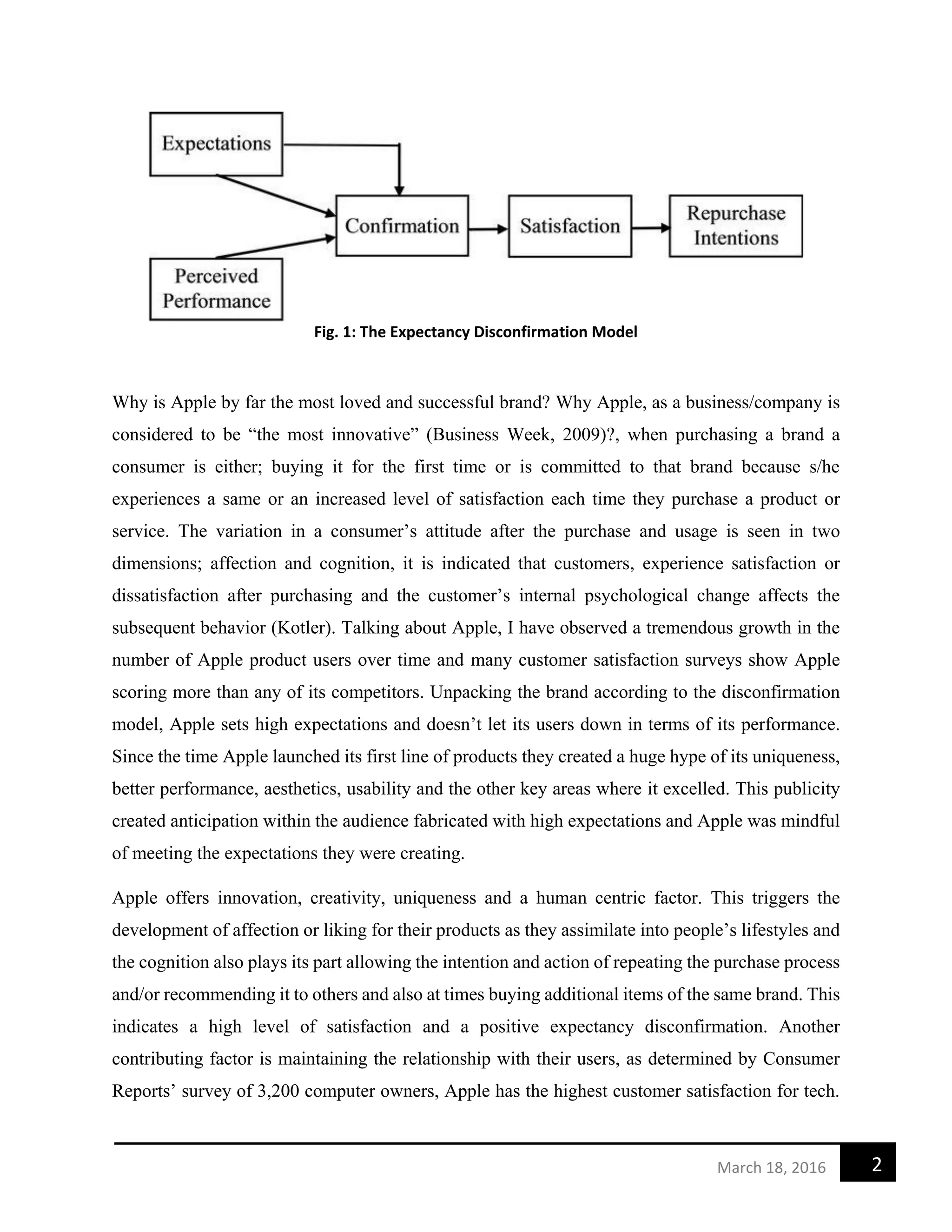
This document discusses the Expectancy Disconfirmation Model and how it can be used to measure consumer satisfaction and brand loyalty. The model measures the difference between a customer's expectations of a product or service and their actual experience. If expectations match experience, it leads to satisfaction, but if expectations are not met, it leads to dissatisfaction. Apple is used as a case study of a brand that sets high expectations and consistently meets them through innovation, uniqueness, and customer service. This leads to high consumer satisfaction, positive disconfirmation, and strong brand loyalty over time.