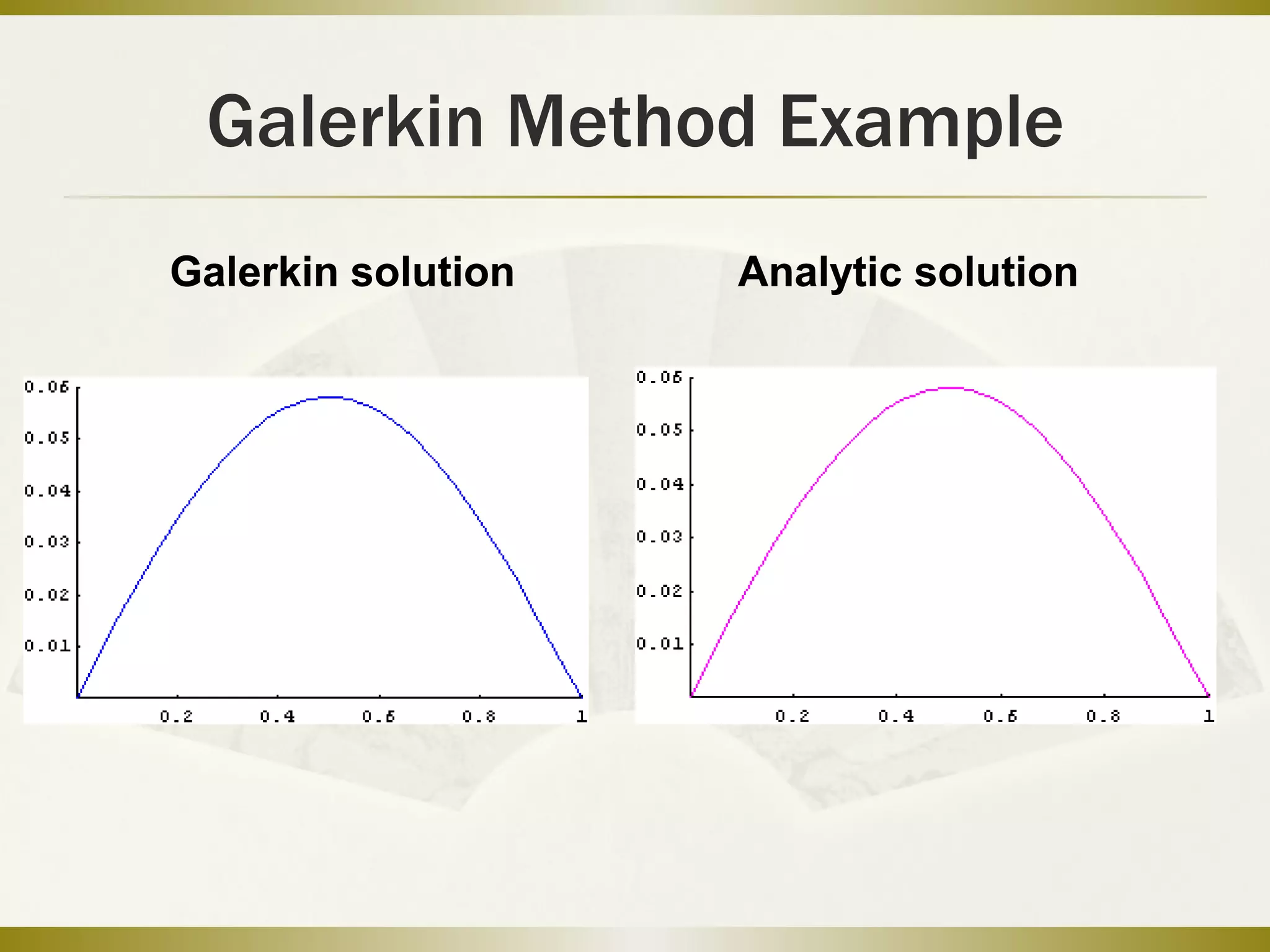
This document discusses the Galerkin method for solving differential equations. It begins by introducing how engineering problems can be expressed as differential equations with boundary conditions. It then explains that the Galerkin method uses an approximation approach to find the function that satisfies the equations. The key steps of the Galerkin method are to introduce a trial solution as a linear combination of basis functions, choose weight functions, take the inner product of the residual and weight functions to generate a system of equations for the unknown coefficients, and solve this system to obtain the approximate solution. An example of applying the Galerkin method to solve a second order differential equation is also provided.




![Galerkin Method
Inner product
Inner product of two functions in a certain
domain:
shows the inner
product of f(x) and g(x) on the interval [ a,
b ].
*One important property: orthogonality
If , f and g are orthogonal to each
other;
**If for arbitrary w(x), =0, f(x) 0
, ( ) ( )
b
a
f g f x g x dx
, 0f g
,w f ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/galerkinmethod-200626150934/75/Galerkin-method-5-2048.jpg)

![Galerkin Method
Weighted residual methods
A weighted residual method uses a finite
number of functions .
The differential equation of the problem is
D(U)=0 on the boundary B(U), for example:
on B[U]=[a,b].
where “L” is a differential operator and “f”
is a given function. We have to solve the
D.E. to obtain U.
0{ ( )}n
i ix
( ) ( ( )) ( ) 0D U L U x f x ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/galerkinmethod-200626150934/75/Galerkin-method-7-2048.jpg)
![Galerkin method
Weighted residual
Step 1.
Introduce a “trial solution” of U:
to replace U(x)
: finite number of basis functions
: unknown coefficients
* Residual is defined as:
0
1
( ) ( ) ( )
n
j j
j
U u x x c x
jc
( )j x
( ) [ ( )] [ ( )] ( )R x D u x L u x f x ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/galerkinmethod-200626150934/75/Galerkin-method-8-2048.jpg)
![Galerkin Method
Weighted residual
Step 2.
Choose “arbitrary” “weight functions” w(x),
let:
With the concepts of “inner product” and
“orthogonality”, we have:
The inner product of the weight function
and the residual is zero, which means that
the trial function partially satisfies the
problem.
So, our goal: to construct such u(x)
, ( ) , ( ) ( ){ [ ( )]} 0
b
a
w R x w D u w x D u x dx ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/galerkinmethod-200626150934/75/Galerkin-method-9-2048.jpg)
![Galerkin Method
Weighted residual
Step 3.
Galerkin weighted residual method:
choose weight function w from the basis
functions , then
These are a set of n-order linear
equations. Solve it, obtain all of the
coefficients .
j
0
1
, [ ( )] ( ){ [ ( ) ( )]} 0
nb
j j j ja
j
w R D u dx x D x c x dx
jc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/galerkinmethod-200626150934/75/Galerkin-method-10-2048.jpg)



![Galerkin Method Example
Step 2.
The “weight functions” are the same as
the basis functions
Step 3.
Substitute the trial function y(x) into
i
0
1
, [ ( )] ( ){ [ ( ) ( )]} 0
nb
j j j ja
j
w R D u dx x D x c x dx
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/galerkinmethod-200626150934/75/Galerkin-method-14-2048.jpg)