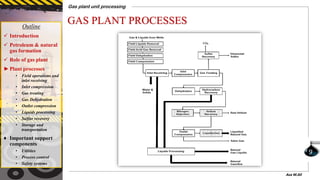
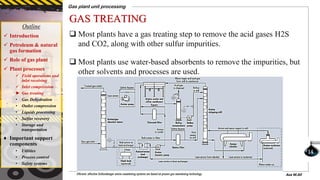
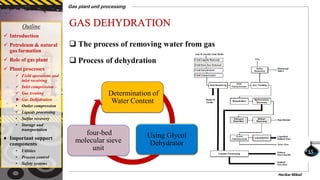
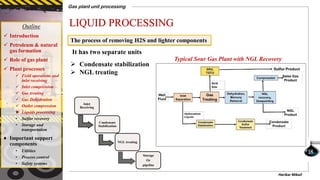
The document provides a comprehensive overview of gas plant unit processing, detailing the roles of gas plants in the petroleum and natural gas industry, including the processes of gas treating, dehydration, compression, and sulfur recovery. It outlines the significance of various components, such as utilities, process control, and safety systems, emphasizing their critical functions in enhancing efficiency and safety in gas processing. Additionally, it discusses the formation of petroleum and natural gas from organic matter and the implications of impurities in natural gas.