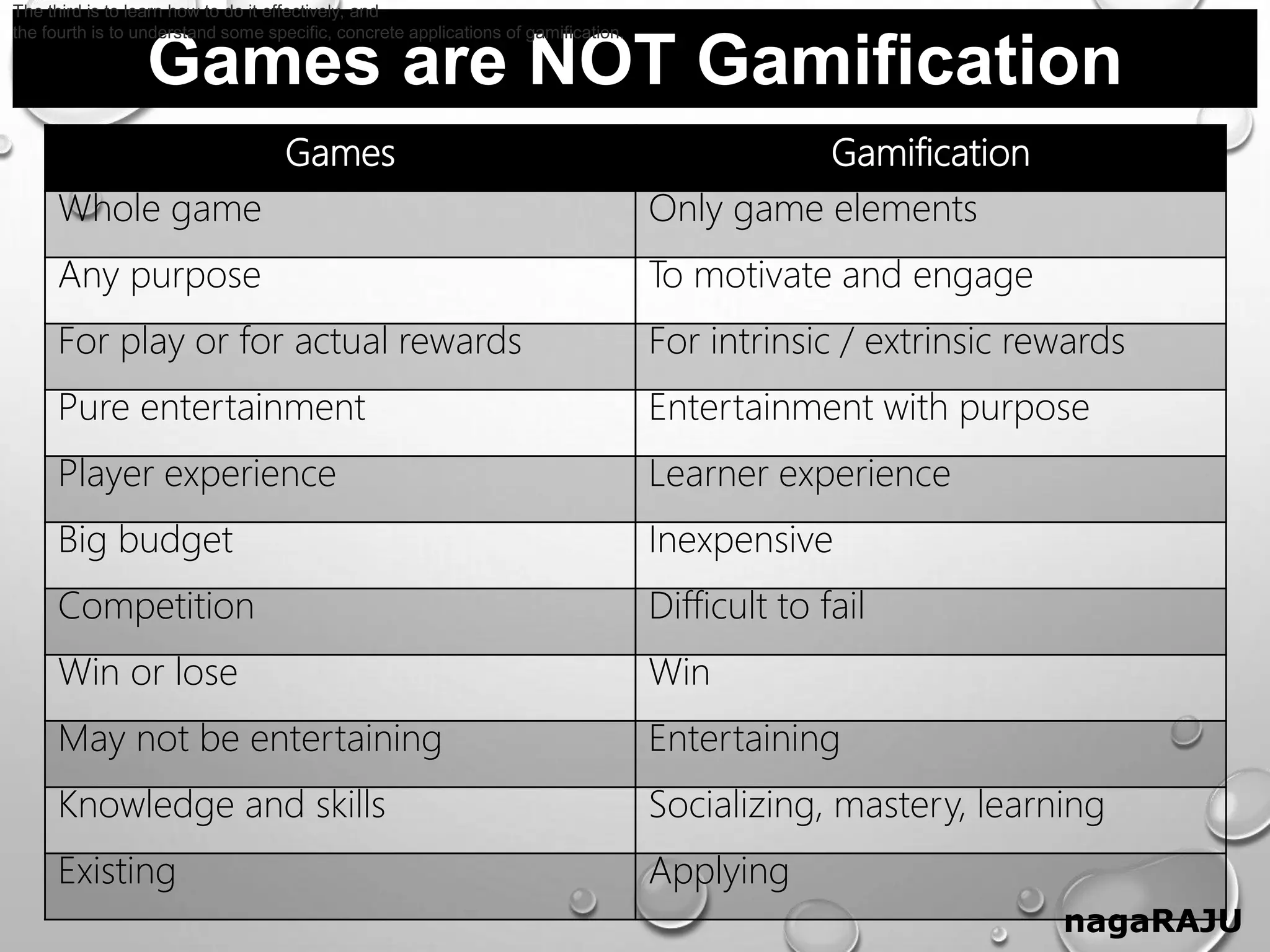
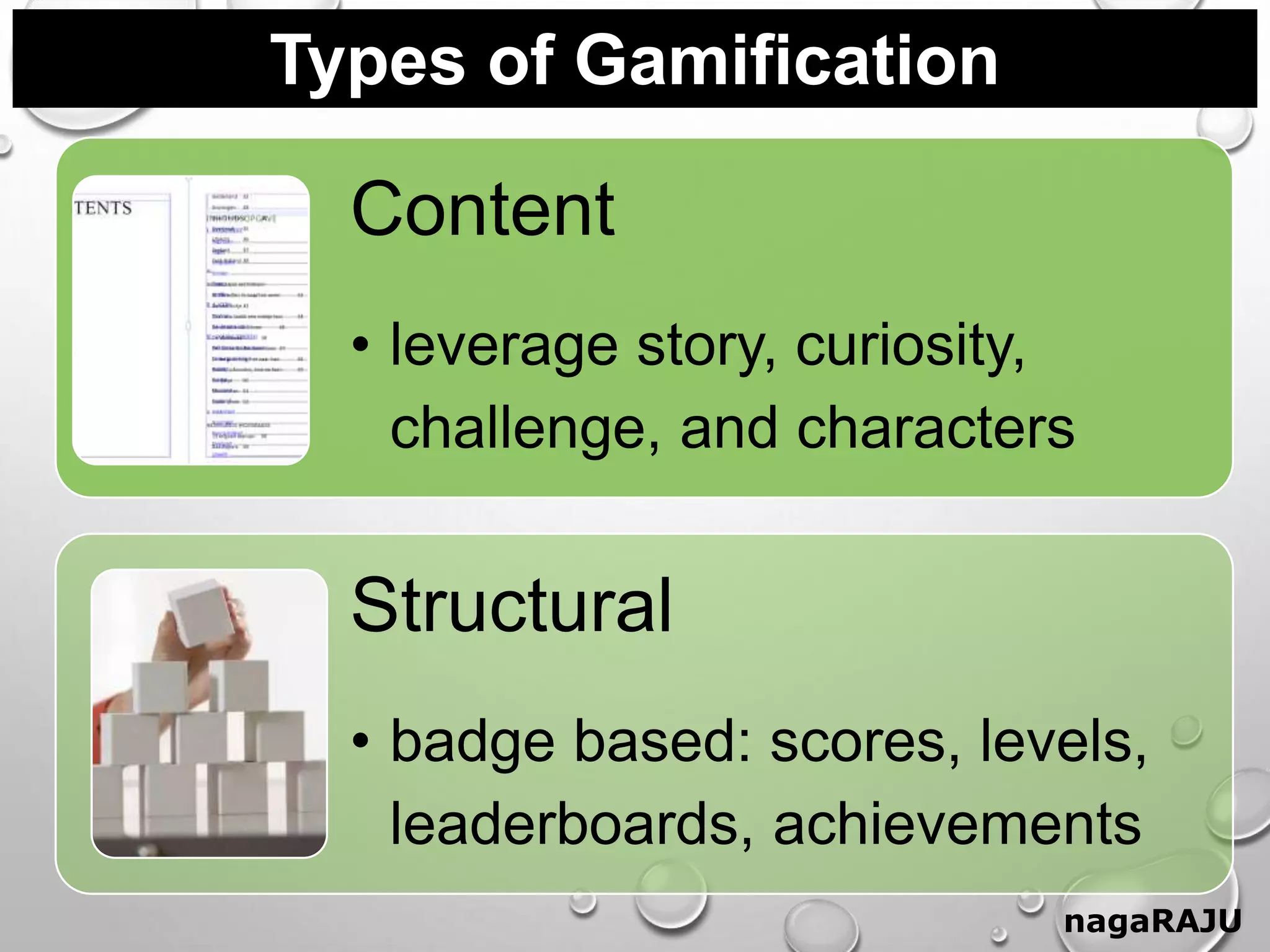
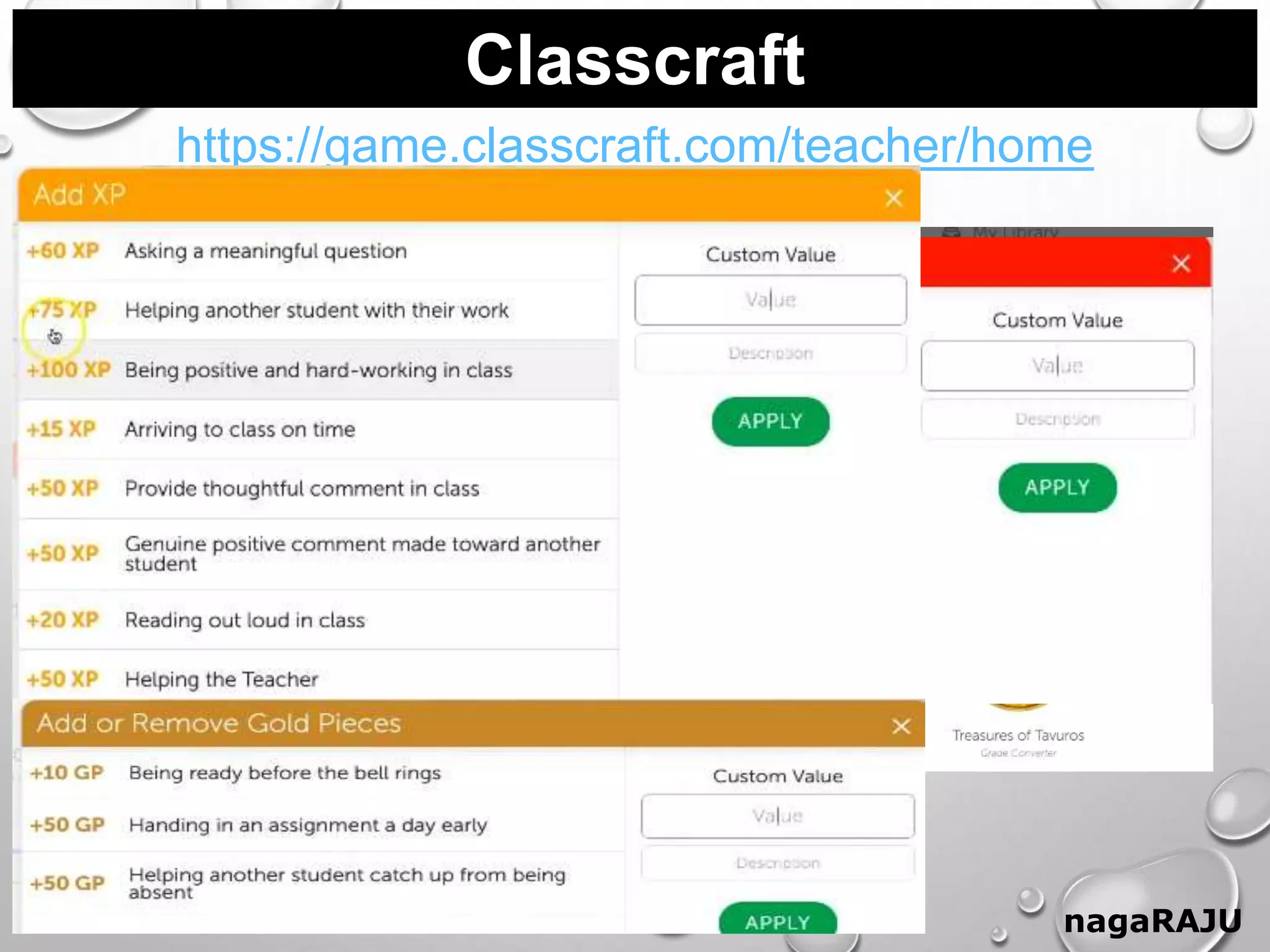
The document discusses gamification and provides information about its key aspects. It defines gamification as using game elements in non-game contexts to motivate and engage users. It notes the differences between games and gamification, and discusses why gamification is used to increase engagement, motivation, retention and skills. It also outlines the history of gamification and provides examples of common game elements like badges, leaderboards and virtual rewards.