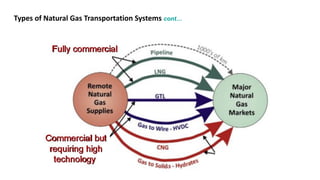
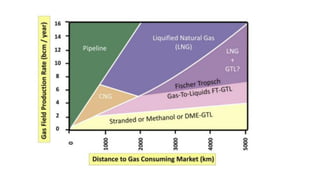
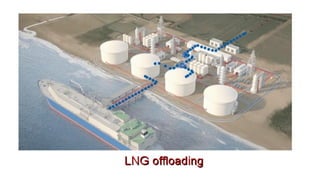
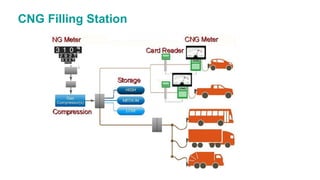
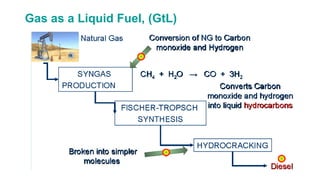
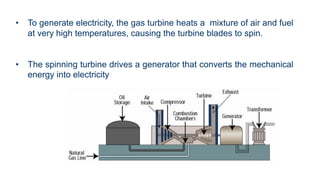
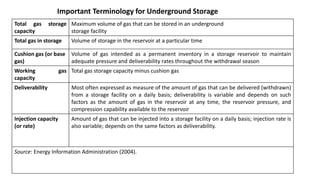
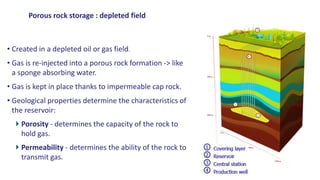
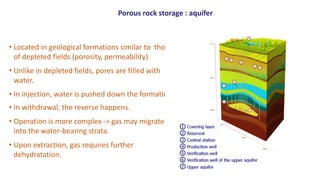
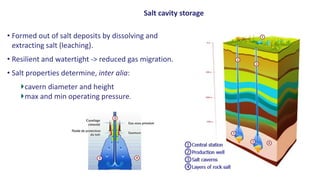
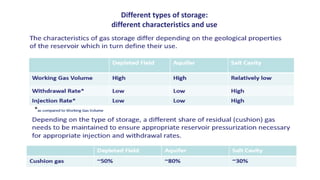
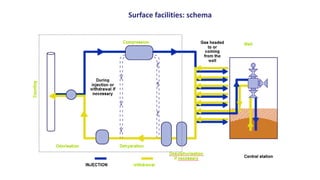
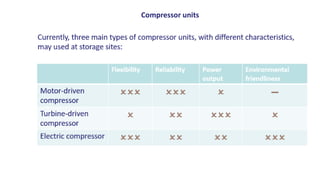
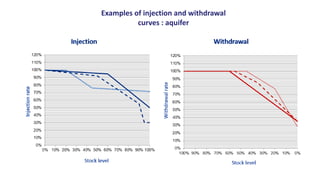
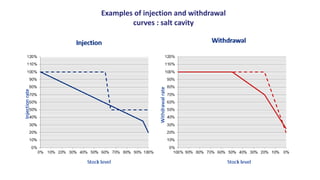
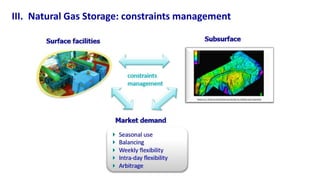
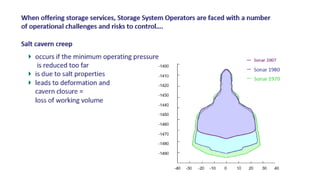
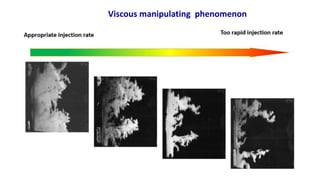
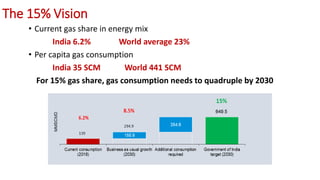
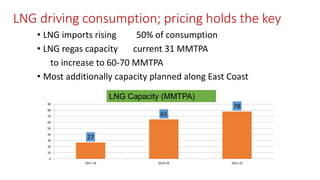
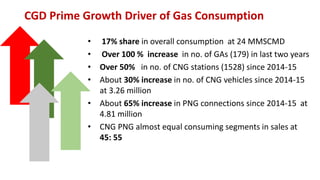
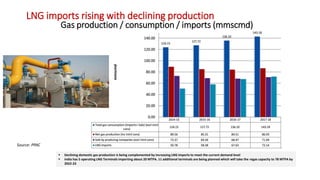
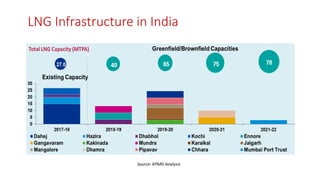
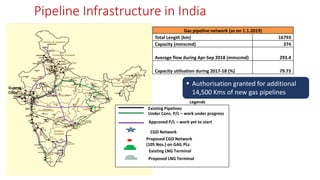
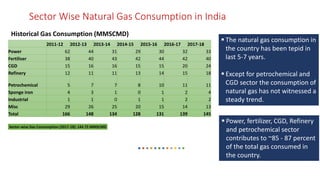
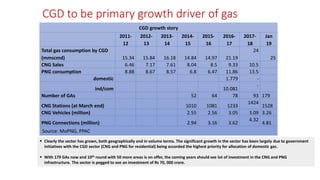
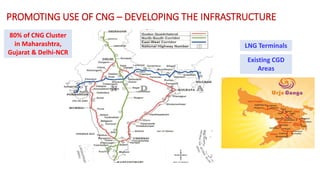
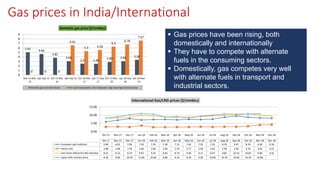
Natural gas can be transported via pipelines, as liquefied natural gas (LNG), or compressed natural gas (CNG). Pipelines are the most common method and have high reliability but lack flexibility. LNG and CNG allow for transportation of remote gas reserves but require large investments for processing infrastructure. Natural gas can also be converted to liquids (gas-to-liquids) or used to generate electricity on-site (gas-to-wire) to enable transportation. Underground storage plays a key role in meeting seasonal demand fluctuations and peak loads.