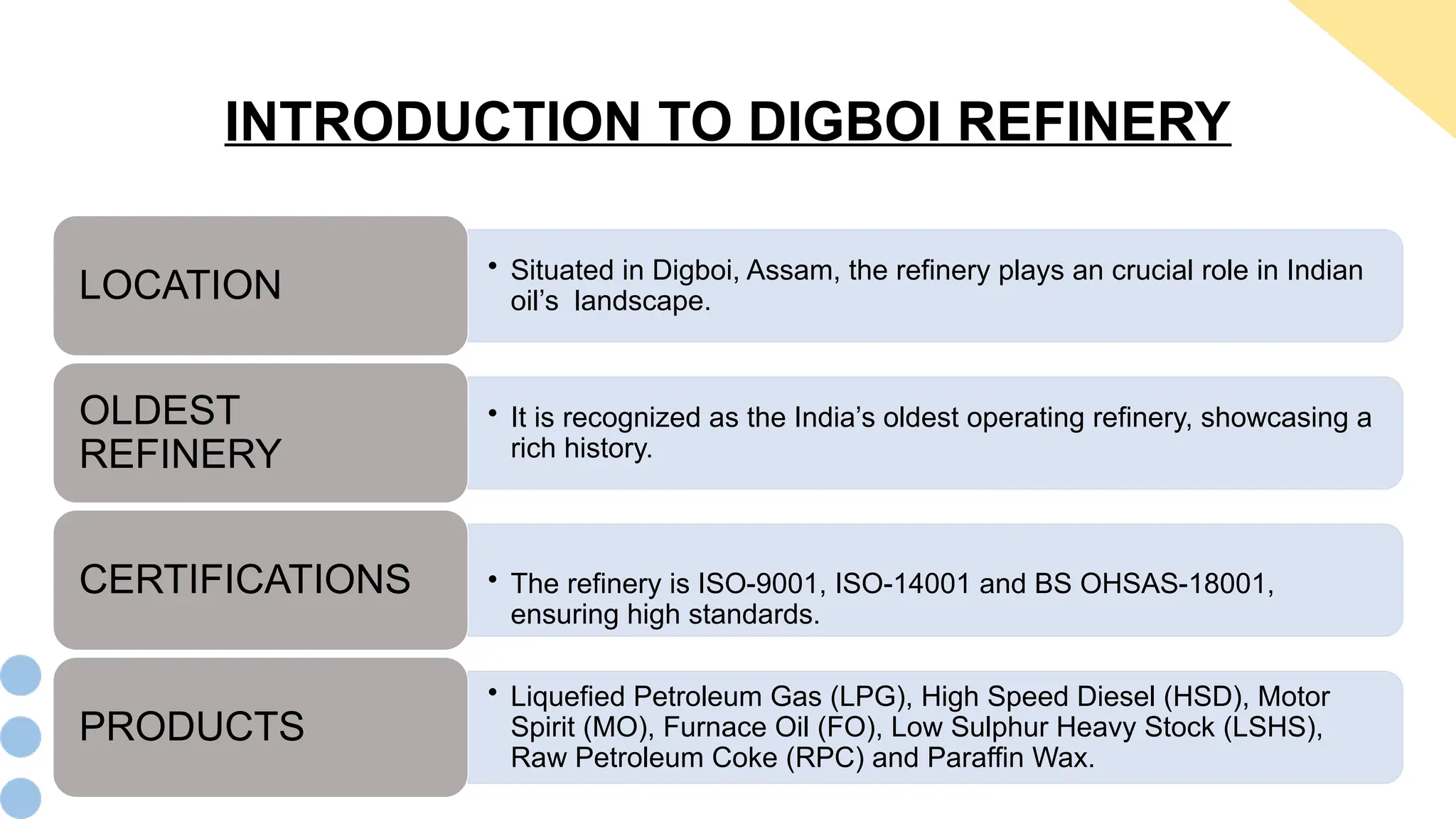
The document discusses the mechanical maintenance practices at the Digboi refinery in Assam, highlighting its historical significance as India's oldest operational refinery. It covers various aspects, including fire safety protocols, mechanical maintenance processes, and the production of paraffin wax and fuels. The authors emphasize the importance of practical exposure and safety in their 30-day internship experience at the refinery.