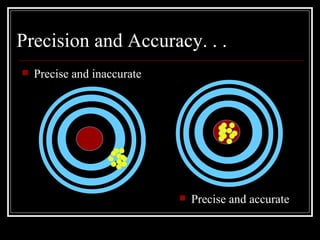
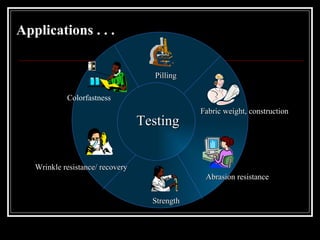
Standards provide rules and guidelines for testing garments and quality control. There are various types of standards including company, industry, government, and full consensus standards. Standards help define safety requirements, set performance levels, reduce costs, prevent mistakes, and provide continuity. Common tests include pilling, colorfastness, fabric weight, wrinkle resistance, and strength. Organizations like AATCC, ASTM, ANSI, BIS, and ISO develop and maintain standards used in the garment industry. Compliance with standards is important for quality control.