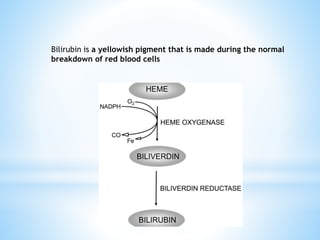
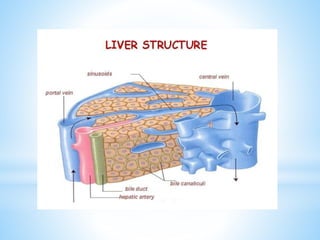
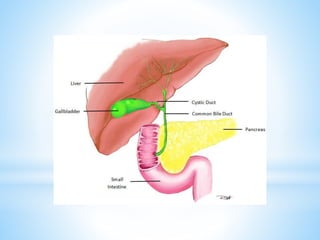
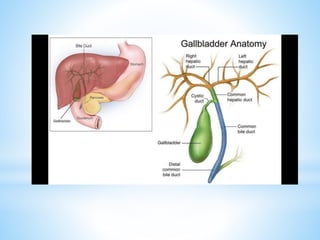
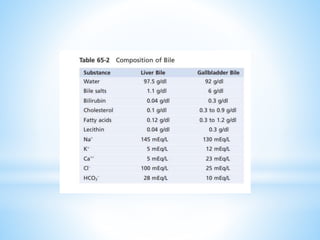
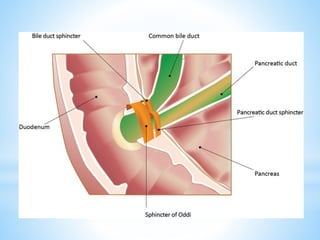
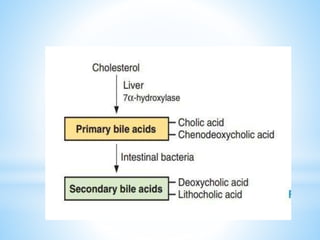
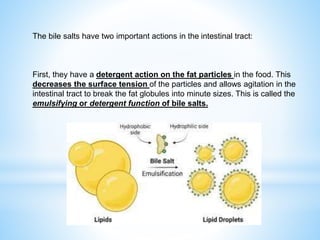
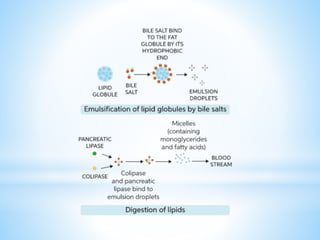
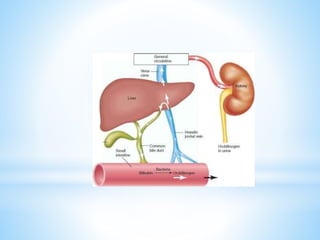
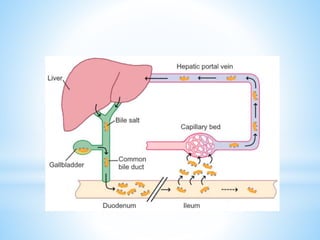
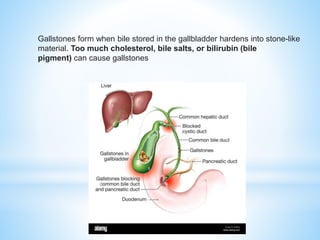
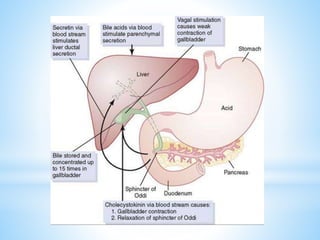
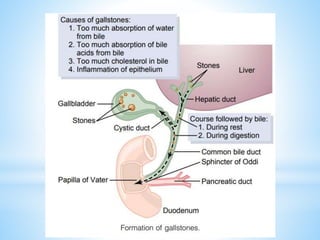
Bile is a greenish-yellow fluid secreted by the liver that aids in fat digestion and absorption. It emulsifies fat particles and aids in the absorption of fat breakdown products. Bile also serves as an excretion route for bilirubin and excess cholesterol. Bile is secreted continuously by the liver but stored in the gallbladder until needed for digestion in the small intestine, where it is released in response to cholecystokinin. The majority of bile salts are then reabsorbed in the ileum and returned to the liver in the enterohepatic circulation.