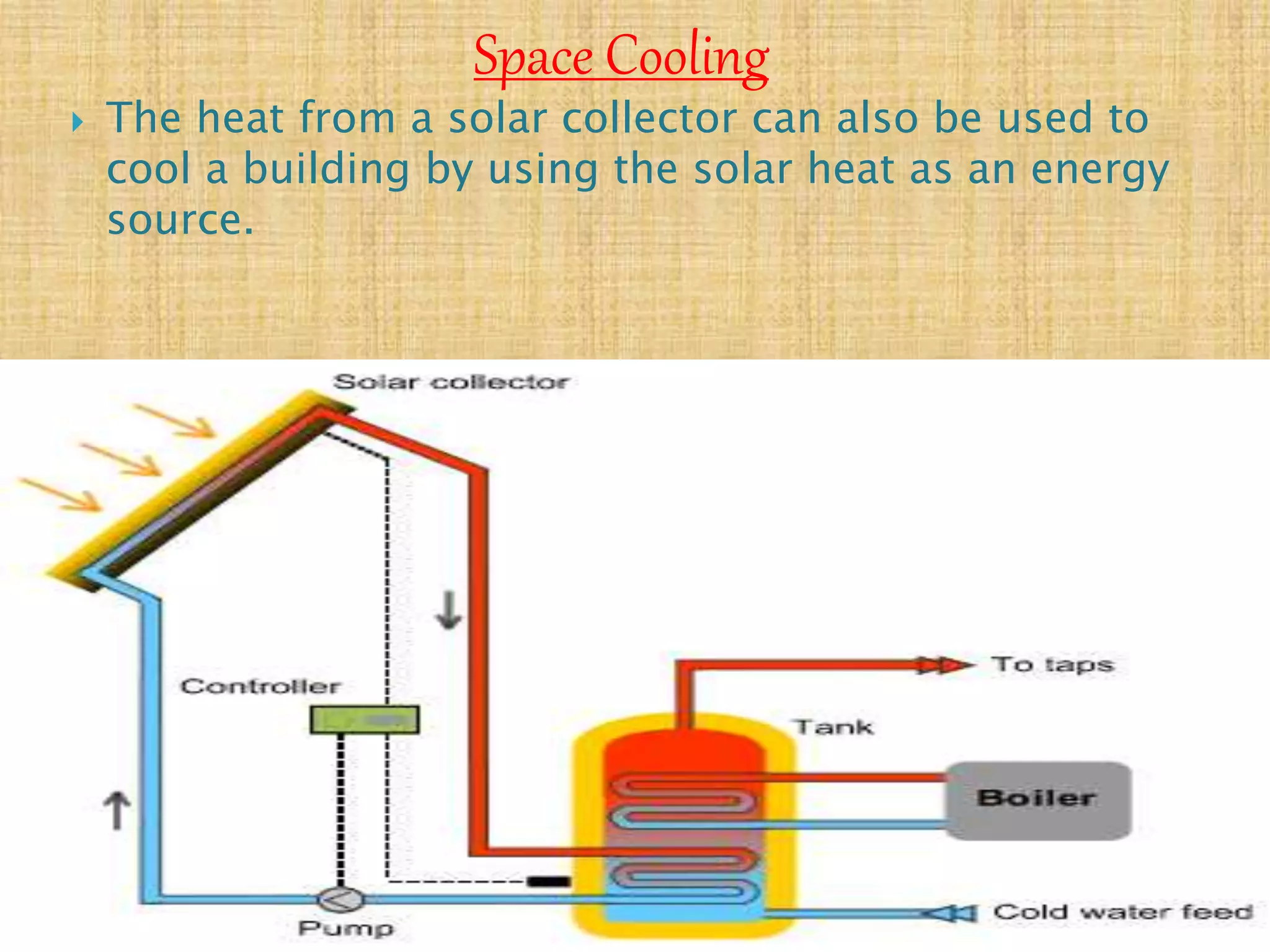
The document discusses renewable sources of energy such as solar, wind, geothermal, biofuel, and hydroelectricity. It provides examples of each type of renewable energy, noting their benefits like being renewable, reducing pollution, and providing sustainable power. The document also discusses some challenges of renewable energy sources like high initial costs to set up plants. In conclusion, the document advocates for greater use of renewable resources as alternatives to finite fossil fuels.