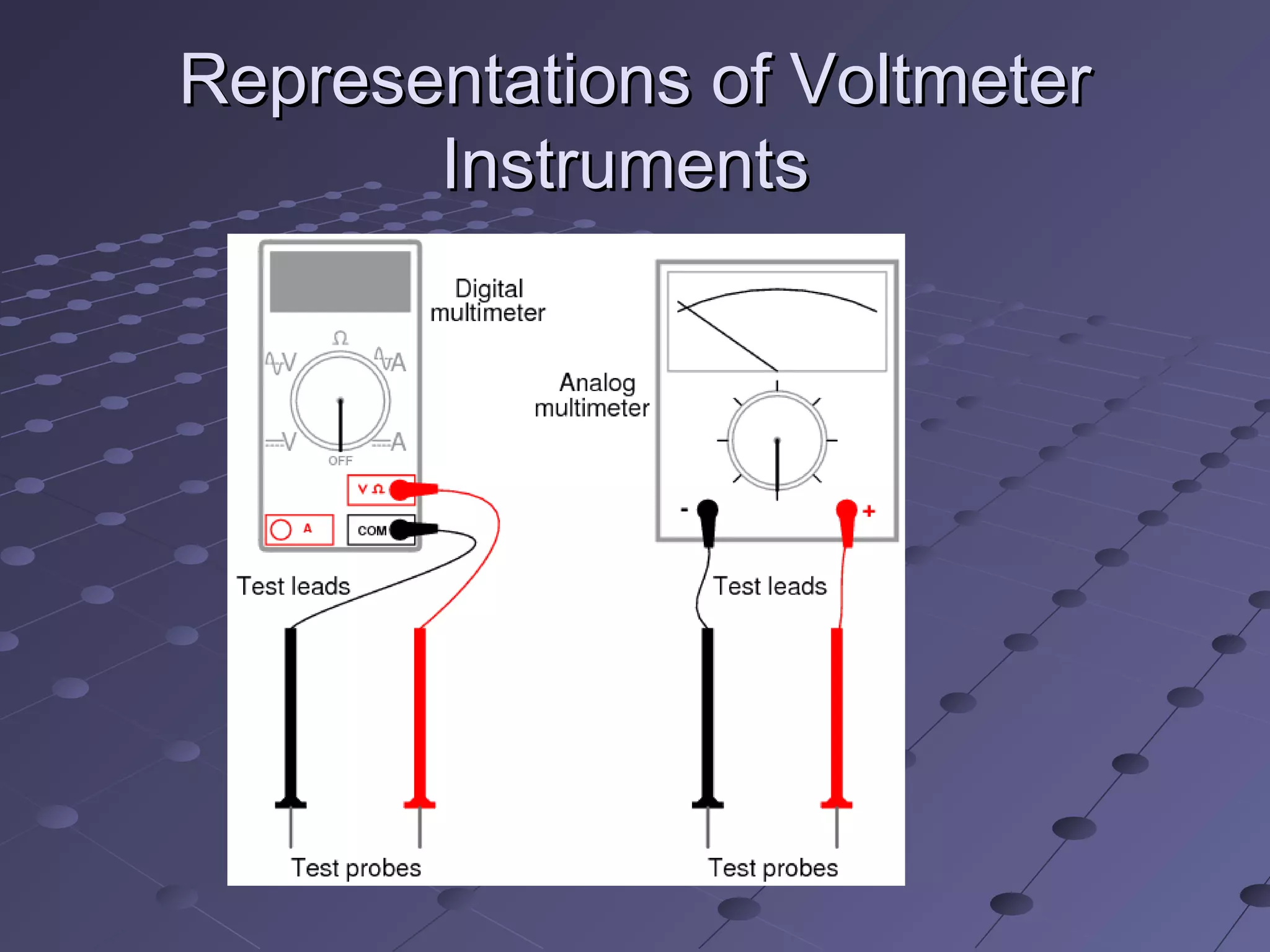
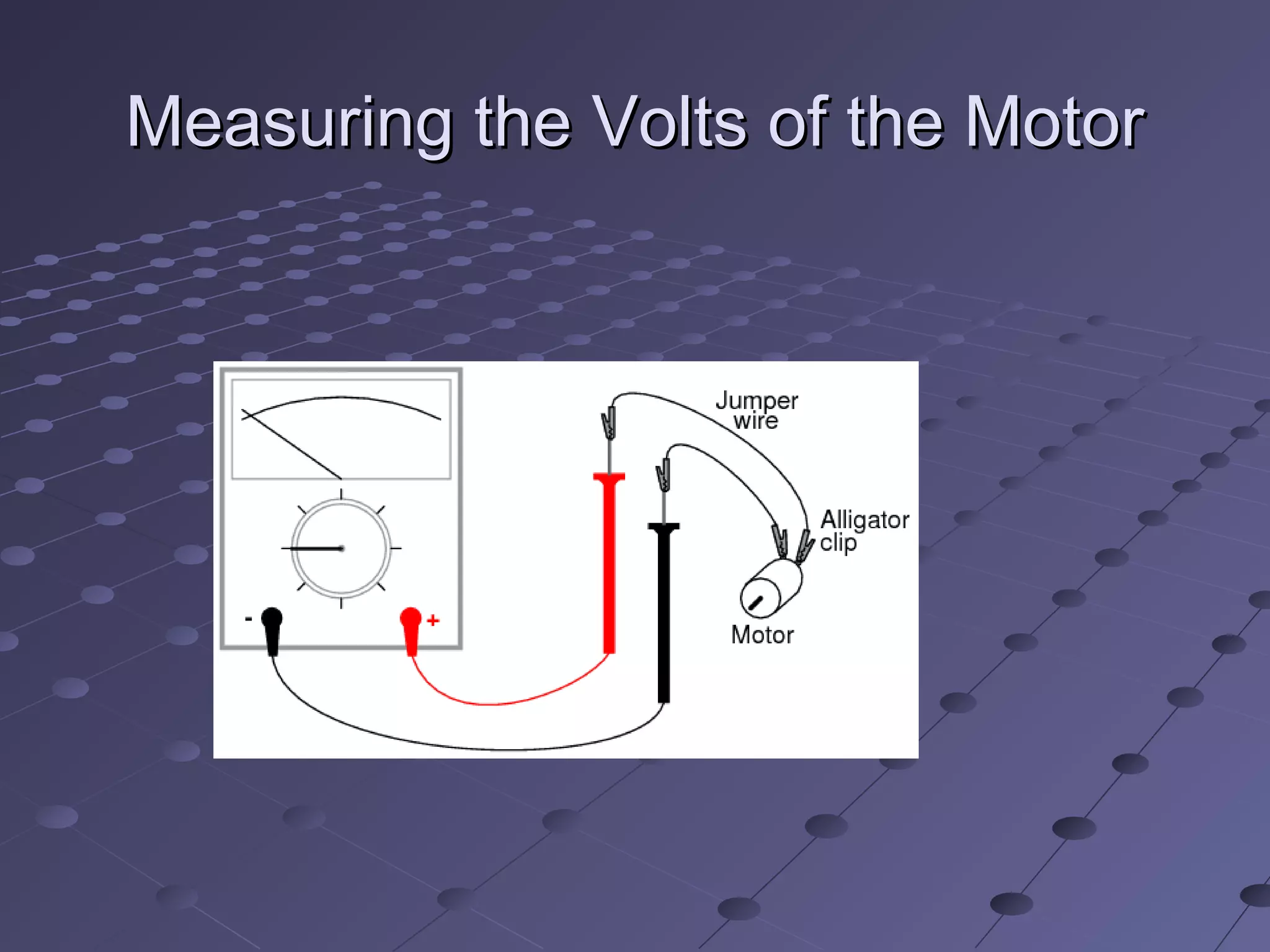
The document discusses a presentation about galvanometers. It introduces the group members giving their names and student IDs. It then states the topic is about galvanometers, discussing their introduction, principle, construction, working, and applications. Galvanometers are electromechanical instruments that detect electric currents through circuits using a sensitive moving coil mechanism. They work on the principle of torque generated by current in a magnetic field, with the coil rotating until restoring and deflecting torques cancel out. Applications mentioned include use as voltmeters to measure voltage in circuits.