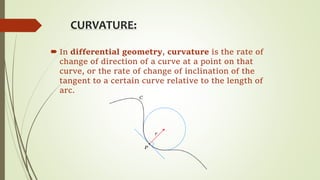
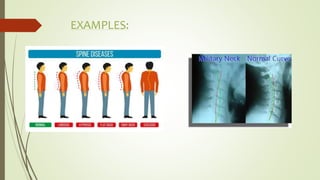
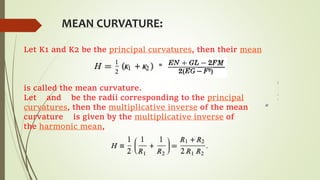
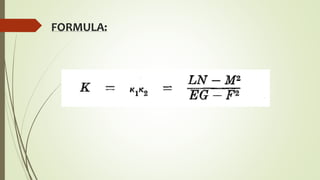This document provides information on different types of curvatures in differential geometry including normal, principal, mean, Gaussian, and geodesic curvatures. It defines each type of curvature, provides examples and formulas. Normal curvature is the amount of curve bending in the direction of the surface normal. Principal curvatures are the maximum and minimum normal curvatures. Mean curvature is the average of the principal curvatures. Gaussian curvature is the product of the principal curvatures. Geodesic curvature measures how far a curve is from being the shortest path between points on a surface.