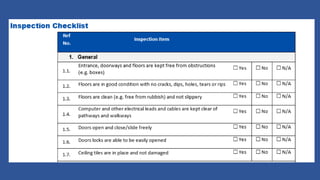
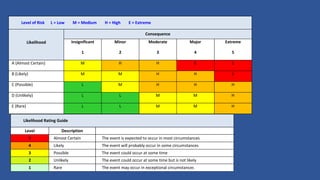
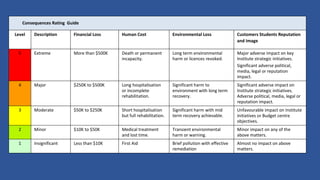
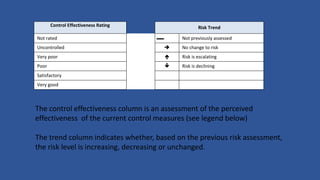
This document outlines the five steps to conducting a risk assessment: 1) identify hazards, 2) decide who may be harmed and how, 3) assess the risks and take action, 4) make a record of findings, and 5) review the risk assessment. It then provides tables to guide rating the likelihood, consequences, control effectiveness, and trend of identified risks. Risks should be documented along with the responsible person, likelihood and consequence scores, current control measures, and effectiveness of controls.